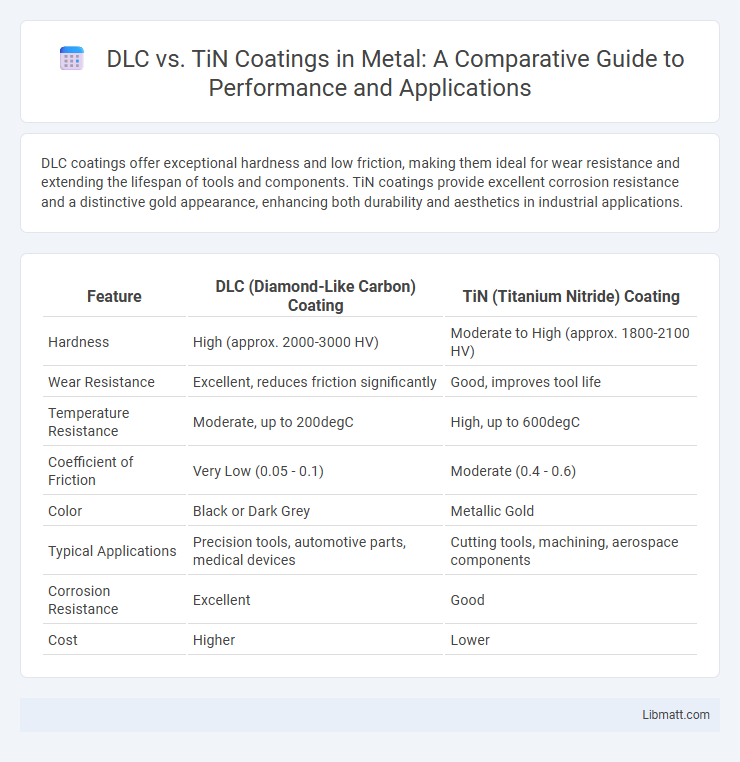
DLC coatings offer exceptional hardness and low friction, making them ideal for wear resistance and extending the lifespan of tools and components. TiN coatings provide excellent corrosion resistance and a distinctive gold appearance, enhancing both durability and aesthetics in industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) Coating | TiN (Titanium Nitride) Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | High (approx. 2000-3000 HV) | Moderate to High (approx. 1800-2100 HV) |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent, reduces friction significantly | Good, improves tool life |
| Temperature Resistance | Moderate, up to 200degC | High, up to 600degC |
| Coefficient of Friction | Very Low (0.05 - 0.1) | Moderate (0.4 - 0.6) |
| Color | Black or Dark Grey | Metallic Gold |
| Typical Applications | Precision tools, automotive parts, medical devices | Cutting tools, machining, aerospace components |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to DLC and TiN Coatings
DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) coatings are amorphous carbon films known for their exceptional hardness, low friction, and high wear resistance, often used in automotive and cutting tools to enhance durability. TiN (Titanium Nitride) coatings are ceramic-based, characterized by a gold-colored appearance, high hardness, and excellent corrosion resistance, commonly applied to improve hardness and extend tool life in metalworking industries. Both coatings serve to improve surface performance but differ significantly in composition, tribological properties, and typical applications.
Composition and Structure of DLC
Diamond-like Carbon (DLC) coatings consist primarily of amorphous carbon with a significant fraction of sp3 hybridized bonds, mimicking the structure of diamond and imparting exceptional hardness and low friction properties. This coating typically includes hydrogen, affecting its density and mechanical characteristics, while its structure ranges from hydrogenated to tetrahedral amorphous carbon forms. In contrast, Titanium Nitride (TiN) coatings feature a crystalline structure composed mainly of titanium and nitrogen atoms, providing high wear resistance and oxidation stability but lacking the ultra-low friction and chemical inertness of DLC.
Composition and Structure of TiN
Titanium Nitride (TiN) coatings consist of titanium and nitrogen atoms arranged in a face-centered cubic crystal structure, providing exceptional hardness and wear resistance. Compared to Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) coatings, TiN offers strong chemical stability and a golden appearance due to its metallic bonding and dense microstructure. Your choice between these coatings depends on application requirements, with TiN excelling in durability and corrosion resistance under extreme conditions.
Key Performance Differences
DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) coatings offer superior hardness and low friction properties, making them ideal for reducing wear and extending tool life in high-stress applications. TiN (Titanium Nitride) coatings provide excellent corrosion resistance and thermal stability, which enhances performance in high-temperature environments. Your choice between DLC and TiN should depend on whether reduced friction or thermal durability is more critical for your specific application.
Wear Resistance Comparison
DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) coatings provide exceptional wear resistance due to their high hardness and low friction coefficient, making them ideal for applications with severe abrasion and sliding conditions. TiN (Titanium Nitride) coatings also offer strong wear resistance, especially in high-temperature environments, but generally have lower hardness and higher friction compared to DLC. Your choice between DLC and TiN coatings should consider the specific wear mechanisms and operational conditions involved, as DLC excels in reducing wear from friction while TiN performs well under mechanical stress and heat.
Corrosion Resistance Analysis
DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) coatings offer exceptional corrosion resistance due to their dense, inert carbon structure that effectively blocks moisture and chemicals from reaching the substrate. TiN (Titanium Nitride) coatings provide moderate corrosion resistance with a hard ceramic surface that slows oxidation but can be compromised by defects or wear. Your choice between these coatings should consider the specific corrosive environment and the desired balance between hardness and chemical inertness.
Thermal Stability of DLC vs TiN
Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) coatings exhibit excellent thermal stability up to approximately 400degC, making them ideal for applications involving moderate heat exposure. Titanium Nitride (TiN) coatings, however, maintain their structural integrity at higher temperatures, often up to 800degC or beyond, providing superior performance in extreme thermal environments. Your choice between DLC and TiN should consider the specific operating temperature requirements to ensure optimal coating durability.
Typical Applications of Each Coating
DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) coatings are widely used in automotive components, cutting tools, and biomedical implants due to their exceptional hardness, low friction, and biocompatibility. TiN (Titanium Nitride) coatings find typical applications in machining tools, molds, and wear-resistant parts where enhanced surface hardness and corrosion resistance are critical. Both coatings significantly improve tool life and performance but suit different operational environments based on their unique properties.
Cost and Deposition Methods
DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) coatings typically cost more than TiN (Titanium Nitride) coatings due to their complex deposition processes such as plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) and sputtering. TiN coatings are commonly applied using physical vapor deposition (PVD) methods, which tend to be faster and more cost-effective for large-scale industrial applications. Understanding these cost and deposition method differences can help you choose the right coating for your specific wear resistance and budget requirements.
Choosing the Right Coating for Your Needs
DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) coatings offer exceptional hardness, low friction, and excellent wear resistance, making them ideal for applications requiring durability and reduced friction, such as cutting tools and medical devices. TiN (Titanium Nitride) coatings provide high hardness, corrosion resistance, and a distinctive gold appearance, commonly used in machine tools and decorative finishes. Choosing the right coating depends on factors like operating environment, desired performance, and budget to optimize Your equipment's lifespan and efficiency.
DLC vs TiN coatings Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com