Tantalum offers superior corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, making it ideal for medical implants and chemical processing equipment, while titanium is favored for its high strength-to-weight ratio and excellent corrosion resistance in aerospace and automotive industries. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize enhanced durability in harsh environments or lightweight structural performance.
Table of Comparison
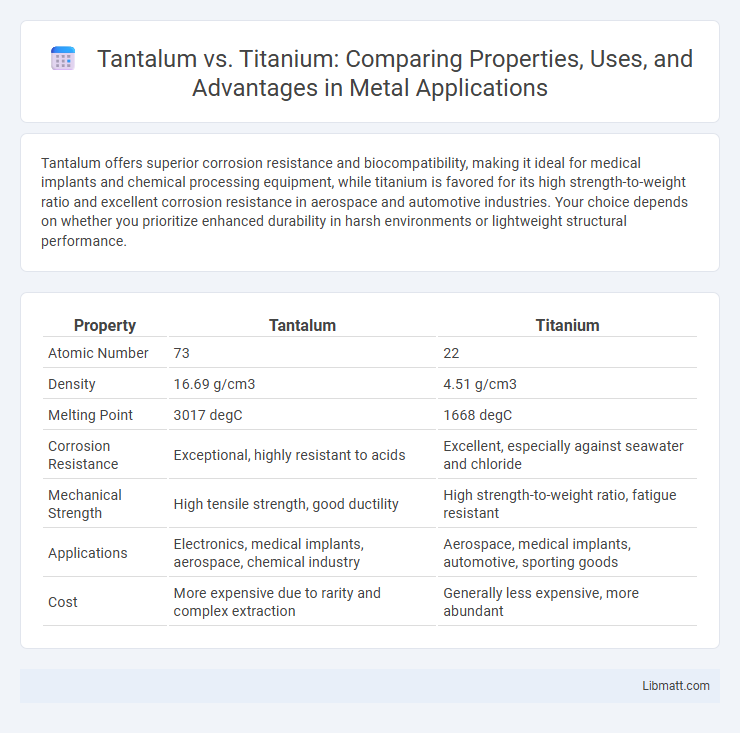
| Property | Tantalum | Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 73 | 22 |
| Density | 16.69 g/cm3 | 4.51 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 3017 degC | 1668 degC |
| Corrosion Resistance | Exceptional, highly resistant to acids | Excellent, especially against seawater and chloride |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength, good ductility | High strength-to-weight ratio, fatigue resistant |
| Applications | Electronics, medical implants, aerospace, chemical industry | Aerospace, medical implants, automotive, sporting goods |
| Cost | More expensive due to rarity and complex extraction | Generally less expensive, more abundant |
Introduction to Tantalum and Titanium
Tantalum, a rare, dense metal prized for its corrosion resistance and high melting point, is widely used in electronics and medical implants. Titanium, known for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and biocompatibility, dominates aerospace, automotive, and medical industries. Both metals offer unique properties critical for advanced engineering and technology applications.
Chemical and Physical Properties Comparison
Tantalum and titanium differ significantly in chemical and physical properties, with tantalum exhibiting exceptional corrosion resistance and a high melting point of 3017degC compared to titanium's 1668degC. Tantalum's density is approximately 16.7 g/cm3, making it much heavier than titanium, which has a density of 4.5 g/cm3, contributing to titanium's strength-to-weight advantage. You should consider these differences when selecting a material for applications requiring corrosion resistance or lightweight structural components.
Strength and Durability Differences
Tantalum offers exceptional corrosion resistance and maintains strength at high temperatures, making it ideal for chemically aggressive environments and aerospace applications. Titanium combines high strength-to-weight ratio with outstanding durability, providing excellent resistance to fatigue and impact while being significantly lighter than tantalum. Choosing between tantalum and titanium depends on whether your priority is corrosion resistance and temperature stability or lightweight strength and toughness.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Tantalum exhibits exceptional corrosion resistance, particularly against strong acids like hydrochloric and sulfuric acid, making it highly durable in aggressive chemical environments. Titanium forms a stable oxide layer that protects it from oxidation, providing excellent resistance in marine and oxidizing conditions but can be less effective against certain acids. Your choice between tantalum and titanium should consider the specific corrosive or oxidative challenges of your application, with tantalum being superior for highly acidic environments.
Biocompatibility in Medical Applications
Tantalum exhibits superior biocompatibility compared to titanium due to its excellent corrosion resistance and ability to promote bone ingrowth, making it highly suitable for orthopedic implants and dental applications. Titanium, while also biocompatible and widely used in medical devices, can sometimes elicit mild allergic reactions in sensitive patients. Your choice between tantalum and titanium should consider factors like tissue integration and patient sensitivity to optimize medical implant performance.
Weight and Density Considerations
Tantalum is significantly denser than titanium, with a density of approximately 16.7 g/cm3 compared to titanium's 4.5 g/cm3, making tantalum much heavier for the same volume. Your choice between these metals depends on weight-sensitive applications, as titanium offers a high strength-to-weight ratio ideal for aerospace and medical implants. Tantalum's high density provides superior radiation shielding and corrosion resistance but adds substantial weight to the component.
Common Industrial Uses
Tantalum is primarily used in the electronics industry for capacitors and high-power resistors due to its excellent corrosion resistance and ability to store and release electric charge efficiently. Titanium finds widespread application in aerospace, medical devices, and chemical processing equipment because of its high strength-to-weight ratio and outstanding resistance to corrosion. Both metals play crucial roles in industries demanding materials with exceptional durability and reliability under extreme conditions.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Tantalum is significantly more expensive than titanium due to its rarity and complex extraction process, with prices often exceeding $150 per kilogram compared to titanium's average cost of around $10 per kilogram. Titanium benefits from abundant global reserves and well-established supply chains, making it readily available for industrial use. Your choice between tantalum and titanium should consider budget constraints alongside the specific application, as cost and material availability directly impact project feasibility.
Machinability and Fabrication
Tantalum offers excellent machinability due to its softness and ductility, allowing precise shaping with minimal tool wear, making it ideal for complex components. Titanium requires specialized tools and techniques for machining because of its high strength and tendency to work-harden, which can increase fabrication time and costs. Your choice between tantalum and titanium should consider the balance between ease of fabrication and mechanical properties required for the application.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Tantalum mining often results in significant environmental degradation due to habitat destruction and the release of toxic byproducts, whereas titanium extraction typically involves more abundant, less environmentally harmful sources like ilmenite and rutile. Titanium is widely regarded as more sustainable, with its lower ecological footprint and greater recyclability compared to tantalum, which is less abundant and concentrated in conflict-prone regions. Your choice between these metals can influence sustainability efforts, favoring titanium for applications prioritizing environmental responsibility.
Tantalum vs titanium Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com