Spiral welded pipe features a helical weld seam that allows for larger diameter pipes and greater flexibility in length, making it ideal for applications requiring long continuous runs. Straight seam welded pipe has a longitudinal weld along its length, providing higher strength and uniformity, which suits projects needing precise dimensional tolerances and strong pressure resistance.
Table of Comparison
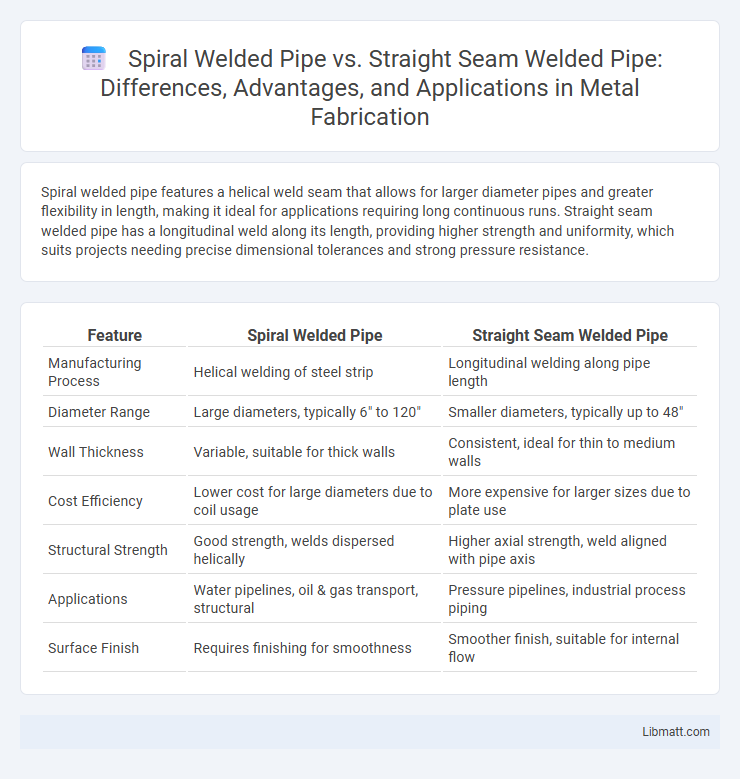
| Feature | Spiral Welded Pipe | Straight Seam Welded Pipe |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Helical welding of steel strip | Longitudinal welding along pipe length |
| Diameter Range | Large diameters, typically 6" to 120" | Smaller diameters, typically up to 48" |
| Wall Thickness | Variable, suitable for thick walls | Consistent, ideal for thin to medium walls |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower cost for large diameters due to coil usage | More expensive for larger sizes due to plate use |
| Structural Strength | Good strength, welds dispersed helically | Higher axial strength, weld aligned with pipe axis |
| Applications | Water pipelines, oil & gas transport, structural | Pressure pipelines, industrial process piping |
| Surface Finish | Requires finishing for smoothness | Smoother finish, suitable for internal flow |
Introduction to Welded Pipes
Welded pipes are manufactured by joining metal strips or plates through welding processes, primarily categorized into spiral welded pipes and straight seam welded pipes. Spiral welded pipes are produced by helically rolling a metal coil and welding along the spiral seam, offering cost-effective solutions for large diameters and applications like water transmission. Straight seam welded pipes feature longitudinal welds along the pipe's length, providing superior strength and precision, making them ideal for structural and high-pressure uses.
Overview of Spiral Welded Pipes
Spiral welded pipes are manufactured by bending a steel strip into a spiral shape and welding along the helical seam, which allows for longer pipe lengths and larger diameter applications compared to straight seam welded pipes. These pipes offer enhanced flexibility in terms of diameter and thickness, making them suitable for transporting water, gas, and oil in extensive pipeline systems. The spiral welding technique improves structural integrity and reduces material waste, optimizing cost-efficiency for large-scale infrastructure projects.
Overview of Straight Seam Welded Pipes
Straight seam welded pipes are manufactured by bending steel plates and welding the edges longitudinally, resulting in a uniform seam along the pipe's length. This welding technique ensures high dimensional accuracy and strength, making straight seam pipes ideal for applications requiring precise tolerances, such as oil and gas pipelines and structural projects. Compared to spiral welded pipes, straight seam pipes offer superior pressure resistance and easier inspection of weld integrity.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Spiral welded pipes are manufactured by continuously winding a steel strip at an angle and welding the edges together, allowing for larger diameters and longer lengths with cost-effective production. Straight seam welded pipes are produced by forming a steel plate into a cylinder and welding along a single longitudinal seam, offering higher strength and better dimensional accuracy. Your choice depends on the specific requirements for diameter, strength, and manufacturing efficiency.
Strength and Durability Differences
Spiral welded pipes exhibit enhanced flexibility and uniform strength distribution due to their helical seam, making them suitable for high-pressure applications and long-distance pipelines. Straight seam welded pipes offer superior tensile strength along the seam, providing exceptional durability in structurally critical settings with minimal stress concentration. The choice between spiral welded pipe and straight seam welded pipe depends on project-specific requirements for pressure tolerance, installation conditions, and expected mechanical stress.
Applications and Industry Uses
Spiral welded pipes are extensively used in large-diameter pipelines for transporting water, oil, and gas, favored for their strength and flexibility in infrastructure projects such as water mains and sewage systems. Straight seam welded pipes find applications in industries requiring precise dimensions and high-pressure capabilities, including mechanical engineering, structural frameworks, and automotive sectors. The choice between spiral and straight seam welded pipes depends on the specific requirements of durability, pressure resistance, and installation environment in oil and gas, construction, and industrial manufacturing.
Cost Efficiency and Production Speed
Spiral welded pipes generally offer better cost efficiency due to their continuous production process, which reduces material waste and lowers labor expenses compared to straight seam welded pipes. Production speed is typically faster for spiral welded pipes since the coil is continuously fed and welded, enabling higher output rates for large diameter pipes. Your choice depends on project requirements, as straight seam welded pipes may suit applications needing tighter tolerances despite their slower fabrication and higher costs.
Quality Standards and Inspection
Spiral welded pipes and straight seam welded pipes are both manufactured under stringent quality standards such as API 5L and ASTM A53 to ensure structural integrity and performance. Inspection methods, including ultrasonic testing and radiographic examination, are employed to detect weld defects and ensure compliance with industry specifications. Choosing your pipe based on the required application and inspection certifications guarantees reliability and safety in your projects.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Spiral welded pipes offer superior strength and flexibility due to their helical seam, making them ideal for large-diameter applications and pressure vessels, with cost-effective manufacturing from using narrower steel coils. Straight seam welded pipes provide higher dimensional accuracy and smoother surfaces, resulting in better resistance to fatigue and crack propagation but tend to have higher production costs and limitations on diameter size. Spiral pipes may face challenges with internal seam discontinuities affecting corrosion resistance, whereas straight seam pipes generally exhibit cleaner welds with improved inspection and maintenance ease.
Choosing the Right Pipe for Your Project
Spiral welded pipes offer superior strength and flexibility, making them ideal for large-diameter pipelines and high-pressure applications, while straight seam welded pipes provide higher dimensional accuracy and smoother internal surfaces, suited for precise engineering projects. Selecting the right pipe depends on factors such as project scale, pressure requirements, and installation environment, with spiral pipes preferred for extensive infrastructure and straight seam pipes chosen for controlled fluid transport. Material grade, welding quality, and cost efficiency also influence the decision to ensure optimal performance and durability in construction or industrial use.
Spiral welded pipe vs straight seam welded pipe Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com