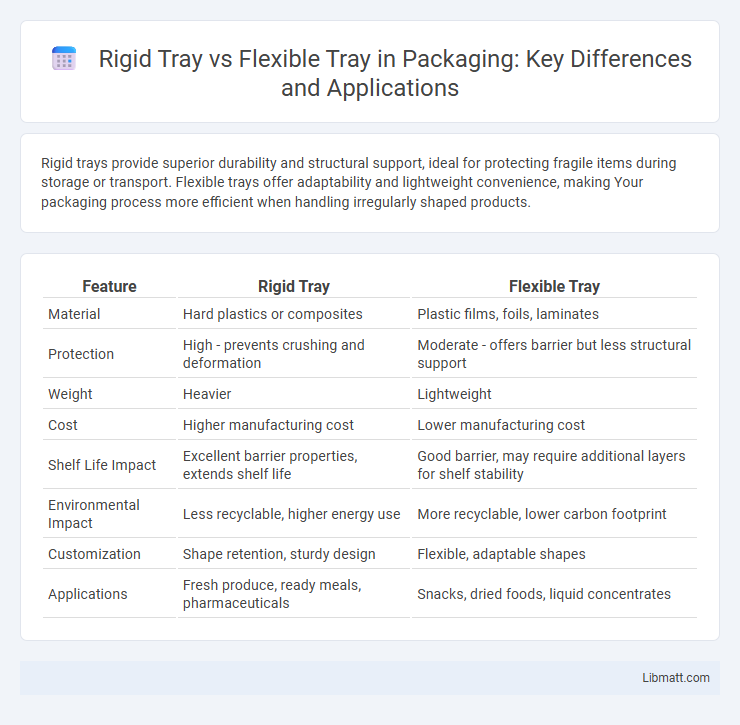
Rigid trays provide superior durability and structural support, ideal for protecting fragile items during storage or transport. Flexible trays offer adaptability and lightweight convenience, making Your packaging process more efficient when handling irregularly shaped products.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rigid Tray | Flexible Tray |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Hard plastics or composites | Plastic films, foils, laminates |
| Protection | High - prevents crushing and deformation | Moderate - offers barrier but less structural support |
| Weight | Heavier | Lightweight |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower manufacturing cost |
| Shelf Life Impact | Excellent barrier properties, extends shelf life | Good barrier, may require additional layers for shelf stability |
| Environmental Impact | Less recyclable, higher energy use | More recyclable, lower carbon footprint |
| Customization | Shape retention, sturdy design | Flexible, adaptable shapes |
| Applications | Fresh produce, ready meals, pharmaceuticals | Snacks, dried foods, liquid concentrates |
Introduction to Rigid and Flexible Trays
Rigid trays are typically made from materials such as plastic, metal, or heavy-duty cardboard, providing superior protection and structural support for delicate or heavy items. Flexible trays, often composed of thin plastic or paper-based materials, offer lightweight, adaptable containment suited for products requiring gentle handling or space efficiency. Choosing between rigid and flexible trays depends on the specific packaging needs, including product fragility, storage conditions, and transportation demands.
Key Differences Between Rigid and Flexible Trays
Rigid trays are made from sturdy materials like plastic or metal, providing superior protection and structural support for fragile or heavy items. Flexible trays, often constructed from materials like silicone or thin plastic, offer adaptability and ease of storage but may lack the durability needed for heavy-duty use. Your choice depends on the balance between the level of protection required and the need for portability or storage efficiency.
Material Composition: Rigid vs Flexible Trays
Rigid trays are typically made from high-density materials such as polystyrene or polypropylene, offering superior structural strength and durability for heavy-duty applications. Flexible trays commonly use materials like polyethylene or elastomers, providing elasticity and adaptability for irregularly shaped products and easy storage. The choice between rigid and flexible tray materials significantly impacts product protection, handling efficiency, and recyclability options.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Rigid trays offer superior durability with their solid structure, resisting cracks and damage under heavy loads, which extends their lifespan significantly in industrial and food packaging applications. Flexible trays, while more adaptable and lightweight, tend to wear out faster due to frequent bending and susceptibility to punctures, reducing their overall durability. Your choice between rigid and flexible trays should consider the specific demands of your use case, balancing longevity with convenience and cost.
Ease of Use and Comfort
Rigid trays provide enhanced stability and support, making them easier to handle and ensuring consistent application, which improves user comfort during extended wear. Flexible trays adapt to the contours of the teeth more effectively, offering a snug fit that reduces discomfort and prevents irritation. Both types prioritize ease of use, but flexible trays are often favored for their lightweight feel and superior comfort in dental treatments.
Storage and Portability Factors
Rigid trays offer enhanced protection with sturdy materials that resist deformation, making them ideal for stacking and secure storage but often at the expense of bulkiness and weight. Flexible trays provide superior portability due to lightweight, foldable designs that occupy minimal space when empty, enabling easy transport and compact storage. Choosing between rigid and flexible trays depends on balancing the need for protective durability against ease of handling and storage efficiency.
Cleaning and Maintenance Requirements
Rigid trays require thorough cleaning with specialized brushes and disinfectants to maintain hygiene, often needing more time and effort due to their fixed shape and material density. Flexible trays, typically made from silicone or soft plastics, offer easier and faster cleaning as they can be bent or folded, allowing for better access to all surfaces and quicker drying times. Both types benefit from regular sanitization, but flexible trays tend to have lower maintenance requirements and reduced risk of microbial buildup due to their adaptability and material properties.
Cost Efficiency and Affordability
Rigid trays generally incur higher production and material costs due to their sturdy structure and durable materials, making them less affordable for short-term or disposable uses. Flexible trays offer significant cost efficiency by using lightweight, low-cost materials that reduce shipping and storage expenses and enable scalable manufacturing processes. For businesses prioritizing affordability and volume, flexible trays present a more economical choice without compromising basic functionality.
Best Applications for Rigid and Flexible Trays
Rigid trays are best suited for applications requiring superior protection and structural support, such as electronics packaging, medical instruments, and food products that need to maintain shape and prevent damage during transportation. Flexible trays excel in uses demanding adaptability, lightweight properties, and cost efficiency, making them ideal for packaging snacks, fresh produce, and single-serve portions. Both tray types optimize product safety and shelf appeal, but choice depends on the balance between durability and flexibility required by the specific application.
Choosing the Right Tray for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate tray depends on durability, reusability, and specific application requirements. Rigid trays offer robust protection for heavy or delicate items, ensuring stability during transport, while flexible trays provide lightweight, space-saving solutions ideal for packaging irregularly shaped or lightweight goods. Evaluating factors such as material compatibility, cost-effectiveness, and environmental impact aids in determining whether a rigid or flexible tray best suits your operational needs.
Rigid tray vs flexible tray Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com