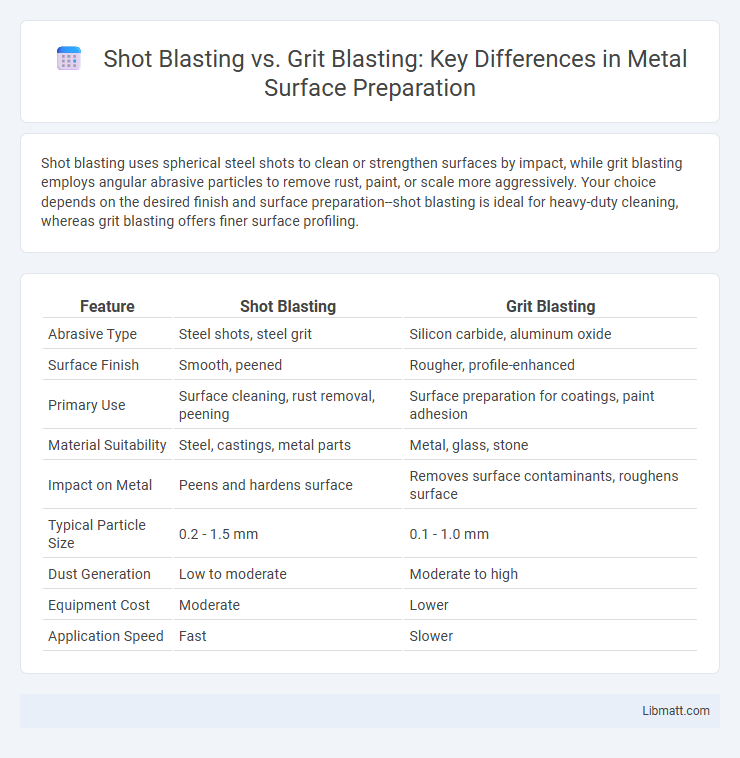
Shot blasting uses spherical steel shots to clean or strengthen surfaces by impact, while grit blasting employs angular abrasive particles to remove rust, paint, or scale more aggressively. Your choice depends on the desired finish and surface preparation--shot blasting is ideal for heavy-duty cleaning, whereas grit blasting offers finer surface profiling.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Shot Blasting | Grit Blasting |
|---|---|---|
| Abrasive Type | Steel shots, steel grit | Silicon carbide, aluminum oxide |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, peened | Rougher, profile-enhanced |
| Primary Use | Surface cleaning, rust removal, peening | Surface preparation for coatings, paint adhesion |
| Material Suitability | Steel, castings, metal parts | Metal, glass, stone |
| Impact on Metal | Peens and hardens surface | Removes surface contaminants, roughens surface |
| Typical Particle Size | 0.2 - 1.5 mm | 0.1 - 1.0 mm |
| Dust Generation | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Equipment Cost | Moderate | Lower |
| Application Speed | Fast | Slower |
Introduction to Surface Preparation Techniques
Shot blasting uses steel shots propelled at high velocity to clean, strengthen, or polish metal surfaces, effectively removing rust and scale. Grit blasting employs abrasive materials such as aluminum oxide or garnet to achieve a rougher surface profile for better paint or coating adhesion. Both surface preparation techniques enhance durability and performance in industrial applications by creating optimal surface conditions.
What is Shot Blasting?
Shot blasting is a surface preparation process that propels small steel shots at high velocity onto a material to remove rust, scale, or old coatings, enhancing surface texture and cleanliness. This technique is commonly used in industries like automotive, construction, and metal fabrication for preparing steel surfaces before painting or coating. Shot blasting improves adhesion and extends the durability of protective finishes by creating a uniformly rough surface.
What is Grit Blasting?
Grit blasting is an abrasive blasting process that propels coarse particles at high velocity to clean or prepare metal surfaces by removing rust, paint, and scale. The abrasive material, usually made from crushed minerals like garnet or aluminum oxide, creates a rough texture that enhances paint or coating adhesion. This method is ideal for heavy-duty surface preparation, improving the durability and longevity of your metal structures.
Key Differences Between Shot Blasting and Grit Blasting
Shot blasting uses steel shots or beads propelled at high velocity for surface cleaning and preparation, ideal for heavy-duty applications on metal surfaces. Grit blasting employs abrasive grains like aluminum oxide or silica, providing finer, more precise surface finishing suitable for delicate or detailed work. Your choice depends on factors such as surface material, desired finish quality, and the intensity of cleaning or preparation required.
Types of Abrasive Media Used
Shot blasting uses spherical steel shots or grit as abrasive media, providing aggressive cleaning and surface profiling ideal for heavy-duty applications like metal fabrication and construction. Grit blasting employs angular abrasive particles such as aluminum oxide, silicon carbide, or crushed glass, offering a more precise surface finish suited for delicate materials or preparing surfaces for coatings. Your choice depends on the desired surface texture and the specific requirements of the material treatment process.
Applications of Shot Blasting
Shot blasting is widely used for surface preparation in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction to remove rust, scale, and old coatings from metal surfaces. It enhances bonding before painting or coating, improves fatigue life by inducing compressive stress, and cleans castings and forgings for better surface finish. Typical applications include cleaning steel structures, preparing concrete surfaces for overlays, and maintaining railway tracks to remove contaminants.
Applications of Grit Blasting
Grit blasting is widely used for surface preparation in industries such as construction, aerospace, and automotive manufacturing due to its effectiveness in removing rust, paint, and scale from metal surfaces. This abrasive blasting method enhances adhesion for coatings and improves the longevity of structural components by creating a clean, roughened surface ideal for bonding. Your maintenance and repair projects benefit from grit blasting's ability to deliver a precise and consistent finish on a variety of materials, ensuring optimal surface integrity.
Pros and Cons of Shot Blasting
Shot blasting offers effective surface cleaning and preparation by using steel shot to remove rust, scale, and paint, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Its pros include high productivity, improved surface adhesion, and the ability to recycle abrasive material, but it can be costly due to equipment investment and may cause surface distortion on thin metals. The primary cons include potential noise pollution, dust generation requiring proper extraction systems, and limited effectiveness on non-metal surfaces compared to grit blasting.
Pros and Cons of Grit Blasting
Grit blasting offers superior surface preparation by effectively removing rust, scale, and old paint, creating an ideal profile for coating adhesion and enhancing durability. However, it generates more dust and is typically louder compared to shot blasting, requiring extensive protective measures and environmental controls. While grit abrasive can be reused less frequently than steel shots, it remains cost-effective for preparing hard or angular surfaces, especially in industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Blasting Method for Your Project
Shot blasting uses spherical steel shots to clean and strengthen surfaces, making it ideal for heavy-duty metal preparation and rust removal. Grit blasting employs angular abrasive particles designed for precise surface profiling and paint removal, suitable for delicate or detailed work. Choosing the right method depends on project requirements such as surface type, desired finish, and environmental considerations.
Shot Blasting vs Grit Blasting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com