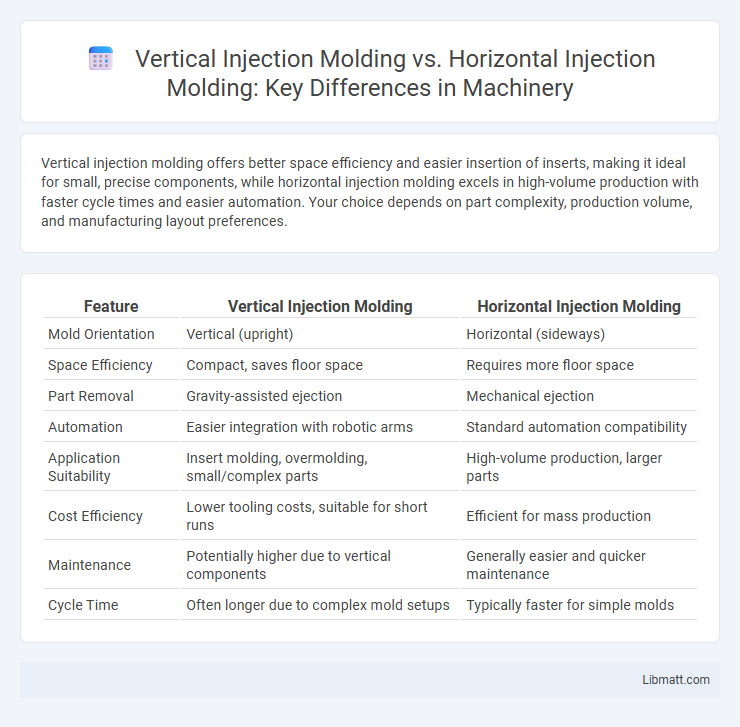
Vertical injection molding offers better space efficiency and easier insertion of inserts, making it ideal for small, precise components, while horizontal injection molding excels in high-volume production with faster cycle times and easier automation. Your choice depends on part complexity, production volume, and manufacturing layout preferences.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vertical Injection Molding | Horizontal Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Mold Orientation | Vertical (upright) | Horizontal (sideways) |
| Space Efficiency | Compact, saves floor space | Requires more floor space |
| Part Removal | Gravity-assisted ejection | Mechanical ejection |
| Automation | Easier integration with robotic arms | Standard automation compatibility |
| Application Suitability | Insert molding, overmolding, small/complex parts | High-volume production, larger parts |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower tooling costs, suitable for short runs | Efficient for mass production |
| Maintenance | Potentially higher due to vertical components | Generally easier and quicker maintenance |
| Cycle Time | Often longer due to complex mold setups | Typically faster for simple molds |
Overview of Vertical and Horizontal Injection Molding
Vertical injection molding features a machine where the mold clamping unit is oriented vertically, allowing easy loading and unloading of inserts or components, which is ideal for insert overmolding and space-saving setups. Horizontal injection molding has a molding unit positioned horizontally, offering higher production speeds and suitability for large and complex parts, making it the preferred choice for mass production in automotive and consumer goods industries. Your choice between vertical and horizontal injection molding depends on the part design, production volume, and automation requirements to optimize efficiency and cost.
Key Differences Between Vertical and Horizontal Injection Molding
Vertical injection molding features an injection unit oriented vertically, ideal for insert molding and space-saving applications, while horizontal molding uses a horizontally aligned injection unit suited for high-volume production and larger parts. The vertical process allows easier automation for insert placement, enhancing precision, whereas horizontal molding offers faster cycle times and simpler ejection systems. Your choice between these methods depends on part complexity, production volume, and factory layout requirements.
Advantages of Vertical Injection Molding
Vertical injection molding offers distinct advantages such as easier insertion and removal of inserts due to its top-down mold access, making it ideal for overmolding and multi-component parts. It provides improved precision and reduced flash as gravity assists in shot placement and mold filling. The compact machine footprint of vertical molds optimizes factory floor space, enhancing operational efficiency in high-volume production environments.
Benefits of Horizontal Injection Molding
Horizontal injection molding offers significant advantages such as higher production efficiency and easier automation integration, making it ideal for large-scale manufacturing. The horizontal orientation facilitates rapid mold changes and better product ejection, reducing cycle times and increasing output consistency. This method also supports a wider range of part sizes and complex geometries, enhancing manufacturing versatility.
Typical Applications for Vertical Injection Molding
Vertical injection molding is commonly used for insert molding applications where components such as metal parts or pre-assembled inserts need precise placement within molded plastic parts. It is ideal for small to medium-sized parts in industries like electronics, medical devices, and automotive components, where space-saving and multi-component integration are critical. The vertical design facilitates easier loading and unloading of inserts, improving efficiency in manufacturing complex assemblies.
Common Uses of Horizontal Injection Molding
Horizontal injection molding is widely used in producing automotive parts, consumer goods, and packaging components due to its efficiency in high-volume manufacturing. This method is preferred for creating complex shapes like containers, caps, and housings because of its ability to handle diverse mold designs and large molds. Its horizontal clamp orientation facilitates easy ejection of finished products, making it ideal for mass production environments.
Equipment Design and Operational Efficiency
Vertical injection molding machines feature a clamping unit positioned vertically, enabling easier insert molding and better access for automation, which enhances operational efficiency in complex part manufacturing. Horizontal injection molding machines, equipped with a horizontally oriented clamping unit, provide faster cycle times and higher production rates due to simpler mold opening and ejection systems. Equipment design in vertical machines supports precision and versatility, while horizontal machines excel in high-volume applications with streamlined material flow.
Cost Comparison: Vertical vs Horizontal Injection Molding
Vertical injection molding often reduces labor costs by allowing easier insert placement and faster cycle times due to gravity-assisted mold closing. Horizontal injection molding generally incurs higher equipment and maintenance expenses but offers better suitability for high-volume production with automated handling. Your cost-efficiency depends on part complexity and production scale, with vertical molding favoring small to mid-sized batches and horizontal molding benefiting large-scale runs.
Material Compatibility and Process Flexibility
Vertical injection molding offers superior material compatibility for insert molding and overmolding applications, allowing precise placement of metal or plastic inserts. Horizontal injection molding excels in process flexibility, supporting a wider range of part sizes and complex geometries with faster cycle times. Both methods accommodate diverse thermoplastics, but vertical molding is favored for high-precision, multi-component assemblies.
Choosing the Right Injection Molding Method for Your Project
Vertical injection molding offers precise control and is ideal for insert molding, reducing cycle times with its compact design. Horizontal injection molding suits high-volume production with faster cycle times and easier automation integration. Selecting the right method depends on project specifications such as part complexity, insert requirements, production volume, and automation needs.
Vertical injection molding vs horizontal injection molding Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com