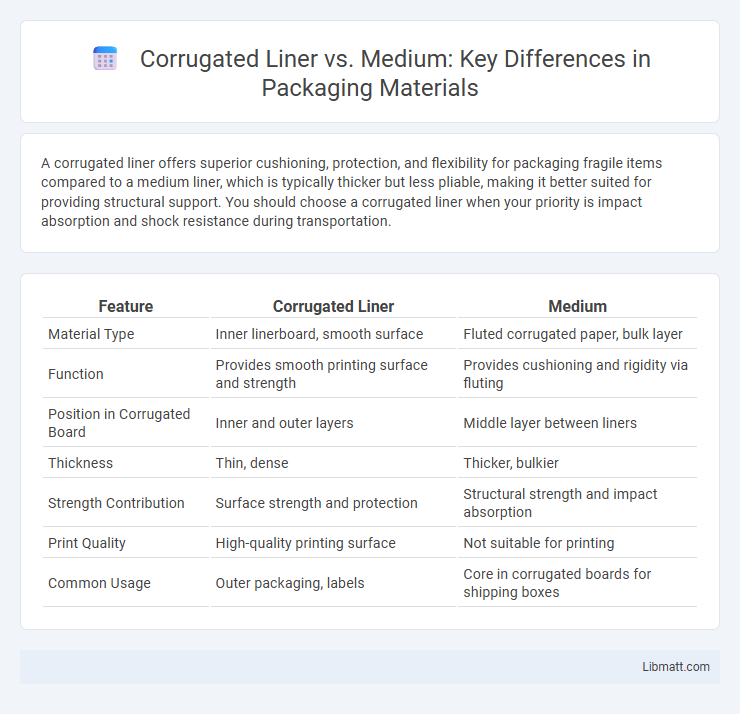
A corrugated liner offers superior cushioning, protection, and flexibility for packaging fragile items compared to a medium liner, which is typically thicker but less pliable, making it better suited for providing structural support. You should choose a corrugated liner when your priority is impact absorption and shock resistance during transportation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Corrugated Liner | Medium |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Inner linerboard, smooth surface | Fluted corrugated paper, bulk layer |
| Function | Provides smooth printing surface and strength | Provides cushioning and rigidity via fluting |
| Position in Corrugated Board | Inner and outer layers | Middle layer between liners |
| Thickness | Thin, dense | Thicker, bulkier |
| Strength Contribution | Surface strength and protection | Structural strength and impact absorption |
| Print Quality | High-quality printing surface | Not suitable for printing |
| Common Usage | Outer packaging, labels | Core in corrugated boards for shipping boxes |
Overview of Corrugated Liner and Medium
Corrugated liners, composed of fluted paper sandwiched between two linerboards, provide superior strength and cushioning for packaging applications, ensuring protection during transit. Medium, also known as the fluted layer alone, is a vital component offering rigidity and support but requires outer liners for complete structural integrity. Your choice between corrugated liner and medium depends on the specific packaging needs, including strength, durability, and cushioning requirements.
Definition and Roles in Corrugated Board
Corrugated liner refers to the flat, outer layers of corrugated board that provide structural strength and durability, while the medium is the wavy, fluted inner layer responsible for cushioning and shock absorption. The liner's role ensures resistance to compression and moisture, contributing to the overall rigidity of the packaging, whereas the medium maintains the board's thickness and protects the contents during handling. Understanding the distinct functions of liner and medium helps you choose the right corrugated board for specific packaging needs.
Material Composition Differences
Corrugated liners are typically made from a single layer of fluted paper sandwiched between two flat linerboards, usually composed of kraft paper, providing strength and rigidity for packaging. Medium, often referred to as fluting medium, consists primarily of a fluted sheet made from recycled fibers or virgin pulp, designed to add cushioning and flexibility between linerboards in corrugated cardboard. Your choice between corrugated liner and medium hinges on the specific structural and protective needs of your packaging solution, as each material offers distinct benefits based on their composition.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Corrugated liners are produced through a continuous corrugation process where fluted medium is pressed between two liners using heated rollers, creating a strong, cushioning structure essential for cardboard boxes. Medium, usually referred to as the fluted layer or single-ply medium, is manufactured by carefully controlling fiber quality and moisture content before undergoing a corrugation process to form the flutes. Your choice between these depends on the required strength and flexibility, as the manufacturing techniques of liners and mediums significantly influence the durability and performance of corrugated board products.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Corrugated liners exhibit superior strength and durability compared to medium boards due to their multi-layered fluted structure, which enhances resistance to crushing and impact forces. Medium boards, being flat sheets of paperboard, offer less structural support and are more prone to bending under pressure. When selecting packaging materials, your choice of a corrugated liner ensures enhanced protection for heavier or fragile items, maximizing load-bearing capacity and lifespan.
Printability and Surface Characteristics
Corrugated liners offer a rougher surface texture compared to medium liners, which enhances ink adhesion and improves printability for high-quality graphics. Medium liners typically exhibit a smoother surface with fewer fibers exposed, resulting in less ink absorption but potentially less vibrant prints. The choice between corrugated liner and medium affects the clarity and durability of printed images, with liners favored for detailed and colorful packaging designs.
Moisture Resistance and Performance
Corrugated liner offers superior moisture resistance due to its multi-layered construction, making it ideal for packaging products exposed to humidity or damp conditions. Medium, often used as the core layer in corrugated board, provides structural strength but lacks the moisture barriers present in corrugated liners. Choosing the right combination enhances your packaging's durability and ensures product protection in varied environmental conditions.
Cost Differences and Economic Impact
Corrugated liners generally cost less per square foot than medium boards due to simpler manufacturing processes and lower material requirements, making them a cost-effective choice for packaging with moderate strength needs. Medium boards, also known as linerboard mediums, provide increased durability and structural integrity, which can reduce product damage and associated costs during shipping despite their higher upfront price. When considering long-term economic impact, investing in medium boards often leads to lower overall expenses by minimizing returns, replacements, and customer dissatisfaction.
Typical Applications for Liner vs Medium
Corrugated liner is typically used for the outer layers of packaging boxes, providing strength and protection for shipping and storage, while medium, the inner fluted layer, offers cushioning and shock absorption. Your choice depends on whether structural rigidity or impact resistance is a priority, with liner being preferable for durability and medium for flexibility in packaging. Common applications for liner include protective cartons and display boxes, whereas medium is often found in shipping containers and protective packaging inserts.
Choosing the Right Material for Packaging Needs
Corrugated liners offer superior strength and cushioning for heavy or fragile items, making them ideal for protective packaging solutions. Medium materials provide flexibility and cost-effectiveness for lighter loads and less demanding shipping conditions. Evaluating the product's weight, fragility, and shipping requirements ensures the selection of the optimal corrugated board combination for durability and efficiency.
Corrugated liner vs medium Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com