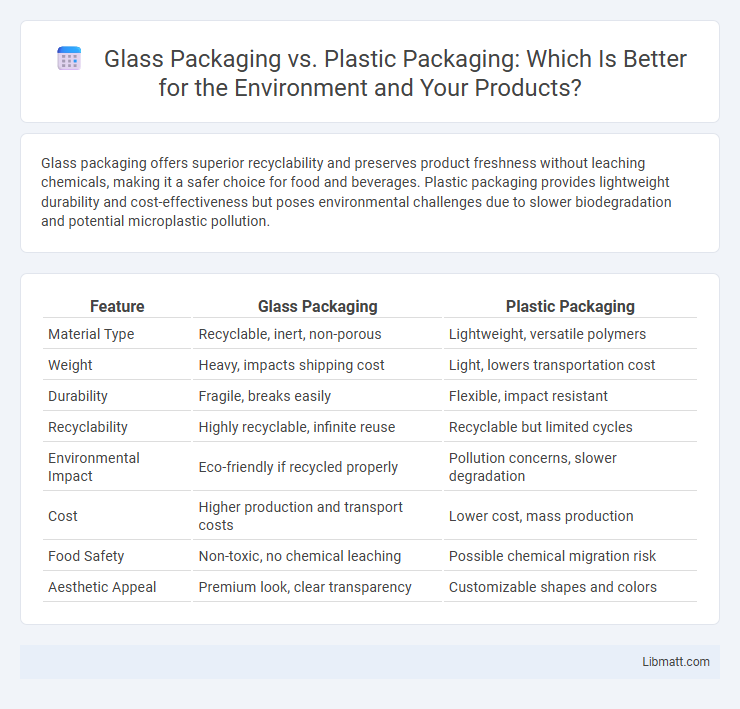
Glass packaging offers superior recyclability and preserves product freshness without leaching chemicals, making it a safer choice for food and beverages. Plastic packaging provides lightweight durability and cost-effectiveness but poses environmental challenges due to slower biodegradation and potential microplastic pollution.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glass Packaging | Plastic Packaging |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Recyclable, inert, non-porous | Lightweight, versatile polymers |
| Weight | Heavy, impacts shipping cost | Light, lowers transportation cost |
| Durability | Fragile, breaks easily | Flexible, impact resistant |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable, infinite reuse | Recyclable but limited cycles |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly if recycled properly | Pollution concerns, slower degradation |
| Cost | Higher production and transport costs | Lower cost, mass production |
| Food Safety | Non-toxic, no chemical leaching | Possible chemical migration risk |
| Aesthetic Appeal | Premium look, clear transparency | Customizable shapes and colors |
Introduction to Glass vs Plastic Packaging
Glass packaging offers superior recyclability and chemical inertness compared to plastic packaging, which often contains harmful additives and has lower recycling rates. Its impermeability preserves product freshness without leaching contaminants, making it ideal for food and beverages. Your choice between glass and plastic packaging impacts sustainability, product safety, and environmental footprint.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Glass packaging offers superior environmental benefits due to its infinite recyclability without loss of quality, reducing landfill waste and resource extraction. Plastic packaging, while lightweight and versatile, contributes significantly to pollution through slower degradation rates and microplastic contamination in ecosystems. Your choice of glass packaging supports sustainability by minimizing carbon footprint and promoting circular economy practices, making it an eco-friendly alternative to conventional plastics.
Health and Safety Considerations
Glass packaging offers superior health and safety benefits compared to plastic, as it is non-toxic, non-reactive, and free from harmful chemicals such as BPA, phthalates, and heavy metals commonly found in plastics. It preserves product integrity by providing an impermeable barrier against contaminants and does not leach substances into food or beverages, ensuring safer consumption. Glass is also more resistant to microbial contamination and easier to sterilize, making it a preferred choice for pharmaceuticals and food products requiring stringent safety standards.
Sustainability and Recycling Rates
Glass packaging offers superior sustainability due to its infinite recyclability without quality degradation, achieving recycling rates up to 70% in many regions. Plastic packaging, while lighter and reducing transportation emissions, often faces challenges with lower recycling rates averaging around 14-30% globally and issues of microplastic pollution. The circular economy benefits significantly from glass's ability to be remelted repeatedly, contrasting with plastic's tendency to downcycle or end up in landfills.
Cost Analysis of Glass and Plastic
Glass packaging typically incurs higher production and transportation costs due to its weight and fragility, impacting overall supply chain expenses. Plastic packaging offers cost advantages with lower material and shipping costs, making it more economical for large-scale distribution. However, long-term environmental costs and recycling efficiency may influence total cost-effectiveness between the two options.
Product Preservation and Shelf Life
Glass packaging offers superior product preservation by providing an impermeable barrier against oxygen, moisture, and contaminants, which significantly extends shelf life compared to plastic packaging. Unlike most plastics, glass does not leach chemicals into products, ensuring purity and maintaining flavor integrity, especially for food and beverages. The high inertness and recyclability of glass also make it a preferred choice for long-term storage and maintaining product quality.
Consumer Perceptions and Preferences
Consumers increasingly favor glass packaging for its perceived premium quality, sustainability, and safety compared to plastic. Glass is often associated with better product preservation and environmental responsibility, influencing purchase decisions and brand loyalty. Your choice of packaging can significantly impact consumer trust and preference, especially among eco-conscious audiences.
Industrial Applications and Versatility
Glass packaging excels in industrial applications requiring chemical inertness, high-temperature resistance, and superior preservation qualities, making it ideal for pharmaceuticals, beverages, and food products with long shelf lives. Plastic packaging offers greater versatility due to its lightweight, shatter-resistance, and moldability, widely used in consumer goods, logistics, and diverse industries where flexibility and cost-effectiveness are critical. Both materials serve distinct industrial needs, with glass preferred for premium, sensitive contents and plastic favored for convenience and mass distribution.
Transportation and Logistics Factors
Glass packaging, though highly recyclable and reusable, presents challenges in transportation due to its heavier weight and fragility, increasing shipping costs and risk of breakage. Plastic packaging offers advantages in logistics with its lightweight nature, durability, and flexibility, reducing transport energy consumption and minimizing damage. Choosing the right packaging impacts your supply chain efficiency, balancing environmental sustainability with cost-effectiveness in transportation and handling.
Future Trends in Packaging Materials
Glass packaging is experiencing a resurgence due to its recyclability, durability, and growing consumer demand for sustainable options, driving innovation in lightweight and shatter-resistant designs. Plastic packaging continues to evolve with advances in biodegradable polymers and recycled content, aiming to reduce environmental impact while maintaining cost-effectiveness and flexibility. Your choice of packaging material will increasingly reflect environmental priorities and regulatory changes shaping future trends in both industries.
Glass packaging vs plastic packaging Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com