Absorbent paper quickly soaks up liquids, making it ideal for cleaning spills, blotting, and crafting, while non-absorbent paper resists moisture, providing durability and suitability for printing and packaging. Understanding these properties helps you choose the right paper type for your specific needs.
Table of Comparison
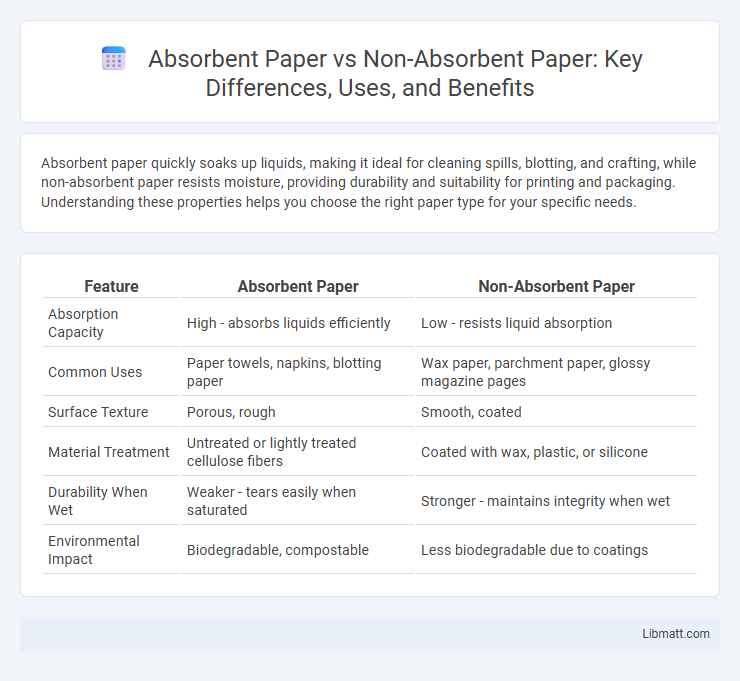
| Feature | Absorbent Paper | Non-Absorbent Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Absorption Capacity | High - absorbs liquids efficiently | Low - resists liquid absorption |
| Common Uses | Paper towels, napkins, blotting paper | Wax paper, parchment paper, glossy magazine pages |
| Surface Texture | Porous, rough | Smooth, coated |
| Material Treatment | Untreated or lightly treated cellulose fibers | Coated with wax, plastic, or silicone |
| Durability When Wet | Weaker - tears easily when saturated | Stronger - maintains integrity when wet |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, compostable | Less biodegradable due to coatings |
Introduction to Absorbent vs Non-Absorbent Paper
Absorbent paper is designed to soak up liquids quickly, making it ideal for uses like cleaning, painting, and medical applications where moisture control is crucial. Non-absorbent paper resists liquid penetration, maintaining its structure and preventing damage, which is essential for packaging, printing, and archival documents. Understanding the difference helps you select the right paper type to meet specific functional requirements and enhance performance in various tasks.
Defining Absorbent Paper: Key Characteristics
Absorbent paper is designed with a porous structure that allows it to quickly soak up liquids, making it ideal for tasks like cleaning spills or blotting ink. Key characteristics include high porosity, fibrous texture, and a composition that promotes rapid liquid uptake. Understanding these properties helps you choose the right type of paper for applications where moisture absorption is critical.
What Makes Paper Non-Absorbent?
Non-absorbent paper typically features a dense fiber structure combined with coatings such as clay, calcium carbonate, or polymers, creating a sealed surface that repels liquids. These coatings block water penetration, making the paper ideal for uses like glossy magazines, photo prints, and waterproof labels. Understanding what makes paper non-absorbent helps you select the right type for applications requiring moisture resistance and durability.
Common Applications of Absorbent Paper
Absorbent paper is widely used in medical applications such as wound dressings, gauze pads, and surgical sponges due to its ability to soak up blood and bodily fluids. In the food industry, absorbent paper serves as liner sheets in packaging to control moisture and maintain product freshness. Laboratory settings utilize absorbent paper for tasks like filtration, blotting, and sample collection, capitalizing on its efficient liquid absorption properties.
Uses of Non-Absorbent Paper in Various Industries
Non-absorbent paper is widely used in industries requiring moisture resistance and surface durability, such as packaging, where it protects sensitive products from water damage. It is essential in printing industries for high-quality image reproduction, preventing ink bleed and ensuring crisp text and graphics. Additionally, non-absorbent paper finds applications in food service for disposable trays and liners, maintaining hygiene and structural integrity against grease and liquids.
Material Composition Differences
Absorbent paper is typically manufactured from cellulose fibers with a porous structure that allows liquids to penetrate and be retained effectively. Non-absorbent paper often features a coating of polymers or wax, creating a barrier that resists moisture absorption and enhances durability. Understanding these material composition differences helps you choose the right paper type for specific applications such as packaging, printing, or cleaning.
Performance in Liquid Handling and Spills
Absorbent paper excels in liquid handling and spills by quickly soaking up fluids, making it ideal for cleaning and filtration tasks. Non-absorbent paper resists liquid penetration, providing durability and preventing sogginess when moisture exposure is minimal or controlled. Understanding these differences helps you select the right paper type for efficient spill management or precise liquid containment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Absorbent paper typically requires more resources and chemical treatments, resulting in a higher environmental footprint compared to non-absorbent paper, which often uses less processing and can be more easily recycled. Sustainable paper choices focus on minimizing deforestation, water usage, and energy consumption, with non-absorbent papers generally offering better recyclability and lower greenhouse gas emissions. Your selection of paper can contribute to reduced waste and support eco-friendly production practices by prioritizing materials with certified sustainability standards.
Cost Comparison and Availability
Absorbent paper generally costs more than non-absorbent paper due to specialized materials and manufacturing processes that enhance liquid retention properties. Non-absorbent paper is widely available and produced in larger quantities, making it more cost-effective for everyday uses such as printing and packaging. Availability of absorbent paper is typically more limited, with distribution focused on niche markets like medical or industrial applications.
Choosing the Right Paper for Your Needs
Absorbent paper, such as tissue or blotting paper, is ideal for tasks requiring moisture absorption, making it perfect for cleaning spills or artistic endeavors involving ink and watercolor. Non-absorbent paper, like glossy photo paper or coated cardstock, suits printing high-resolution images or documents where ink needs to stay on the surface without bleeding. Selecting the right type depends on your specific application needs, balancing absorbency with desired texture and durability.
absorbent paper vs non-absorbent paper Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com