A column type crane features a vertical pillar fixed to the ground or a foundation, allowing it to rotate and lift loads within a limited radius, making it ideal for localized material handling in workshops or factories. Your choice between the column type crane and gantry crane should consider the gantry crane's large span and height capabilities, which provide greater flexibility for moving heavy loads across wide outdoor or indoor areas.
Table of Comparison
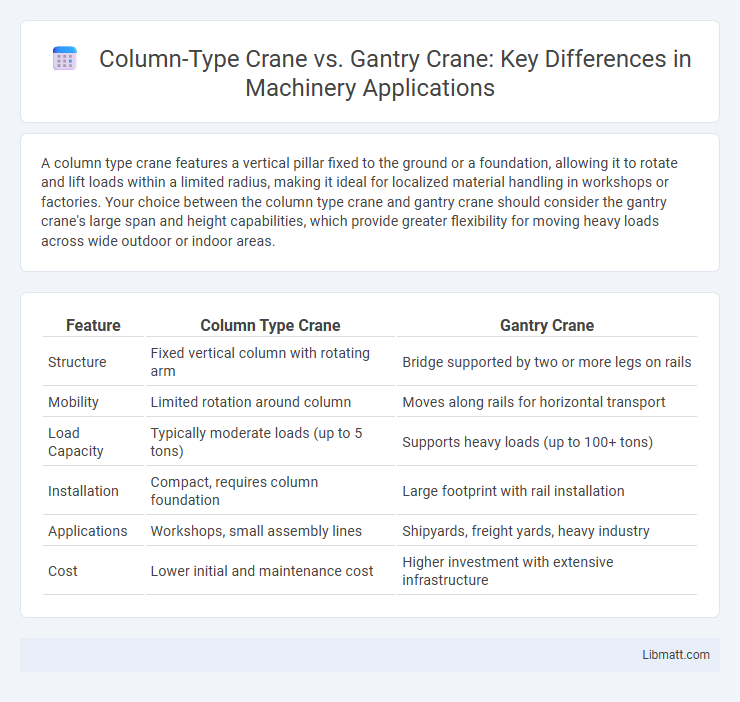
| Feature | Column Type Crane | Gantry Crane |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Fixed vertical column with rotating arm | Bridge supported by two or more legs on rails |
| Mobility | Limited rotation around column | Moves along rails for horizontal transport |
| Load Capacity | Typically moderate loads (up to 5 tons) | Supports heavy loads (up to 100+ tons) |
| Installation | Compact, requires column foundation | Large footprint with rail installation |
| Applications | Workshops, small assembly lines | Shipyards, freight yards, heavy industry |
| Cost | Lower initial and maintenance cost | Higher investment with extensive infrastructure |
Introduction to Column Type Cranes and Gantry Cranes
Column type cranes feature a vertical pillar supporting a horizontal jib, ideal for limited-space operations and precise lifting tasks. Gantry cranes span a workspace with a bridge supported by legs on wheels or rails, providing versatile, heavy-duty hoisting over large areas. Your choice depends on workspace dimensions and load requirements, with column cranes suited for confined areas and gantry cranes optimized for expansive, open environments.
Key Differences Between Column Type and Gantry Cranes
Column type cranes feature a vertical support pillar fixed to the floor, providing high load capacity with limited horizontal movement ideal for confined spaces. Gantry cranes operate on a rail system with a bridge supported by two or more legs, offering extensive horizontal coverage suited for outdoor or large-scale industrial environments. The primary differences lie in their structural design, movement capabilities, and typical application areas, with column cranes being more compact and gantry cranes providing greater reach and flexibility.
Structural Design and Components
Column type cranes feature a vertical column fixed to the ground or a foundation, supporting a horizontal jib that rotates to lift and move loads within a fixed radius. Gantry cranes consist of a bridge supported by two or more legs that move on a runway or rails, providing greater mobility and the ability to handle heavier loads over a larger area. Your choice depends on the spatial requirements and load capacities dictated by the structural design and components of each crane type.
Load Capacity Comparison
Column type cranes generally offer moderate load capacities, typically ranging from 1 to 20 tons, making them ideal for tasks in confined spaces and smaller-scale operations. Gantry cranes boast significantly higher load capacities, often exceeding 100 tons, allowing them to handle heavy industrial lifting and large container movements efficiently. Choosing between the two depends on your specific load requirements, workspace constraints, and the scale of the lifting tasks involved.
Installation and Space Requirements
Column type cranes require minimal floor space due to their fixed base and are installed by mounting onto a single column, making them ideal for environments with limited workspace. Gantry cranes need a broader area for their supporting legs and rails, as they span over the workspace and often require additional structural support or foundations. Your choice depends on the available space and installation feasibility, with column cranes offering compact solutions and gantry cranes providing flexibility for larger load coverage.
Mobility and Flexibility
Column type cranes offer limited mobility as they are fixed to a single location, providing high stability but restricted movement within their operational radius. Gantry cranes feature enhanced mobility and flexibility, capable of moving along tracks to cover larger work areas and handle heavy loads across multiple zones. Your choice depends on the need for stationary precision versus dynamic material handling across expansive spaces.
Common Applications and Use Cases
Column type cranes excel in indoor environments such as manufacturing plants and warehouses, where precise vertical lifting and maneuverability around fixed columns are essential. Gantry cranes are ideal for outdoor applications like shipyards, construction sites, and freight yards, offering extensive horizontal coverage and heavy-duty lifting capabilities across large areas. Your choice depends on spatial constraints and operational requirements, with column cranes suited for confined spaces and gantry cranes designed for heavy, versatile lifting tasks.
Safety Features and Considerations
Column type cranes feature a fixed vertical column, enhancing stability and reducing rollover risks, with safety mechanisms including overload protection and emergency stop systems. Gantry cranes, supported by a framework spanning over the workspace, incorporate safety features like anti-collision systems and limit switches to prevent trolley or hoist over-travel. Both types require regular maintenance and operator training to ensure safe lifting operations and compliance with industrial safety standards.
Maintenance and Operational Costs
Column type cranes generally have lower maintenance and operational costs due to their fixed installation and fewer moving components, reducing the need for frequent repairs. Gantry cranes, with their versatile mobility and larger structural components, often incur higher maintenance expenses, including track alignment and wheel servicing. The initial investment for gantry cranes is typically higher, but they offer greater flexibility for diverse lifting tasks in multiple locations, impacting overall operational costs differently than column cranes.
Choosing the Right Crane for Your Project
Column type cranes provide excellent stability and 360-degree rotation, making them ideal for confined spaces and repetitive lifting tasks. Gantry cranes offer greater flexibility and load capacity, suitable for heavy-duty operations and outdoor environments. Assess your project's spatial constraints, lifting requirements, and operational frequency to choose the most efficient crane that meets your specific needs.
Column type crane vs gantry crane Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com