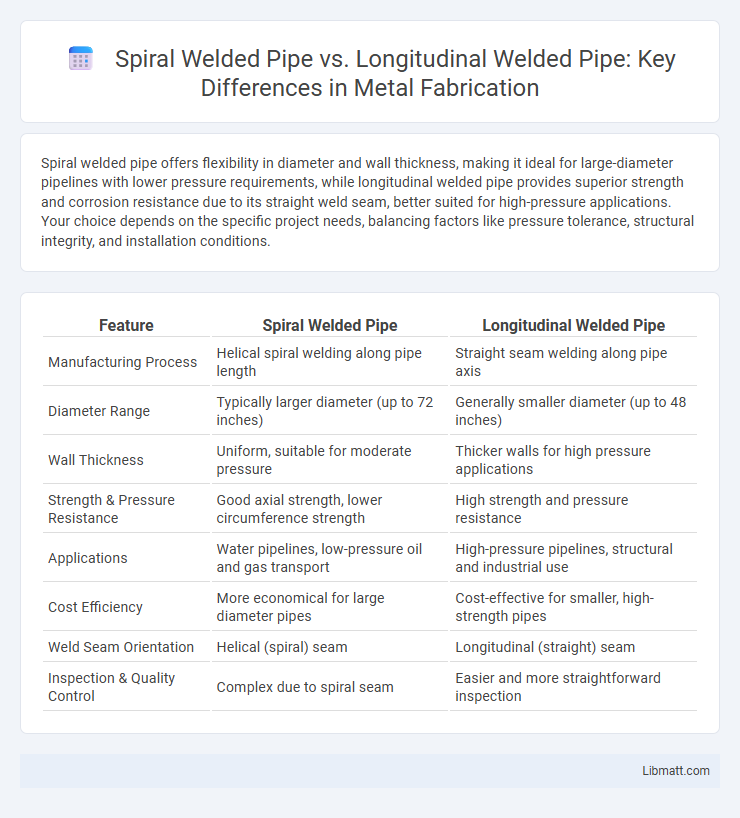
Spiral welded pipe offers flexibility in diameter and wall thickness, making it ideal for large-diameter pipelines with lower pressure requirements, while longitudinal welded pipe provides superior strength and corrosion resistance due to its straight weld seam, better suited for high-pressure applications. Your choice depends on the specific project needs, balancing factors like pressure tolerance, structural integrity, and installation conditions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Spiral Welded Pipe | Longitudinal Welded Pipe |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Helical spiral welding along pipe length | Straight seam welding along pipe axis |
| Diameter Range | Typically larger diameter (up to 72 inches) | Generally smaller diameter (up to 48 inches) |
| Wall Thickness | Uniform, suitable for moderate pressure | Thicker walls for high pressure applications |
| Strength & Pressure Resistance | Good axial strength, lower circumference strength | High strength and pressure resistance |
| Applications | Water pipelines, low-pressure oil and gas transport | High-pressure pipelines, structural and industrial use |
| Cost Efficiency | More economical for large diameter pipes | Cost-effective for smaller, high-strength pipes |
| Weld Seam Orientation | Helical (spiral) seam | Longitudinal (straight) seam |
| Inspection & Quality Control | Complex due to spiral seam | Easier and more straightforward inspection |
Introduction to Welded Pipes
Welded pipes are essential components in construction and industrial applications, manufactured by joining metal plates or strips through welding processes. Spiral welded pipes are produced by spirally winding and welding a steel strip, enabling larger diameter pipes with fewer seams, whereas longitudinal welded pipes are created by welding along the pipe's length, offering higher strength and uniformity for pressure-sensitive applications. The choice between spiral welded and longitudinal welded pipes depends on factors like diameter requirements, pressure conditions, and specific industry standards.
What is Spiral Welded Pipe?
