Chain drives provide flexibility and are ideal for transmitting power over longer distances with some misalignment, while gear drives offer higher precision and torque capacity for compact, high-speed applications. Choosing between chain and gear drives depends on your specific needs for efficiency, maintenance, and load handling.
Table of Comparison
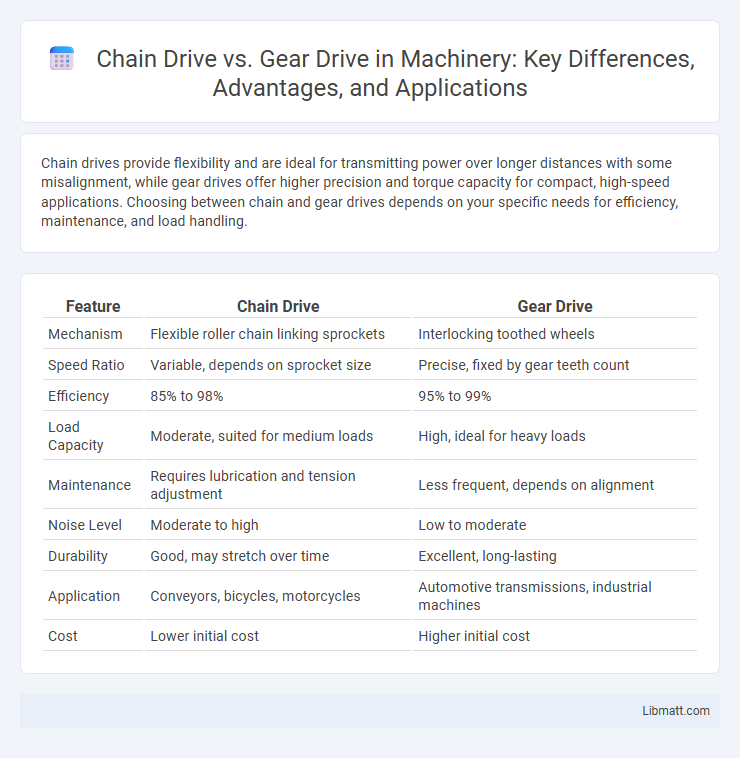
| Feature | Chain Drive | Gear Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Flexible roller chain linking sprockets | Interlocking toothed wheels |
| Speed Ratio | Variable, depends on sprocket size | Precise, fixed by gear teeth count |
| Efficiency | 85% to 98% | 95% to 99% |
| Load Capacity | Moderate, suited for medium loads | High, ideal for heavy loads |
| Maintenance | Requires lubrication and tension adjustment | Less frequent, depends on alignment |
| Noise Level | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
| Durability | Good, may stretch over time | Excellent, long-lasting |
| Application | Conveyors, bicycles, motorcycles | Automotive transmissions, industrial machines |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
Introduction to Chain Drive and Gear Drive
Chain drives utilize a series of linked metal chains to transmit mechanical power between sprockets, offering flexibility and efficient torque transfer in applications like bicycles and motorcycles. Gear drives consist of interlocking toothed wheels that mesh precisely to transfer motion and power, delivering high efficiency and accuracy in industrial machinery and automotive transmissions. Both systems are essential in mechanical design, with chain drives favoring moderate speed and shock load conditions while gear drives excel in high precision and load-bearing requirements.
Key Components and Mechanisms
Chain drives utilize a linked chain and sprockets to transfer mechanical power, where the chain wraps around sprockets to transmit motion efficiently over longer distances and flexible layouts. Gear drives consist of meshing toothed wheels that directly engage, providing precise speed ratios and high torque transmission in compact assemblies. Your choice depends on factors such as load capacity, speed consistency, and spatial constraints, as gear drives excel in accuracy while chain drives offer adaptability.
Working Principles of Chain Drive
Chain drives transmit mechanical power through a series of linked metal chains engaging with sprockets, converting rotational motion between shafts. The strength and flexibility of the chain allow it to handle high torque loads while maintaining consistent speed ratios. Your machinery benefits from efficient power transfer and reduced slippage due to the positive engagement between chain links and sprockets.
Working Principles of Gear Drive
Gear drives operate by meshing toothed wheels to transmit torque and rotational motion between shafts, ensuring precise speed ratios and mechanical advantage. The interlocking teeth eliminate slippage, allowing consistent power transfer even under high loads and variable speeds. Typical applications include automotive transmissions, industrial machinery, and precision instruments, where durability and efficiency are critical.
Efficiency Comparison
Chain drives typically offer higher mechanical efficiency than gear drives, with efficiency rates often ranging from 95% to 98%, due to their lower friction losses during power transmission. Gear drives, while more precise and capable of transmitting higher torque, usually have efficiency levels between 85% and 95%, influenced by gear type, lubrication, and alignment. In applications requiring high-speed and long-distance power transfer, chain drives are preferred for minimizing energy loss and maintaining performance.
Durability and Maintenance Requirements
Chain drives typically require more frequent maintenance such as lubrication and tension adjustments to prevent wear and elongation. Gear drives offer superior durability with enclosed systems that protect against contaminants, resulting in lower maintenance demands over time. The choice between them depends on application conditions, with gear drives favored for high-load, long-term usage due to their robust construction.
Cost Analysis: Chain vs Gear Drive
Chain drives generally offer a lower initial cost compared to gear drives, making them a cost-effective choice for applications requiring versatile torque transmission. Gear drives, while more expensive upfront due to precision manufacturing and material strength, provide higher durability and efficiency in long-term heavy-duty use. Your decision should weigh the balance between upfront investment and maintenance expenses, considering the operational demands of your machinery.
Application Areas and Suitability
Chain drives excel in applications requiring flexibility and ease of maintenance, commonly found in bicycles, motorcycles, and conveyor systems where moderate speeds and variable distances between shafts are typical. Gear drives suit high-precision, high-torque environments such as automotive transmissions, industrial machinery, and robotics, offering superior efficiency, reliability, and load capacity for tightly coupled components. Assess your operational needs, including speed, torque, alignment, and maintenance preferences, to determine whether a chain drive or gear drive provides the optimal performance for your specific application.
Pros and Cons of Each Drive System
Chain drive offers high efficiency and flexibility in transmitting power over longer distances, but it requires regular maintenance due to wear and lubrication needs. Gear drive provides precise motion control with a compact design and low maintenance, though it can be noisy and less tolerant of misalignment. Your choice depends on the application's demand for durability, noise level, and maintenance capacity.
Choosing the Right Drive for Your Needs
When selecting between chain drive and gear drive, consider factors such as load capacity, maintenance requirements, and environmental conditions. Chain drives offer flexibility and ease of repair, making them ideal for applications with varying distances between shafts and requiring periodic adjustments. Gear drives provide higher efficiency, precision, and longer lifespan in demanding, high-torque conditions, ensuring your machinery operates smoothly under consistent loads.
Chain drive vs gear drive Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com