Black oxide offers a thin, corrosion-resistant finish that enhances the steel's durability and reduces light reflection, while bluing provides a traditional, aesthetically pleasing blue-black coating primarily for rust prevention. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize corrosion resistance or a classic appearance for firearms or metal tools.
Table of Comparison
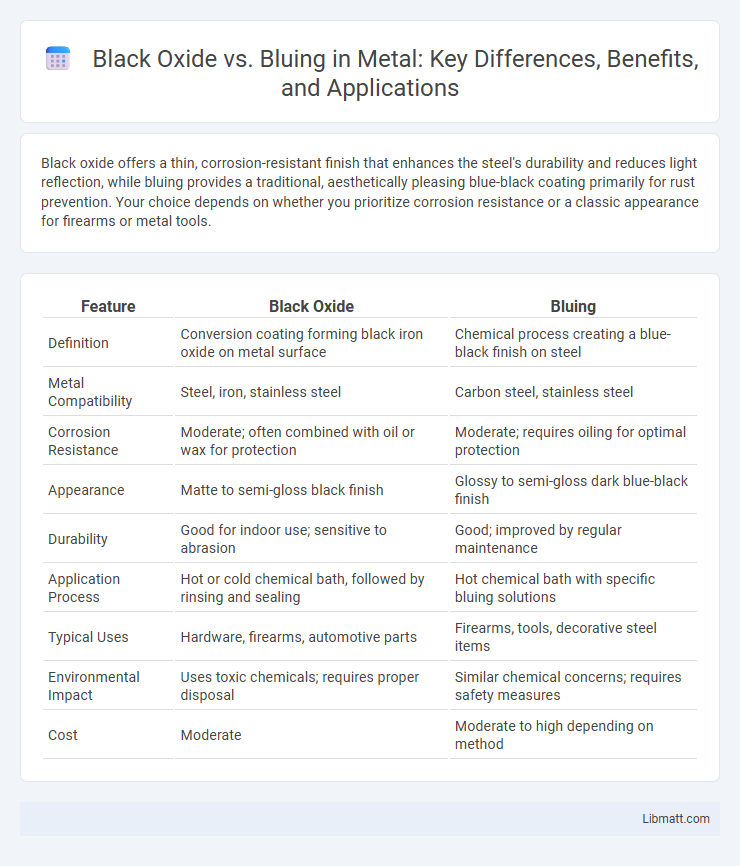
| Feature | Black Oxide | Bluing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conversion coating forming black iron oxide on metal surface | Chemical process creating a blue-black finish on steel |
| Metal Compatibility | Steel, iron, stainless steel | Carbon steel, stainless steel |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate; often combined with oil or wax for protection | Moderate; requires oiling for optimal protection |
| Appearance | Matte to semi-gloss black finish | Glossy to semi-gloss dark blue-black finish |
| Durability | Good for indoor use; sensitive to abrasion | Good; improved by regular maintenance |
| Application Process | Hot or cold chemical bath, followed by rinsing and sealing | Hot chemical bath with specific bluing solutions |
| Typical Uses | Hardware, firearms, automotive parts | Firearms, tools, decorative steel items |
| Environmental Impact | Uses toxic chemicals; requires proper disposal | Similar chemical concerns; requires safety measures |
| Cost | Moderate | Moderate to high depending on method |
Introduction: Black Oxide vs Bluing
Black oxide and bluing are both surface treatments used to enhance corrosion resistance and improve the appearance of steel. Black oxide forms a thin, magnetite layer through a chemical reaction, offering moderate protection and a sleek matte finish, while bluing involves controlled oxidation producing a blue-black hue that provides enhanced rust resistance and a classic look. Your choice between black oxide and bluing depends on the desired durability, aesthetic, and specific application requirements.
What is Black Oxide?
Black oxide is a chemical conversion coating applied to ferrous metals to enhance corrosion resistance, reduce light reflection, and improve surface aesthetics. This process creates a thin, black protective layer by oxidizing the metal surface, commonly used on steel components in firearms, tools, and automotive parts. You benefit from black oxide's uniform finish and durability, which helps extend the lifespan of metal products without adding significant thickness.
What is Bluing?
Bluing is a chemical process that creates a layer of magnetite (Fe3O4) on steel surfaces, providing mild corrosion resistance and an attractive dark blue-black finish. Commonly used on firearms and tools, bluing enhances both the appearance and durability of metal parts. This treatment helps protect Your steel items from rust while maintaining their smooth texture and classic look.
Key Differences Between Black Oxide and Bluing
Black oxide and bluing are both chemical processes used to create a black finish on metal surfaces, but black oxide typically produces a thinner, more uniform coating that enhances corrosion resistance without significantly altering the dimensions of the part. Bluing forms a thicker oxide layer, often providing a glossier, more decorative finish while offering moderate rust protection but may require oiling for enhanced durability. The choice between black oxide and bluing depends on factors like desired appearance, corrosion resistance level, and application requirements such as firearm treatment or industrial uses.
Protection and Corrosion Resistance
Black oxide and bluing both provide surface protection and corrosion resistance for metal parts, but black oxide offers a more durable and uniform coating that enhances wear resistance and reduces light reflection. Bluing, traditionally used on firearms, provides a thinner protective layer primarily designed to prevent rust through a chemical reaction, but it requires regular maintenance to sustain its corrosion resistance. Your choice depends on the specific environmental conditions and durability requirements, with black oxide favored for industrial applications and bluing for aesthetic and moderate protection.
Appearance and Finish Comparison
Black oxide produces a uniform, matte black finish that enhances corrosion resistance and reduces glare, commonly used on steel parts for industrial applications. Bluing offers a glossy, dark blue to black sheen with a smoother reflective surface, often preferred for firearms and decorative metalwork. Both finishes improve rust resistance but differ significantly in visual appeal, with black oxide providing a subdued, non-reflective look and bluing delivering a brighter, polished appearance.
Application Processes Explained
Black oxide and bluing are chemical treatments applied to metal surfaces to improve corrosion resistance and achieve a dark finish; black oxide uses an alkaline oxidizing salt solution for steel, creating a matte or semi-gloss black oxide layer. Bluing involves immersing steel in a hot alkaline solution of potassium nitrate, sodium hydroxide, and water, producing a thin layer of magnetite that offers rust resistance and a polished, glossy blue-black appearance. Both processes require precise temperature control and thorough cleaning before application to ensure optimal adhesion and uniform coating.
Durability and Maintenance
Black oxide coatings provide moderate corrosion resistance and are more durable in high-friction environments, requiring minimal maintenance with occasional oiling to prevent rust. Bluing offers a traditional aesthetic but is less durable, prone to wear and rust without regular maintenance such as re-oiling and refinishing. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize long-lasting protection or classic appearance with more upkeep.
Cost and Practical Uses
Black oxide coating typically offers a more cost-effective solution compared to bluing, making it ideal for industrial applications requiring corrosion resistance on steel parts. Bluing provides a traditional, aesthetically pleasing finish mainly used on firearms and decorative metalwork but demands more maintenance to prevent rust. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize budget-friendly protection or appearance with moderate upkeep.
Choosing the Best Finish for Your Needs
Black oxide provides a thin, corrosion-resistant coating ideal for industrial applications requiring minimal dimensional change and enhanced wear resistance. Bluing offers a traditional, aesthetically appealing finish primarily used on firearms and tools to improve rust resistance while maintaining a sleek, dark appearance. When choosing the best finish, consider black oxide for durability and uniform protection, whereas bluing suits projects where a classic look and moderate rust resistance are priorities.
black oxide vs bluing Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com