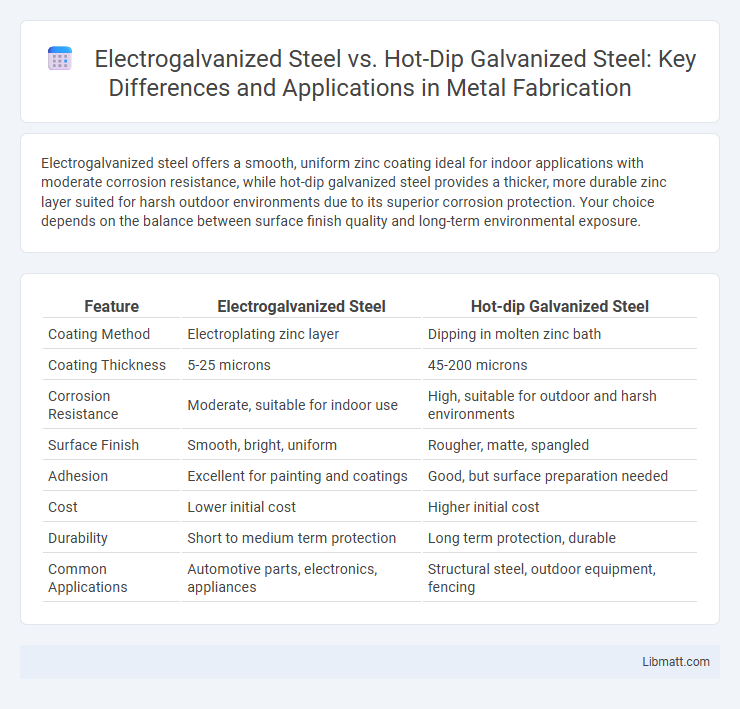
Electrogalvanized steel offers a smooth, uniform zinc coating ideal for indoor applications with moderate corrosion resistance, while hot-dip galvanized steel provides a thicker, more durable zinc layer suited for harsh outdoor environments due to its superior corrosion protection. Your choice depends on the balance between surface finish quality and long-term environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Electrogalvanized Steel | Hot-dip Galvanized Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Method | Electroplating zinc layer | Dipping in molten zinc bath |
| Coating Thickness | 5-25 microns | 45-200 microns |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate, suitable for indoor use | High, suitable for outdoor and harsh environments |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, bright, uniform | Rougher, matte, spangled |
| Adhesion | Excellent for painting and coatings | Good, but surface preparation needed |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Durability | Short to medium term protection | Long term protection, durable |
| Common Applications | Automotive parts, electronics, appliances | Structural steel, outdoor equipment, fencing |
Introduction to Galvanized Steel
Galvanized steel is a type of steel coated with a layer of zinc to protect it from corrosion, commonly used in construction and automotive industries. Electrogalvanized steel features a thin, uniform zinc layer applied through an electric current, offering precise coating control and smooth finish, ideal for indoor applications. Hot-dip galvanized steel is immersed in molten zinc, creating a thicker, more durable coating that provides superior corrosion resistance, making it suitable for outdoor and harsh environments.
What is Electrogalvanized Steel?
Electrogalvanized steel is a type of steel coated with a thin layer of zinc through an electroplating process, which provides corrosion resistance and enhances surface finish. The zinc coating is typically uniform and smoother compared to hot-dip galvanized steel, making it ideal for applications requiring superior paint adhesion and aesthetic appearance. This method is commonly used in automotive parts, appliances, and electronic components due to its precise coating control and compatibility with subsequent surface treatments.
What is Hot-dip Galvanized Steel?
Hot-dip galvanized steel is coated by immersing the base steel into molten zinc, forming a robust, metallurgically bonded layer that offers superior corrosion resistance. This process creates a thick, durable coating ideal for outdoor and industrial applications exposed to harsh environments. You can rely on hot-dip galvanized steel for long-lasting protection against rust and wear.
Key Differences in Manufacturing Processes
Electrogalvanized steel is produced by immersing the steel in a controlled chromic acid-sulfuric acid solution, then electroplating a thin layer of zinc onto its surface using an electrical current. Hot-dip galvanized steel undergoes a process where the steel is submerged in molten zinc at temperatures around 450degC, creating a thicker, more robust zinc coating. Your choice depends on the intended application, as electrogalvanized steel offers a smoother finish and better paint adhesion, while hot-dip galvanizing provides superior corrosion resistance in harsher environments.
Corrosion Resistance Comparison
Electrogalvanized steel features a thin zinc coating applied through electroplating, providing moderate corrosion resistance suitable for indoor or dry environments. Hot-dip galvanized steel undergoes immersion in molten zinc, resulting in a thicker, more durable coating that offers superior protection against rust and harsh outdoor conditions. The robust zinc layer of hot-dip galvanizing significantly extends the lifespan of steel in corrosive environments compared to the thinner, less resilient electrogalvanized layer.
Surface Appearance and Finish
Electrogalvanized steel features a smooth, shiny, and uniform surface finish due to its controlled electroplating process, making it ideal for aesthetic applications where appearance is critical. Hot-dip galvanized steel exhibits a thicker, matte, and uneven coating characterized by a rougher texture formed by the immersion in molten zinc, offering superior corrosion resistance but a less refined look. The choice between these coatings hinges on balancing visual appeal with durability requirements.
Mechanical Properties and Applications
Electrogalvanized steel offers a smoother surface finish with uniform zinc coating, providing moderate corrosion resistance and excellent dimensional accuracy, making it ideal for applications requiring precise tolerances such as automotive body panels and appliances. Hot-dip galvanized steel boasts a thicker, more durable zinc layer that delivers superior corrosion protection and enhanced mechanical strength, suitable for outdoor structures, construction materials, and industrial components exposed to harsh environments. Your choice depends on the specific mechanical property requirements and the environmental exposure of the application.
Cost Analysis: Electrogalvanized vs Hot-dip Galvanized
Electrogalvanized steel typically incurs lower initial costs due to its thinner zinc coating and faster production process, making it suitable for applications with budget constraints. Hot-dip galvanized steel, while more expensive upfront, offers superior corrosion resistance and longer lifespan, which reduces maintenance and replacement costs over time. Your choice depends on balancing immediate expenses against long-term durability and performance needs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Electrogalvanized steel involves a thin zinc coating applied through an electric current, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced waste compared to hot-dip galvanized steel, which uses a thicker zinc layer applied by immersing the steel in molten zinc. Your choice between these materials can affect environmental sustainability, as electrogalvanized steel produces less hazardous runoff and lower emissions during production. Hot-dip galvanizing offers longer corrosion resistance, potentially extending the steel's lifespan and reducing the frequency of replacements, which supports sustainability through durability.
Choosing the Right Galvanized Steel for Your Project
Electrogalvanized steel offers a smooth, uniform coating ideal for precision applications and indoor use, while hot-dip galvanized steel provides a thicker, more durable layer suited for harsh outdoor environments and heavy-duty protection. Selecting the right galvanized steel depends on factors like corrosion resistance needs, cost considerations, and environmental exposure. Projects requiring long-term durability against weather and chemicals benefit from hot-dip galvanizing, whereas electrogalvanized steel fits well in automotive or electronic components where surface finish and dimensional accuracy are critical.
Electrogalvanized Steel vs Hot-dip Galvanized Steel Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com