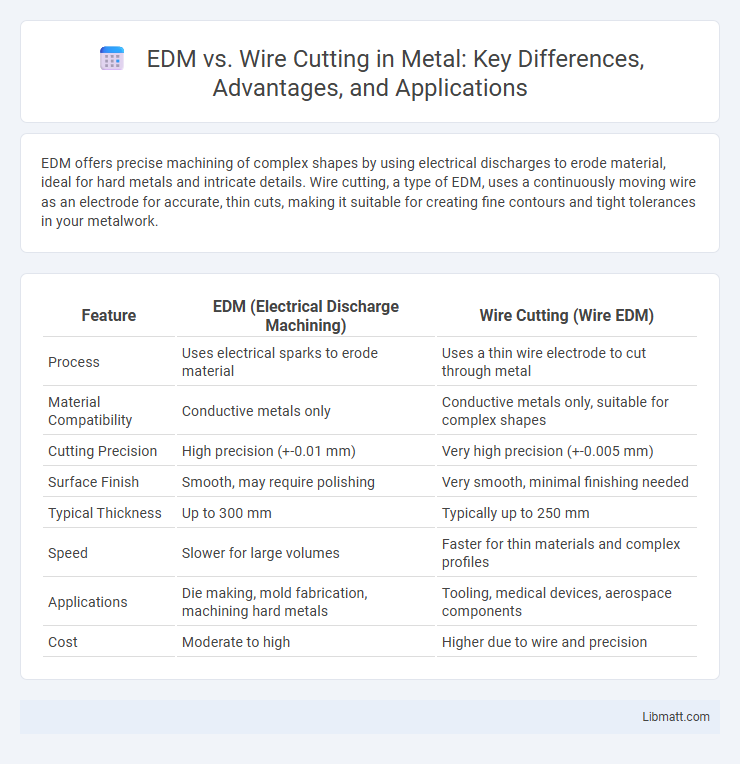
EDM offers precise machining of complex shapes by using electrical discharges to erode material, ideal for hard metals and intricate details. Wire cutting, a type of EDM, uses a continuously moving wire as an electrode for accurate, thin cuts, making it suitable for creating fine contours and tight tolerances in your metalwork.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) | Wire Cutting (Wire EDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Uses electrical sparks to erode material | Uses a thin wire electrode to cut through metal |
| Material Compatibility | Conductive metals only | Conductive metals only, suitable for complex shapes |
| Cutting Precision | High precision (+-0.01 mm) | Very high precision (+-0.005 mm) |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, may require polishing | Very smooth, minimal finishing needed |
| Typical Thickness | Up to 300 mm | Typically up to 250 mm |
| Speed | Slower for large volumes | Faster for thin materials and complex profiles |
| Applications | Die making, mold fabrication, machining hard metals | Tooling, medical devices, aerospace components |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Higher due to wire and precision |
Introduction to EDM and Wire Cutting
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) utilizes controlled electrical discharges to erode material from electrically conductive workpieces with high precision and minimal mechanical stress. Wire cutting, a subset of EDM known as Wire EDM, employs a continuously fed thin wire as an electrode to achieve intricate shapes and tight tolerances in hard metals. Both processes are essential in industries requiring detailed machining, such as aerospace, mold making, and medical device manufacturing.
How EDM Works: Principles and Process
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) functions by eroding material through controlled electrical sparks between an electrode and the workpiece submerged in a dielectric fluid. This process removes material precisely without direct contact, allowing intricate shapes and hard metals to be machined with exceptional accuracy. Your production benefits from EDM's ability to achieve fine details and smooth finishes that traditional wire cutting methods might struggle to deliver.
Understanding Wire Cutting Technology
Wire cutting technology, also known as wire EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), uses a thin, electrically charged wire to precisely cut through conductive materials by eroding metal with sparks. This process allows for intricate shapes and tight tolerances in hard metals like steel, titanium, and carbides, outperforming traditional machining methods in terms of precision and surface finish. Understanding wire cutting technology highlights its advantage in manufacturing complex components with minimal thermal distortion and high repeatability.
Key Differences Between EDM and Wire Cutting
EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) uses electrical sparks to erode material, making it ideal for intricate shapes and hard metals, while wire cutting, a subset of EDM, specifically employs a continuously moving wire as the electrode for precision cutting. EDM allows for complex internal contours without tool pressure, whereas wire cutting excels in producing straight, accurate cuts with minimal kerf loss. Your choice depends on the desired precision, material hardness, and part geometry.
Materials Suitable for EDM vs. Wire Cutting
EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) is ideal for machining hard, conductive materials such as hardened steel, titanium, carbide, and superalloys that are difficult to process with conventional methods. Wire cutting is best suited for cutting electrically conductive materials, including stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper, with high precision and minimal thermal distortion. Unlike wire cutting, EDM can machine complex shapes in materials with poor machinability, making it essential for aerospace, mold making, and medical device manufacturing.
Accuracy and Precision Comparison
EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) offers superior accuracy and precision compared to wire cutting due to its ability to machine intricate shapes with tight tolerances down to microns. Wire cutting, while efficient for simpler geometries, typically has slightly larger dimensional deviation and surface roughness. For your applications demanding high precision and minimal material stress, EDM provides more consistent and reliable results.
Speed and Efficiency: EDM vs. Wire Cutting
Wire cutting offers faster material removal rates for thin to medium-thickness metals, making it ideal for rapid prototyping and small to medium batch production. EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) excels in precision and can machine harder materials or complex shapes with high accuracy, though it operates at slower speeds compared to wire cutting. To optimize your manufacturing efficiency, choose wire cutting for speed and EDM when intricate detail or material hardness demands superior precision.
Surface Finish and Quality Considerations
EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) offers superior surface finish and precision, ideal for intricate geometries and hard materials, producing minimal mechanical stresses and fine surface textures. Wire cutting provides consistent finish quality with tight tolerances, suitable for straight cuts and complex profiles, but may require secondary processes for ultra-smooth surfaces. Your choice depends on the surface finish requirements and material hardness, with EDM favoring detailed quality and wire cutting excelling in repeatability and speed.
Cost Analysis of EDM and Wire Cutting
EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) generally incurs higher operational costs due to slower processing speeds and greater electrode wear compared to wire cutting, which offers more efficient material removal and lower waste. Wire cutting reduces expenses by using a continuous wire electrode, minimizing tooling costs and improving precision, especially for intricate shapes and thin materials. Your choice between EDM and wire cutting should weigh factors like production volume, part complexity, and budget constraints to optimize cost efficiency.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Application
EDM excels in producing intricate shapes and fine details in hard metals where precision is paramount, while wire cutting offers high accuracy and clean cuts ideal for complex contours and thin materials. Your choice should consider factors like material hardness, desired tolerances, and part geometry to ensure optimal machining performance. Evaluating these criteria helps determine whether EDM's electrical erosion or wire cutting's mechanical slicing best suits your specific application needs.
EDM vs wire cutting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com