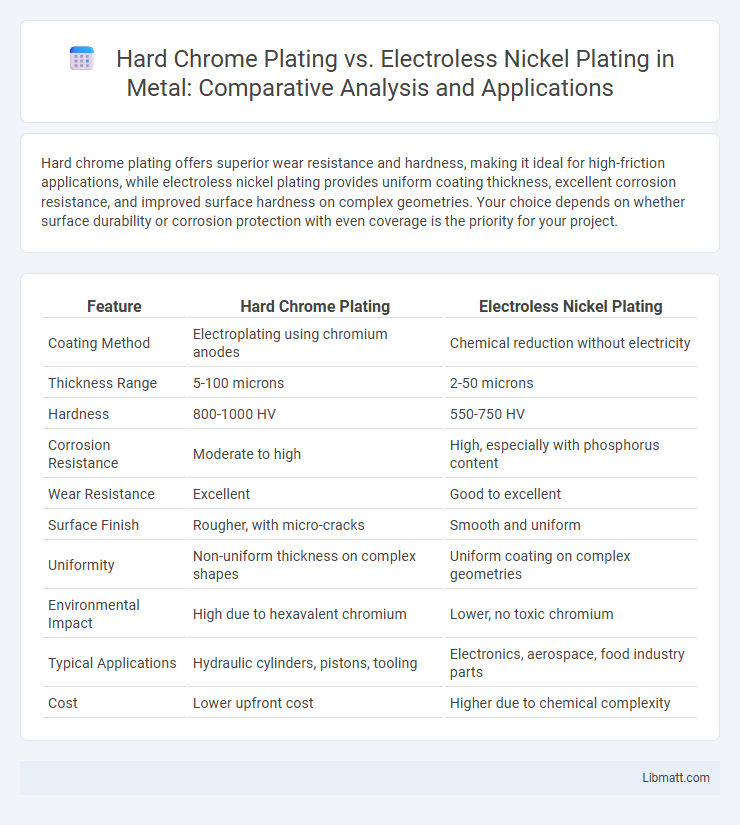
Hard chrome plating offers superior wear resistance and hardness, making it ideal for high-friction applications, while electroless nickel plating provides uniform coating thickness, excellent corrosion resistance, and improved surface hardness on complex geometries. Your choice depends on whether surface durability or corrosion protection with even coverage is the priority for your project.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hard Chrome Plating | Electroless Nickel Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Method | Electroplating using chromium anodes | Chemical reduction without electricity |
| Thickness Range | 5-100 microns | 2-50 microns |
| Hardness | 800-1000 HV | 550-750 HV |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate to high | High, especially with phosphorus content |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Good to excellent |
| Surface Finish | Rougher, with micro-cracks | Smooth and uniform |
| Uniformity | Non-uniform thickness on complex shapes | Uniform coating on complex geometries |
| Environmental Impact | High due to hexavalent chromium | Lower, no toxic chromium |
| Typical Applications | Hydraulic cylinders, pistons, tooling | Electronics, aerospace, food industry parts |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher due to chemical complexity |
Overview of Hard Chrome Plating and Electroless Nickel Plating
Hard chrome plating provides a thick, highly durable layer of chromium applied through an electroplating process, renowned for its excellent wear resistance, low friction, and corrosion protection in heavy-duty industrial applications. Electroless nickel plating deposits a uniform, non-electrolytic nickel-phosphorus or nickel-boron alloy layer, offering superior hardness, corrosion and wear resistance, and precise thickness control, especially on complex geometries. Both coatings enhance surface properties but differ fundamentally in application methods, uniformity, and chemical composition, influencing their suitability across mechanical, automotive, and aerospace sectors.
