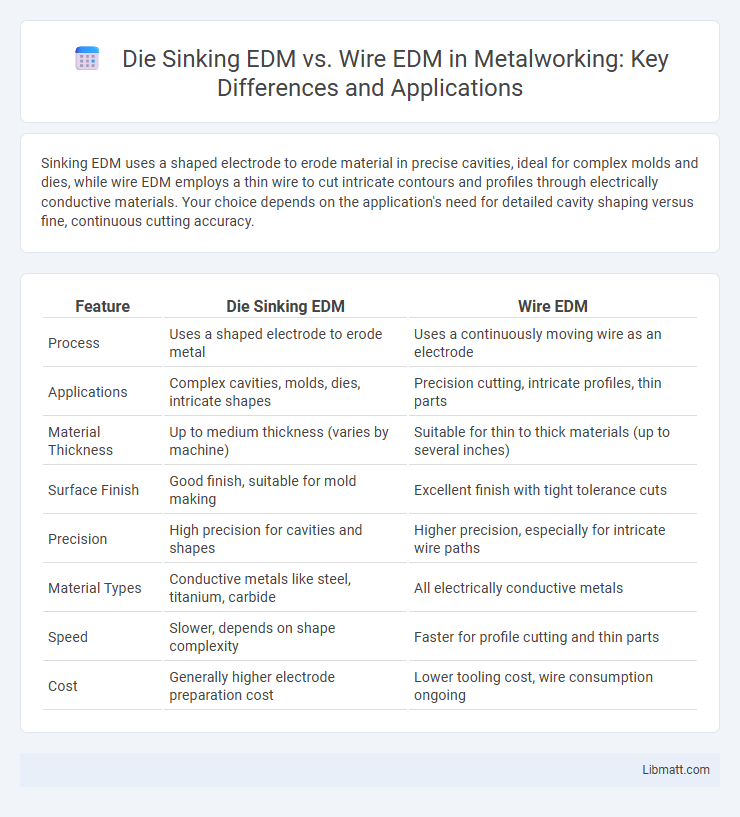
Sinking EDM uses a shaped electrode to erode material in precise cavities, ideal for complex molds and dies, while wire EDM employs a thin wire to cut intricate contours and profiles through electrically conductive materials. Your choice depends on the application's need for detailed cavity shaping versus fine, continuous cutting accuracy.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Die Sinking EDM | Wire EDM |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Uses a shaped electrode to erode metal | Uses a continuously moving wire as an electrode |
| Applications | Complex cavities, molds, dies, intricate shapes | Precision cutting, intricate profiles, thin parts |
| Material Thickness | Up to medium thickness (varies by machine) | Suitable for thin to thick materials (up to several inches) |
| Surface Finish | Good finish, suitable for mold making | Excellent finish with tight tolerance cuts |
| Precision | High precision for cavities and shapes | Higher precision, especially for intricate wire paths |
| Material Types | Conductive metals like steel, titanium, carbide | All electrically conductive metals |
| Speed | Slower, depends on shape complexity | Faster for profile cutting and thin parts |
| Cost | Generally higher electrode preparation cost | Lower tooling cost, wire consumption ongoing |
Introduction to EDM: Die Sinking vs Wire EDM
Die Sinking EDM utilizes a shaped electrode to erode complex cavities into hard metals, making it ideal for intricate molds and dies. Wire EDM employs a thin, continuously moving wire as an electrode to cut precise contours and shapes in conductive materials, often used for detailed parts with tight tolerances. Your choice between these methods depends on the required geometry, material type, and finishing precision.
Working Principles of Die Sinking EDM
Die sinking EDM operates by immersing a shaped electrode into a workpiece submerged in dielectric fluid, where electrical discharges generate intense heat to erode the material precisely according to the electrode shape. The process relies on controlled spark erosion that removes metal in a series of rapid, small material vaporization and melting events, enabling intricate cavity and mold creation. Unlike wire EDM, which employs a continuously moving wire as an electrode, die sinking EDM uses a static shaped electrode to achieve complex three-dimensional geometries.
Fundamentals of Wire EDM Technology
Wire EDM technology uses a thin, electrically charged wire to cut through conductive metals with high precision by eroding material through spark discharges. Unlike die sinking EDM which employs shaped electrodes, Wire EDM continuously feeds a fine wire, enabling complex contours and tight tolerances without electrode wear. The process is ideal for machining hard materials and intricate geometries due to its non-contact nature and excellent surface finish.
Key Differences Between Die Sinking and Wire EDM
Die sinking EDM uses a shaped electrode to erode material through controlled sparks, ideal for complex cavity and mold making, while wire EDM employs a continuously moving thin wire as the electrode to cut intricate shapes and contours with high precision. Die sinking EDM excels in producing deep, detailed cavities with varying profiles, whereas wire EDM is preferred for precise external contours and intricate cuts on hard materials. The main distinctions include electrode type, cutting capability, surface finish, and suitability for different part geometries and production volumes.
Material Compatibility: Die Sinking EDM vs Wire EDM
Die Sinking EDM excels in machining complex cavities and shapes in hard materials like hardened steel, titanium, and superalloys, offering precise control over intricate geometries. Wire EDM is highly effective for cutting thin sections and fine contours in electrically conductive materials such as stainless steel, copper, and aluminum, producing smooth edges without mechanical stress. Your choice depends on material type and part design, with Die Sinking EDM favored for detailed 3D forms and Wire EDM optimal for precise 2D profiles and thin materials.
Precision and Surface Finish Comparison
Die sinking EDM offers high precision and is ideal for intricate shapes with fine details, achieving tight tolerances in complex cavities. Wire EDM provides superior surface finish quality due to its continuous wire cutting process, resulting in smoother edges and minimal thermal distortion. Your choice depends on whether ultra-fine surface finish or intricate precision is the priority in the manufacturing process.
Applications in Industry: Die Sinking vs Wire EDM
Die sinking EDM is ideal for creating complex cavities and intricate shapes in molds and dies used in automotive and aerospace industries, offering precision in deep, detailed cuts on hard metals. Wire EDM excels in producing thin, accurate parts and fine contours in electrical components and medical devices, making it indispensable for cutting complex profiles and delicate geometries. Your choice between these methods depends on the precision, shape complexity, and material thickness required for your industrial application.
Tooling Requirements and Setup Time
Die sinking EDM requires customized graphite or copper electrodes, leading to longer tooling preparation and increased setup time due to electrode fabrication and alignment. Wire EDM uses a continuously fed brass or molybdenum wire, significantly reducing tooling requirements and enabling faster setup processes. Your choice depends on part complexity and production volume, with wire EDM generally offering quicker turnaround for intricate contours.
Cost Efficiency and Production Speed Analysis
Die sinking EDM offers higher cost efficiency for small to medium production runs due to lower tooling expenses and simpler setup processes. Wire EDM excels in production speed and precision, especially for complex shapes and hard materials, reducing cycle times and enhancing throughput. Your choice depends on balancing initial investment and desired output volume for optimal manufacturing performance.
Choosing the Right EDM Method for Your Needs
Die sinking EDM excels in machining intricate cavities and deep dies with complex geometries, making it ideal for detailed mold and tool making. Wire EDM offers precision cutting of thin, hardened materials with minimal thermal distortion, suitable for creating fine contours and delicate parts. Selecting between die sinking and wire EDM depends on factors like workpiece geometry, material type, and required tolerances to achieve optimal machining performance.
die sinking EDM vs wire EDM Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com