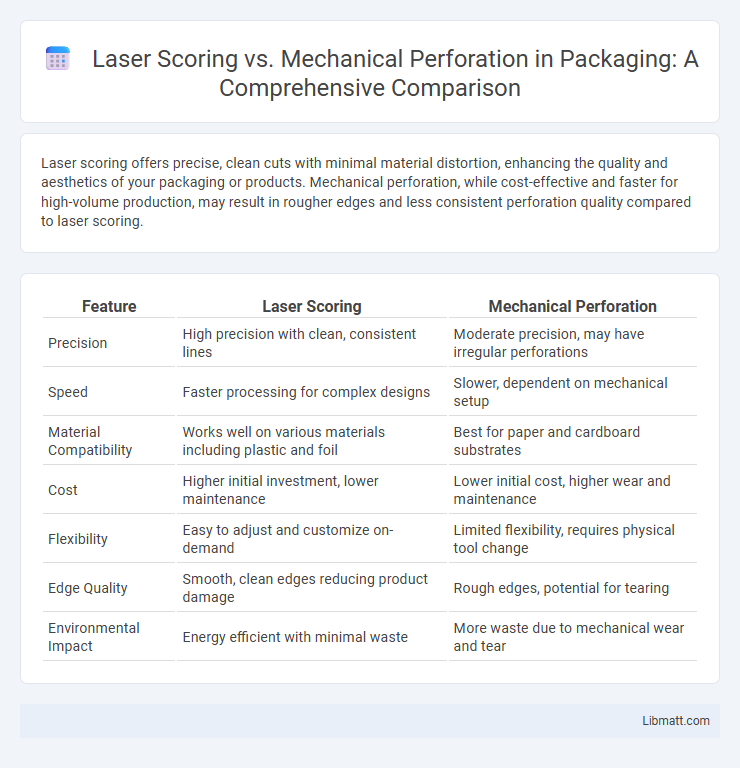
Laser scoring offers precise, clean cuts with minimal material distortion, enhancing the quality and aesthetics of your packaging or products. Mechanical perforation, while cost-effective and faster for high-volume production, may result in rougher edges and less consistent perforation quality compared to laser scoring.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Laser Scoring | Mechanical Perforation |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | High precision with clean, consistent lines | Moderate precision, may have irregular perforations |
| Speed | Faster processing for complex designs | Slower, dependent on mechanical setup |
| Material Compatibility | Works well on various materials including plastic and foil | Best for paper and cardboard substrates |
| Cost | Higher initial investment, lower maintenance | Lower initial cost, higher wear and maintenance |
| Flexibility | Easy to adjust and customize on-demand | Limited flexibility, requires physical tool change |
| Edge Quality | Smooth, clean edges reducing product damage | Rough edges, potential for tearing |
| Environmental Impact | Energy efficient with minimal waste | More waste due to mechanical wear and tear |
Introduction to Packaging Perforation Techniques
Laser scoring offers precise and clean cuts for packaging perforation, enhancing tearability without compromising package integrity. Mechanical perforation uses blades or needles to create holes, providing cost-effective and traditional solutions but with less accuracy and potential material deformation. Choosing between laser scoring and mechanical perforation depends on packaging material, design complexity, and production volume requirements.
What is Laser Scoring?
Laser scoring is a precision cutting technique that uses a focused laser beam to create controlled, shallow grooves on the surface of materials, enabling easy folding or tearing without compromising structural integrity. This method offers high accuracy, minimal material waste, and faster processing compared to traditional mechanical perforation, which relies on physical blades or pins to puncture holes. Laser scoring is widely used in packaging, printing, and manufacturing industries for enhancing product functionality and aesthetic appeal.
Understanding Mechanical Perforation
Mechanical perforation uses rotary blades or needles to create precise holes or patterns in materials, ensuring consistent depth and spacing for controlled tearing or ventilation. This method excels in producing clean, uniform perforations on paper, plastic films, and packaging materials without generating heat or altering the substrate's properties. Compared to laser scoring, mechanical perforation offers durability and cost-efficiency for high-volume production, especially in applications requiring strong material integrity.
Precision and Consistency: Laser vs Mechanical
Laser scoring delivers superior precision and consistency compared to mechanical perforation, utilizing focused beams to create clean, uniform lines without physical contact. This technology minimizes material distortion and ensures exact depth control, resulting in highly repeatable perforation patterns. Your production process benefits from reduced errors and enhanced quality, especially in detailed or delicate applications.
Speed and Efficiency Comparison
Laser scoring achieves higher speed and precision compared to mechanical perforation due to its non-contact process, reducing setup time and minimizing material waste. Mechanical perforation involves physical contact that can slow production and increase maintenance needs due to tool wear. Industries prioritize laser scoring for high-volume applications where rapid and efficient processing is critical.
Impact on Packaging Material Integrity
Laser scoring creates precise, clean lines on packaging materials without compromising structural integrity, ensuring the material remains sturdy and intact. Mechanical perforation applies physical pressure, which can cause micro-tears or weaken the material, potentially leading to premature damage or reduced protection. Your choice between these methods affects the durability and reliability of packaging, crucial for maintaining product safety.
Cost Implications for Manufacturers
Laser scoring offers precision and flexibility in packaging design, often reducing material wastage and lowering labor costs compared to mechanical perforation. Mechanical perforation requires significant initial investment in tooling and maintenance, leading to higher costs for small to mid-scale production runs. Manufacturers seeking scalability and cost-efficiency tend to favor laser scoring due to its lower operational expenses and adaptability to varied packaging materials.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Laser scoring offers precise, clean cuts ideal for electronics, medical device packaging, and automotive industries requiring intricate designs and minimal material distortion. Mechanical perforation excels in food packaging, labels, and tear-open sachets where cost-effectiveness and high-speed production are prioritized. Your choice depends on the specific industry demands for precision, speed, and material compatibility.
Environmental Considerations
Laser scoring produces minimal waste and reduces material consumption by creating precise cuts without physical contact, lowering environmental impact compared to mechanical perforation. Mechanical perforation generates more scrap and often requires higher energy consumption due to blade wear and maintenance. Laser technology offers improved sustainability by decreasing resource use and enabling cleaner production processes in packaging and manufacturing industries.
Choosing the Right Perforation Method
Laser scoring offers precise and customizable perforation patterns ideal for delicate materials and detailed designs, while mechanical perforation provides cost-effective, high-speed processing suitable for thick or rigid substrates. Selecting the right perforation method depends on factors such as material type, production volume, desired accuracy, and budget constraints. Evaluating laser scoring for fine detail and flexibility or mechanical perforation for durability and efficiency ensures optimal performance and product quality.
Laser scoring vs mechanical perforation Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com