Composition and Chemical Properties
Hard chrome plating primarily consists of chromium deposited from a chromic acid solution, exhibiting exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion protection due to its dense chromium layer. Electroless nickel plating is composed of a uniform nickel-phosphorus or nickel-boron alloy deposited chemically without electric current, offering excellent corrosion resistance, uniform thickness, and enhanced lubricity. The chemical properties differ as hard chrome is an electroplated pure metal layer with high hardness, while electroless nickel provides a chemically reductive, catalytic deposition process resulting in a versatile alloy with unique magnetic and chemical resistance characteristics.
Surface Finish and Appearance Comparison
Hard chrome plating provides a bright, reflective surface with excellent hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring a polished appearance and high durability. Electroless nickel plating offers a uniform, smooth, and matte to semi-bright finish with superior corrosion resistance and consistent thickness on complex geometries. While hard chrome is preferred for its glossy, mirror-like finish, electroless nickel excels in delivering a more controlled and even surface appearance, especially on intricate parts.
Wear and Corrosion Resistance
Hard chrome plating offers superior wear resistance due to its high hardness and low friction properties, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications prone to abrasion. Electroless nickel plating provides excellent corrosion resistance, especially in acidic and alkaline environments, due to its uniform, pore-free coating that protects against rust and chemical attack. Choosing between these coatings depends on your specific needs for enhanced durability against wear or protection from corrosive elements.
Thickness and Uniformity of Coating
Hard chrome plating typically achieves coating thicknesses ranging from 25 to 250 microns, but its uniformity can be inconsistent due to the line-of-sight deposition process, often resulting in uneven layers on complex geometries. Electroless nickel plating provides highly uniform coatings with thicknesses generally between 5 and 50 microns, maintaining consistent deposition regardless of part shape or surface contours. The superior uniformity of electroless nickel plating makes it ideal for applications requiring precise dimensional tolerances and even wear resistance.
Adhesion and Durability
Hard chrome plating offers exceptional adhesion due to its strong mechanical bonding with substrates, resulting in superior wear resistance and long-lasting durability in high-friction applications. Electroless nickel plating provides uniform deposition with excellent corrosion resistance, but its adhesion may be less robust than hard chrome, requiring proper surface preparation to enhance durability. Both coatings improve surface hardness, yet hard chrome generally outperforms electroless nickel in extreme abrasion environments.
Application Methods and Process Differences
Hard chrome plating involves electroplating where a high voltage current deposits a thick layer of chromium onto the substrate, requiring the workpiece to serve as the cathode in an electrolytic bath. Electroless nickel plating uses a chemical reduction process without electricity, depositing a uniform nickel-phosphorus or nickel-boron alloy layer through an autocatalytic reaction. The electroplating method typically produces harder, more wear-resistant coatings with greater thickness control, while electroless plating offers superior uniformity on complex geometries and enhanced corrosion resistance due to its even coverage.
Typical Industrial Applications
Hard chrome plating is widely used in automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery industries for components requiring high wear resistance and low friction, such as piston rods, hydraulic cylinders, and gears. Electroless nickel plating finds typical applications in electronics, chemical processing, and food processing equipment due to its uniform coating, excellent corrosion resistance, and superior hardness. Both coatings serve critical roles in improving component lifespan and performance under demanding industrial conditions.
Cost and Economic Considerations
Hard chrome plating generally offers lower initial costs compared to electroless nickel plating, making it more economical for large-scale industrial applications. Electroless nickel plating provides uniform coating thickness and corrosion resistance, which can reduce maintenance costs and extend part lifespan, justifying its higher upfront investment. Total cost analysis often favors hard chrome for wear resistance but electroless nickel plating excels in complex geometries and long-term corrosion protection, impacting overall economic efficiency.
Choosing the Right Plating for Your Needs
Hard chrome plating offers exceptional hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications requiring durability and corrosion resistance. Electroless nickel plating provides uniform coverage and excellent corrosion protection, especially on complex geometries and non-conductive substrates. Your choice depends on factors like surface hardness, corrosion environment, and dimensional precision required for optimal performance.
Hard chrome plating vs electroless nickel plating Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com