Water-based quenching offers rapid cooling and excellent heat dissipation, making it ideal for preventing grain growth in metals, while polymer-based quenching provides controlled cooling rates that reduce thermal stress and distortions. Your choice depends on the desired balance between cooling speed and component integrity during heat treatment processes.
Table of Comparison
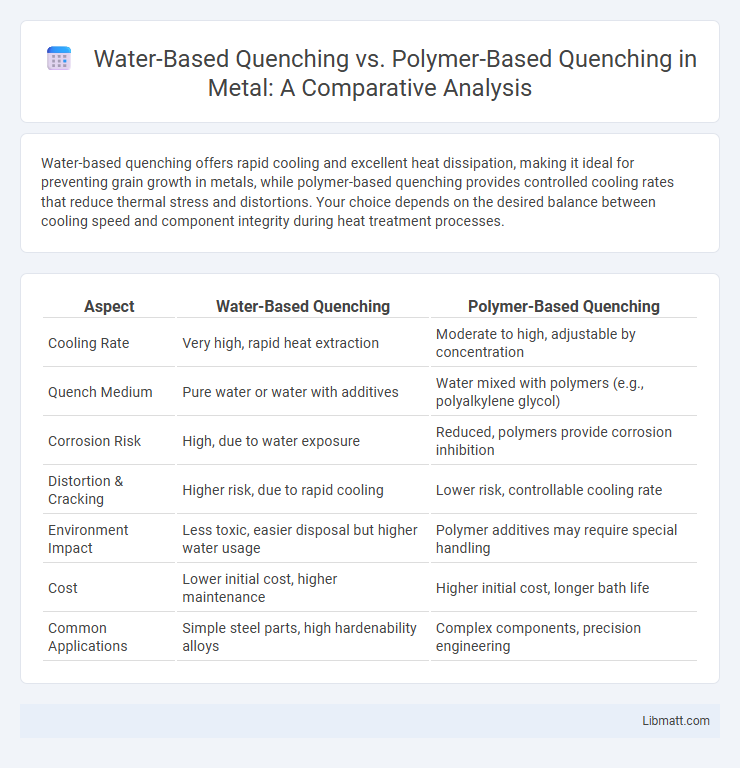
| Aspect | Water-Based Quenching | Polymer-Based Quenching |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Rate | Very high, rapid heat extraction | Moderate to high, adjustable by concentration |
| Quench Medium | Pure water or water with additives | Water mixed with polymers (e.g., polyalkylene glycol) |
| Corrosion Risk | High, due to water exposure | Reduced, polymers provide corrosion inhibition |
| Distortion & Cracking | Higher risk, due to rapid cooling | Lower risk, controllable cooling rate |
| Environment Impact | Less toxic, easier disposal but higher water usage | Polymer additives may require special handling |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, higher maintenance | Higher initial cost, longer bath life |
| Common Applications | Simple steel parts, high hardenability alloys | Complex components, precision engineering |
Introduction to Quenching Methods
Water-based quenching involves using water or water-based solutions to rapidly cool heated metals, offering high cooling rates essential for hardening steel. Polymer-based quenching employs aqueous polymer solutions that provide adjustable cooling rates by varying polymer concentration, reducing thermal shock and distortion compared to water quenching. Both methods are crucial in heat treatment processes, selecting appropriate quenching media depends on the desired microstructure and mechanical properties.
Fundamentals of Water-Based Quenching
Water-based quenching relies on the high thermal conductivity and heat capacity of water, enabling rapid cooling of heated metals to alter their microstructure and enhance mechanical properties like hardness and strength. This method reduces the risk of thermal distortion and cracking compared to oil quenching but can cause uneven cooling if not properly controlled. Your choice of water-based quenchants can include plain water, water with additives, or polymer solutions, each affecting cooling rates and resulting material characteristics.
Key Properties of Polymer-Based Quenching
Polymer-based quenching solutions offer enhanced cooling control compared to traditional water-based quenching due to their adjustable polymer concentration, which directly influences cooling rate and uniformity. These solutions provide superior heat extraction properties, reduced distortion, and minimized residual stresses in metals, making them ideal for complex or precision-engineered parts. Your choice of polymer concentration enables optimized quenching performance tailored to specific metallurgical requirements and component geometries.
Heat Transfer Mechanisms Compared
Water-based quenching relies primarily on rapid vaporization and convection to remove heat, resulting in a faster cooling rate due to the high thermal conductivity and heat capacity of water. Polymer-based quenching fluids incorporate water with soluble polymers that form a controllable, viscous film during cooling, reducing the boiling rate and producing a more uniform, moderate cooling process. The presence of polymers modifies heat transfer by stabilizing bubble formation and controlling the Leidenfrost effect, which decreases the risk of thermal stress and distortion in metals compared to pure water quenching.
Cooling Rate Differences: Water vs Polymer
Water-based quenching offers a significantly faster cooling rate due to its high thermal conductivity and low viscosity, which enables rapid heat extraction from hot metals. Polymer-based quenching fluids, typically composed of water mixed with polymers like polyalkylene glycol, provide slower and more controllable cooling rates, reducing the risk of thermal stresses and distortion. The adjustable concentration of polymer solutions allows for customizable cooling curves, optimizing the balance between hardness and toughness in heat-treated steel components.
Impact on Metallurgical Structures
Water-based quenching rapidly cools metals, promoting the formation of martensite and increasing hardness but also raising the risk of thermal stresses and cracking. Polymer-based quenching slows the cooling rate, resulting in a more uniform microstructure with reduced internal stresses and improved toughness. You can select the quenching method based on desired metallurgical properties, balancing hardness and structural integrity.
Advantages of Water-Based Quenching
Water-based quenching offers superior cooling rates compared to polymer-based quenching, which enhances hardness and strength in steel components. It is more environmentally friendly, as it uses plain water without chemical additives, reducing disposal costs and environmental impact. You benefit from easier maintenance and lower overall costs due to the simpler composition and lack of polymer degradation during repeated use.
Advantages of Polymer-Based Quenching
Polymer-based quenching offers superior control over cooling rates compared to water-based quenching, reducing the risk of distortion and cracking during heat treatment. Your components benefit from enhanced surface finish quality and improved dimensional stability, making polymer quenchants ideal for complex geometries. This method also provides customizable quenching characteristics by adjusting polymer concentrations, optimizing the balance between hardness and toughness.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Water-based quenching systems are favored for their non-toxic, biodegradable nature and ease of disposal, posing fewer environmental hazards compared to polymer-based quenchants, which may contain synthetic additives requiring specialized waste management. Polymer-based quenching fluids offer improved fire resistance and reduced risk of thermal shock, enhancing workplace safety during high-temperature metal treatment. Choosing between these quenching methods, your decision should weigh environmental impact and operational safety to align with regulatory compliance and sustainable manufacturing practices.
Choosing the Optimal Quenching Medium
Water-based quenching offers rapid cooling rates ideal for hardening steel, but it can cause higher distortion and cracking risks compared to polymer-based quenching. Polymer-based quenching solutions provide more controlled cooling, reducing thermal stress and improving part uniformity while maintaining effective hardness. Selecting the optimal quenching medium depends on your material composition, desired mechanical properties, and tolerance for distortion.
water-based quenching vs polymer-based quenching Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com