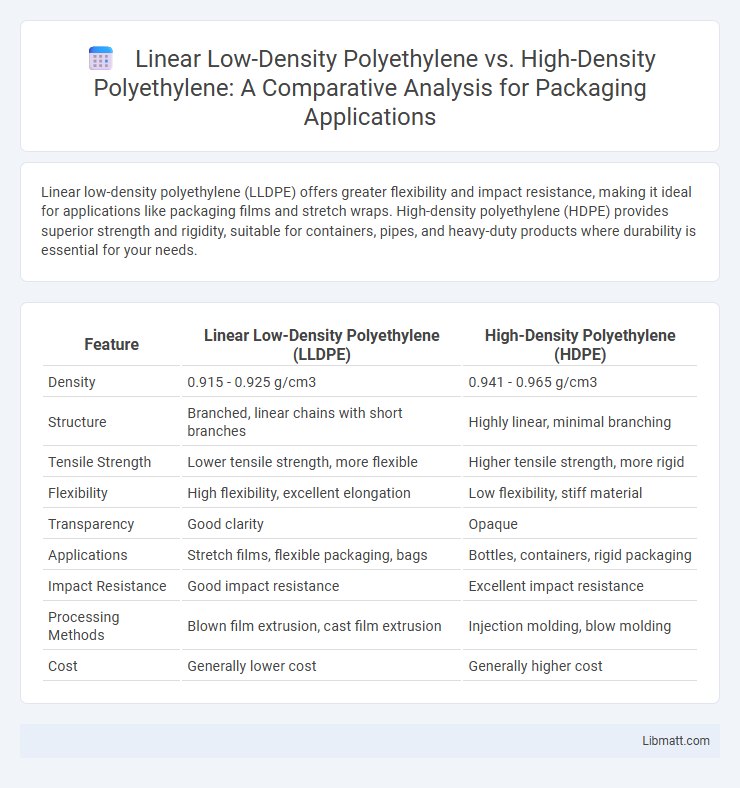
Linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) offers greater flexibility and impact resistance, making it ideal for applications like packaging films and stretch wraps. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) provides superior strength and rigidity, suitable for containers, pipes, and heavy-duty products where durability is essential for your needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) | High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 0.915 - 0.925 g/cm3 | 0.941 - 0.965 g/cm3 |
| Structure | Branched, linear chains with short branches | Highly linear, minimal branching |
| Tensile Strength | Lower tensile strength, more flexible | Higher tensile strength, more rigid |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, excellent elongation | Low flexibility, stiff material |
| Transparency | Good clarity | Opaque |
| Applications | Stretch films, flexible packaging, bags | Bottles, containers, rigid packaging |
| Impact Resistance | Good impact resistance | Excellent impact resistance |
| Processing Methods | Blown film extrusion, cast film extrusion | Injection molding, blow molding |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Generally higher cost |
Introduction to Polyethylene Types
Linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) features a more branched molecular structure resulting in flexible films with higher tensile strength, ideal for packaging applications. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) has a linear structure with minimal branching, offering greater rigidity, chemical resistance, and impact strength suitable for containers and piping. Understanding these differences helps you select the most appropriate polyethylene type based on performance requirements and application needs.
What is Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE)?
Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) is a type of polyethylene characterized by its linear polymer chains with short, uniform branching, which enhances its tensile strength and flexibility compared to traditional low-density polyethylene (LDPE). LLDPE is commonly used in film applications such as packaging, stretch wrap, and agriculture due to its excellent impact resistance and clarity. Understanding LLDPE can help you choose the right material for applications requiring durability and flexibility over the more rigid and crystalline properties of high-density polyethylene (HDPE).
What is High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)?
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its high strength-to-density ratio, making it ideal for products requiring durability and stiffness such as pipes, containers, and plastic bottles. HDPE has a linear structure with minimal branching, resulting in a dense, crystalline material that exhibits excellent chemical resistance and impact strength. Compared to Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE), HDPE offers higher tensile strength and greater rigidity but is less flexible, influencing its typical applications in heavy-duty packaging and construction materials.
Chemical Structure and Composition Differences
Linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) consists of short, uniform branches attached to a linear polymer backbone, resulting in a less crystalline and more flexible structure. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) features minimal branching, yielding a tightly packed, highly crystalline structure with greater density and rigidity. The variations in branching and crystallinity significantly influence their mechanical properties and applications in packaging and industrial products.
Mechanical and Physical Properties Comparison
Linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) exhibits higher tensile strength and better impact resistance compared to high-density polyethylene (HDPE), making it ideal for flexible applications. HDPE offers greater stiffness, higher tensile modulus, and superior chemical resistance, suited for rigid containers and piping systems. Your choice between LLDPE and HDPE should depend on the required balance between flexibility and mechanical strength for your application.
Processing Methods: LLDPE vs HDPE
Linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) is primarily processed using extrusion and blow molding due to its excellent flexibility and toughness, allowing for the production of thin films and packaging materials. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is commonly processed through injection molding, blow molding, and rotational molding, benefiting from its higher crystallinity and strength to create rigid products like containers and piping. The processing temperatures for LLDPE typically range between 160-230degC, while HDPE requires slightly higher temperatures, around 200-275degC, reflecting differences in molecular structure and thermal properties.
Applications and Industry Uses
Linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) is predominantly used in flexible packaging, such as stretch films, bags, and agricultural covers, due to its excellent tensile strength and flexibility. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) finds extensive applications in rigid containers, pipes, and molded products, favored for its high stiffness, chemical resistance, and impact strength. Your choice between LLDPE and HDPE depends on the specific requirements of the packaging or manufacturing process, balancing flexibility and durability needs in various industrial sectors.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) has a lower environmental impact due to its flexibility and thin film applications, which use less material and generate less plastic waste compared to high-density polyethylene (HDPE). HDPE, known for its rigidity and strength, offers higher recyclability rates with established recycling streams and is often preferred for durable goods and containers. Your choice between LLDPE and HDPE should consider the balance between environmental footprint and recyclability based on the specific application.
Cost and Market Availability
Linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) generally costs more than high-density polyethylene (HDPE) due to its more complex manufacturing process involving copolymerization. HDPE dominates the market with higher availability and widespread use in products like containers and pipes, benefiting from established production infrastructure. LLDPE, while less abundant, is favored in flexible packaging and film applications where its superior tensile strength justifies the premium price.
Choosing Between LLDPE and HDPE
Choosing between Linear Low-Density Polyethylene (LLDPE) and High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) depends on application requirements such as flexibility, tensile strength, and chemical resistance. LLDPE offers superior flexibility and impact resistance, making it ideal for stretch films and packaging applications, while HDPE provides higher density and stiffness suitable for containers, piping, and corrosion-resistant products. Understanding the specific mechanical properties and environmental stress-cracking resistance of both polymers ensures optimal material selection tailored to product performance needs.
Linear low-density polyethylene vs high-density polyethylene Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com