Pre-galvanized steel is coated with zinc before fabrication, providing uniform corrosion resistance and a smoother finish ideal for controlled manufacturing processes. Post-galvanized steel is coated after fabrication, offering enhanced protection to welds and finished surfaces, making it suitable for complex or custom metalwork where additional durability is required.
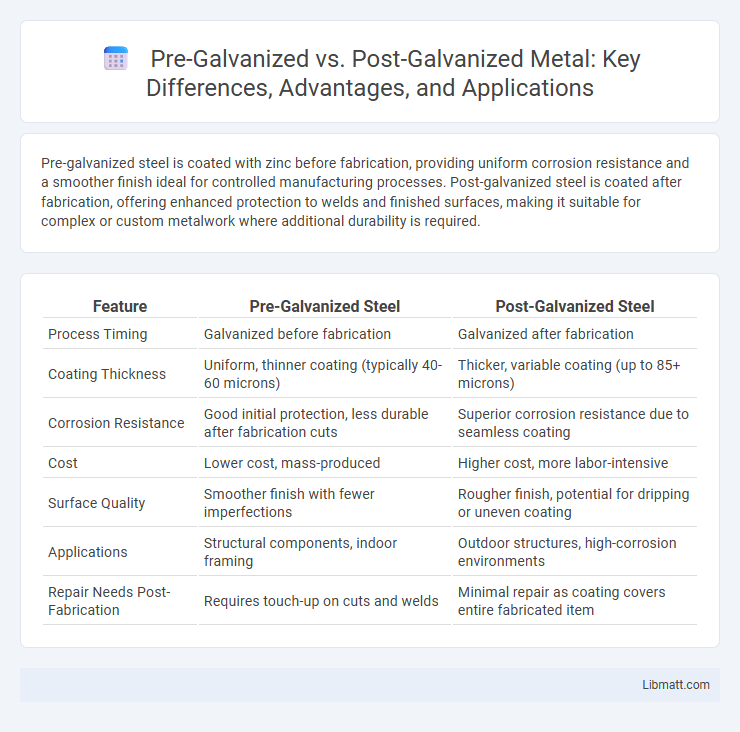
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pre-Galvanized Steel | Post-Galvanized Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Process Timing | Galvanized before fabrication | Galvanized after fabrication |
| Coating Thickness | Uniform, thinner coating (typically 40-60 microns) | Thicker, variable coating (up to 85+ microns) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good initial protection, less durable after fabrication cuts | Superior corrosion resistance due to seamless coating |
| Cost | Lower cost, mass-produced | Higher cost, more labor-intensive |
| Surface Quality | Smoother finish with fewer imperfections | Rougher finish, potential for dripping or uneven coating |
| Applications | Structural components, indoor framing | Outdoor structures, high-corrosion environments |
| Repair Needs Post-Fabrication | Requires touch-up on cuts and welds | Minimal repair as coating covers entire fabricated item |
Introduction to Galvanization
Galvanization involves coating steel or iron with a protective layer of zinc to prevent rust and corrosion, significantly extending the lifespan of metal products. Pre-galvanized steel is coated with zinc before fabrication, ensuring a uniform protective layer, while post-galvanized steel is dipped in zinc after fabrication, allowing for better coverage of welds and joints. Understanding your project's requirements will help determine whether pre-galvanized or post-galvanized materials offer the most effective corrosion resistance.
What is Pre-Galvanized Steel?
Pre-galvanized steel is steel that has been coated with a layer of zinc before the fabrication process, providing corrosion resistance from the outset. This zinc coating is applied in a continuous hot-dip galvanizing process, ensuring uniform protection and enhanced durability. Pre-galvanized steel is commonly used in construction, automotive, and appliance manufacturing for its cost efficiency and consistent quality compared to post-galvanized options.
What is Post-Galvanized Steel?
Post-galvanized steel refers to steel that undergoes the galvanizing process after it has been fabricated into its final shape or form. This method involves coating the finished steel product with a layer of zinc to enhance corrosion resistance. Post-galvanizing is commonly used for custom or complex steel structures where pre-galvanizing is impractical or impossible.
Manufacturing Process Comparison
Pre-galvanized steel undergoes the galvanizing process before fabrication, involving continuous hot-dip coating of steel coils with a zinc layer that provides uniform protection prior to cutting or shaping. Post-galvanized steel is fabricated first and then dipped or sprayed with molten zinc, ensuring corrosion resistance on finished components but often resulting in uneven zinc distribution and challenges in coating welded joints. The pre-galvanizing process offers high efficiency and consistent coating thickness, while post-galvanizing provides better protection to complex shapes but may require additional surface preparation and quality control.
Corrosion Resistance: Pre vs Post Galvanizing
Pre-galvanized steel offers uniform zinc coating applied before fabrication, providing consistent corrosion resistance ideal for controlled manufacturing environments. Post-galvanized steel undergoes hot-dip galvanizing after fabrication, resulting in thicker zinc layers that enhance protection in exposed or harsh conditions. Corrosion resistance in post-galvanized products typically exceeds pre-galvanized counterparts due to the ability to coat complex shapes and weld seams completely.
Durability and Longevity Differences
Pre-galvanized steel features a zinc coating applied before fabrication, providing uniform protection but exposing cut edges to corrosion risks, potentially reducing durability. Post-galvanized steel undergoes galvanization after fabrication, ensuring complete coverage including welds and cut sections, significantly enhancing corrosion resistance and longevity. The thicker zinc layer in post-galvanizing processes results in superior durability, especially in harsh environments, compared to pre-galvanized steel.
Surface Finish and Aesthetic Considerations
Pre-galvanized steel offers a uniform, smooth surface finish that enhances aesthetic appeal and is ideal for visible applications requiring a clean, consistent look. Post-galvanized steel often exhibits a rougher texture and less uniform coating due to the hot-dip process, which can result in a varied appearance. For your project, choosing pre-galvanized steel ensures a more controlled and attractive surface finish, especially when visual quality is a priority.
Cost Analysis: Pre-Galvanized vs Post-Galvanized
Pre-galvanized steel typically incurs lower total costs due to streamlined manufacturing processes and reduced labor expenses compared to post-galvanized steel, which demands additional processing after fabrication. Post-galvanized steel often results in higher material waste and increased labor costs because the galvanizing occurs after cutting and shaping, requiring more precise coverage and extra handling. Cost efficiency favors pre-galvanized steel for large-scale projects, while post-galvanized steel offers flexibility but at a premium price.
Common Applications and Best Use Cases
Pre-galvanized steel is commonly used in construction materials, automotive parts, and household appliances where uniform coating and cost-efficiency are important before fabrication. Post-galvanized steel, with its thick, durable zinc layer applied after fabrication, is ideal for structural components exposed to harsh outdoor environments, such as guardrails, electrical towers, and marine equipment. Your choice depends on whether corrosion resistance during processing or enhanced durability in extreme conditions is the priority.
Choosing the Right Galvanization Method
Choosing the right galvanization method depends on the specific application and environmental conditions. Pre-galvanized steel offers uniform coating thickness and is ideal for manufacturing processes requiring precise dimensions, while post-galvanized steel ensures complete corrosion protection by galvanizing after fabrication. Assessing factors like exposure to harsh environments, fabrication complexity, and budget helps determine whether pre-galvanized or post-galvanized steel is the optimal choice.
pre-galvanized vs post-galvanized Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com