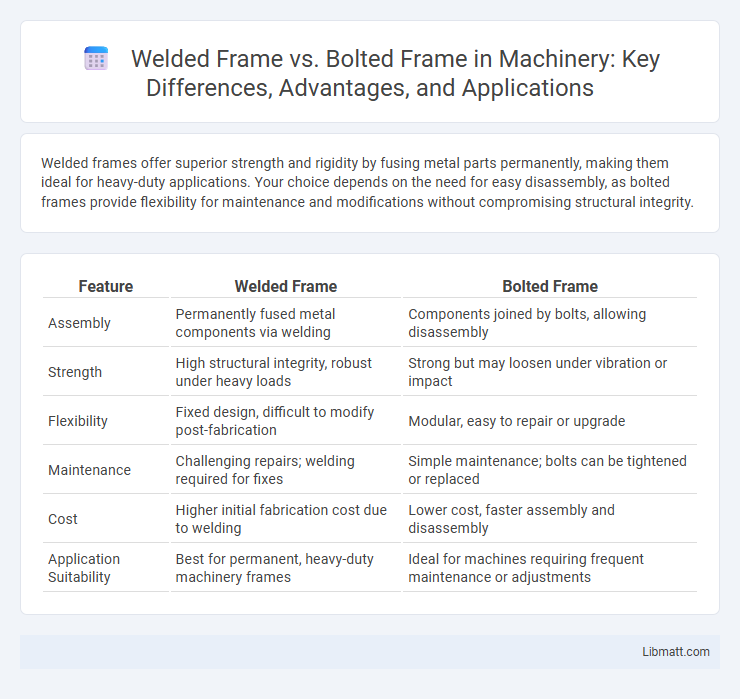
Welded frames offer superior strength and rigidity by fusing metal parts permanently, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Your choice depends on the need for easy disassembly, as bolted frames provide flexibility for maintenance and modifications without compromising structural integrity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Welded Frame | Bolted Frame |
|---|---|---|
| Assembly | Permanently fused metal components via welding | Components joined by bolts, allowing disassembly |
| Strength | High structural integrity, robust under heavy loads | Strong but may loosen under vibration or impact |
| Flexibility | Fixed design, difficult to modify post-fabrication | Modular, easy to repair or upgrade |
| Maintenance | Challenging repairs; welding required for fixes | Simple maintenance; bolts can be tightened or replaced |
| Cost | Higher initial fabrication cost due to welding | Lower cost, faster assembly and disassembly |
| Application Suitability | Best for permanent, heavy-duty machinery frames | Ideal for machines requiring frequent maintenance or adjustments |
Introduction to Welded and Bolted Frames
Welded frames are constructed by fusing metal components together through high-heat processes, creating seamless joints known for their strength and rigidity. Bolted frames, on the other hand, use mechanical fasteners to join components, offering flexibility and ease of assembly or disassembly. Understanding these fundamental differences helps you select the most suitable frame type for structural integrity and maintenance requirements.
Structural Integrity and Strength Comparison
Welded frames provide superior structural integrity and strength due to their continuous metal joints, which distribute stress evenly and reduce the risk of loosening over time. Bolted frames, while easier to assemble and repair, may experience joint flexibility and stress concentration, potentially compromising long-term durability under heavy loads. Your choice between welded and bolted frames should weigh the demand for rigidity and load-bearing capacity against ease of maintenance and assembly.
Assembly Time and Ease of Installation
Welded frames offer faster assembly times due to their pre-fabricated, rigid structure requiring minimal on-site adjustments, making installation straightforward and efficient. Bolted frames provide flexibility for modifications and easier transportation but typically involve longer assembly times because each connection must be manually aligned and secured. Your choice depends on whether rapid installation or adaptability is the priority for your project.
Flexibility and Modularity
Welded frames offer superior structural rigidity but lack flexibility and modularity due to their permanently joined components, making modifications or expansions challenging. Bolted frames provide enhanced adaptability by allowing you to easily assemble, disassemble, or reconfigure parts, supporting quick adjustments to changing design needs. Your choice depends on whether long-term stability or flexible, modular construction is a priority in your project.
Maintenance and Repair Considerations
Welded frames typically require less frequent maintenance due to their rigid, seamless construction, which minimizes the risk of joint loosening or corrosion at connection points. Bolted frames offer easier repair options, as individual components can be disassembled and replaced without affecting the entire structure, reducing downtime and repair costs. The choice between welded and bolted frames heavily depends on maintenance accessibility, environmental exposure, and long-term structural integrity requirements.
Cost Analysis: Welded vs Bolted Frames
Welded frames generally have higher initial fabrication costs due to skilled labor and specialized equipment requirements, but they provide greater structural integrity and reduced maintenance expenses over time. Bolted frames often feature lower upfront costs and simpler assembly, ideal for modular construction and easy disassembly. Long-term cost analysis favors welded frames in heavy-duty, permanent structures while bolted frames suit projects prioritizing flexibility and rapid installation.
Applications and Industry Preferences
Welded frames are preferred in automotive and heavy machinery industries due to their enhanced strength, rigidity, and ability to withstand high stress and vibration, making them ideal for structural components and load-bearing applications. Bolted frames offer greater flexibility and ease of assembly or disassembly, which suits modular equipment, temporary structures, and industries like construction and manufacturing that require frequent maintenance or reconfiguration. Your choice between welded and bolted frames depends on the specific application demands, including load requirements, environmental conditions, and maintenance accessibility.
Durability and Longevity
Welded frames offer superior durability and longevity due to their continuous metal joints, which provide enhanced strength and resistance to stress compared to bolted frames. Bolted frames may experience loosening over time from vibrations or heavy use, reducing structural integrity and requiring periodic maintenance. Choosing a welded frame ensures your equipment maintains stability and performance for a longer lifespan under demanding conditions.
Environmental and Safety Impacts
Welded frames typically offer superior structural integrity and reduced risk of joint failure under stress, enhancing safety in construction and industrial applications. However, welding processes can generate hazardous fumes and consume more energy, raising environmental concerns compared to bolted frames, which allow for easier disassembly and recycling, thus minimizing waste. You should weigh the trade-offs between the long-term durability of welded frames and the sustainability benefits of bolted connections when choosing the best option for your project.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Frame System
Welded frames offer superior strength and rigidity by creating a seamless connection that enhances structural integrity, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Bolted frames provide greater flexibility and ease of assembly or disassembly, which suits projects requiring future modifications or maintenance. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize long-term durability or adaptable construction.
Welded frame vs bolted frame Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com