Spiral welded pipe is a type of steel pipe formed by spirally rolling a steel strip and welding the edges together along a continuous helical seam, allowing for longer lengths and larger diameters at lower manufacturing costs. This pipe is commonly used in water, gas, and oil transportation due to its strength and flexibility in handling pressure variations. Compared to longitudinal welded pipe, spiral welded pipe offers enhanced adaptability for large-diameter applications in infrastructure projects.
What is Longitudinal Welded Pipe?
Longitudinal welded pipe is manufactured by bending a flat steel plate into a cylindrical shape and then welding it along the seam parallel to the pipe's axis, resulting in a strong and precise weld line. This type of pipe is ideal for high-pressure applications, as the longitudinal weld ensures superior strength and resistance to internal pressure compared to spiral welded pipes. Your choice between spiral welded pipe and longitudinal welded pipe should consider factors like pressure requirements, application type, and desired weld quality.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Spiral welded pipes are produced by spirally wrapping a continuous steel strip and welding it along the spiral seam, allowing for larger diameters and longer lengths with cost efficiency. Longitudinal welded pipes involve welding steel plates or coils along the length of the pipe, resulting in a straight seam that provides higher strength and uniformity but is typically more expensive and limited in size. The spiral welding process enables flexibility for large-diameter pipelines in water, oil, and gas transport, while longitudinal welding is preferred for applications demanding precise dimensional tolerances and superior structural integrity.
Strength and Structural Integrity
Spiral welded pipes offer enhanced flexibility and uniform strength due to their helical weld seam, making them ideal for applications requiring resistance to external pressure and bending. Longitudinal welded pipes provide superior structural integrity along their length, ensuring optimal performance under axial stress and internal pressure. When selecting pipes, consider your project's load requirements, as longitudinal welded pipes typically deliver higher tensile strength, while spiral welded pipes excel in managing multidirectional stresses.
Dimensional Range and Flexibility
Spiral welded pipes offer greater dimensional range and flexibility, accommodating diameters from 16 inches to 144 inches and varying wall thicknesses, making them ideal for large-scale infrastructure projects. Longitudinal welded pipes typically have smaller diameter ranges, usually up to 24 inches, with tighter tolerances and higher precision suitable for transporting high-pressure fluids. Your choice depends on project requirements for size versatility and the flexibility to adapt to pipeline route configurations.
Applications and Uses
Spiral welded pipes are commonly used in large-diameter pipelines for water, gas, and oil transport due to their cost-effectiveness and ability to handle high pressures and large volumes. Longitudinal welded pipes, preferred for structural applications such as building frameworks, pressure vessels, and offshore platforms, offer superior strength and resistance to high-pressure conditions. Your choice between spiral and longitudinal welded pipes should depend on specific project requirements including diameter, pressure ratings, and structural integrity.
Cost Considerations
Spiral welded pipes generally offer lower production costs due to their continuous welding process, which reduces labor and material waste compared to longitudinal welded pipes. Longitudinal welded pipes require precise alignment and multiple weld passes, leading to higher fabrication expenses. Cost efficiency in spiral welded pipes makes them preferable for large diameter applications where budget constraints are critical.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Spiral welded pipes feature a helical seam that distributes stress evenly, enhancing corrosion resistance and overall durability, making them ideal for high-pressure and corrosive environments. Longitudinal welded pipes have straight seams that can be more susceptible to stress concentration and potential corrosion along the weld line, although modern welding techniques have improved their strength and resistance. Your choice between spiral and longitudinal welded pipes should consider the specific corrosion challenges and durability requirements of your project to ensure long-term performance.
Choosing the Right Pipe: Spiral vs Longitudinal
Spiral welded pipes offer superior flexibility in diameter and length, making them ideal for large-scale water and gas pipelines where customization is critical. Longitudinal welded pipes provide higher structural integrity and are preferred for high-pressure applications such as oil and gas transport due to their consistent welding seam alignment. Selecting between spiral and longitudinal welded pipes depends on project requirements for pressure tolerance, diameter specification, and cost-efficiency.
Spiral Welded Pipe vs Longitudinal Welded Pipe Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com