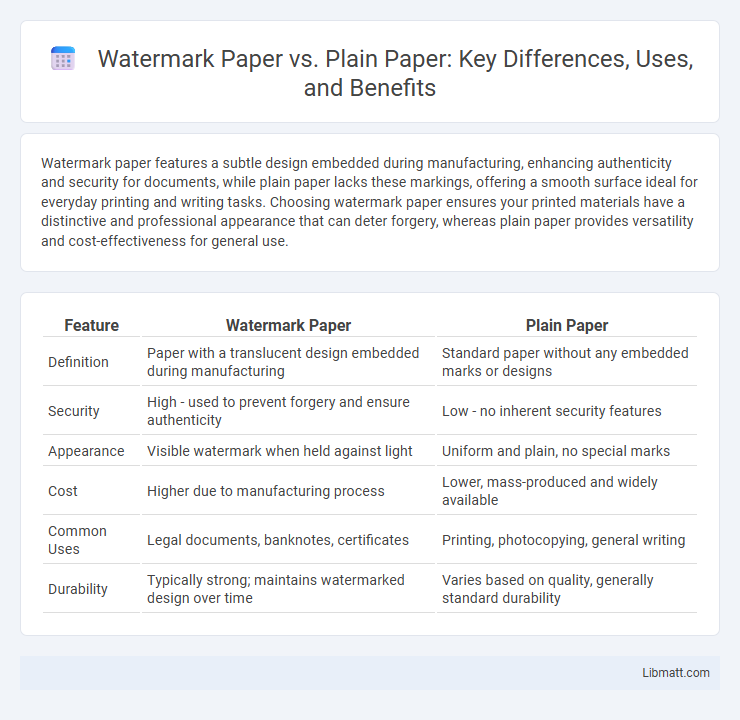
Watermark paper features a subtle design embedded during manufacturing, enhancing authenticity and security for documents, while plain paper lacks these markings, offering a smooth surface ideal for everyday printing and writing tasks. Choosing watermark paper ensures your printed materials have a distinctive and professional appearance that can deter forgery, whereas plain paper provides versatility and cost-effectiveness for general use.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Watermark Paper | Plain Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Paper with a translucent design embedded during manufacturing | Standard paper without any embedded marks or designs |
| Security | High - used to prevent forgery and ensure authenticity | Low - no inherent security features |
| Appearance | Visible watermark when held against light | Uniform and plain, no special marks |
| Cost | Higher due to manufacturing process | Lower, mass-produced and widely available |
| Common Uses | Legal documents, banknotes, certificates | Printing, photocopying, general writing |
| Durability | Typically strong; maintains watermarked design over time | Varies based on quality, generally standard durability |
Introduction to Watermark Paper vs Plain Paper
Watermark paper features embedded designs or patterns visible when held against light, enhancing authenticity and security for documents like certificates and currency. Plain paper lacks these embedded marks, offering a smooth and uniform surface suited for everyday printing and writing tasks. The presence of watermarks distinguishes the paper's purpose and perceived value, making it essential for secure printing applications.
Definition and Characteristics of Watermark Paper
Watermark paper is a type of specialty paper that contains a translucent design or pattern embedded during the manufacturing process, which becomes visible when held up to light. This feature is commonly used for authentication, security measures, and aesthetic enhancement in documents such as banknotes, certificates, and legal papers. Unlike plain paper, watermark paper offers an additional layer of protection against forgery and adds distinctive visual appeal.
Key Features of Plain Paper
Plain paper is characterized by its smooth surface and consistent texture, making it ideal for everyday printing and writing tasks. It lacks any embedded designs or watermarks, providing a clean, blank canvas suitable for various ink types and printing methods. You can rely on plain paper for affordable, versatile use in documents, notes, and general office needs.
Historical Significance of Watermarked Paper
Watermarked paper has been a critical tool in authenticating and dating historical documents since the 13th century, used by papermakers to signify origin and quality. This subtle design, embedded during the paper manufacturing process, served as an early form of brand identification and security against forgery. Its presence in manuscripts and official papers provides valuable insights into historical trade routes, economic conditions, and artistic trends of different eras.
Security Benefits of Using Watermark Paper
Watermark paper offers enhanced security benefits by incorporating embedded designs or patterns that are difficult to replicate, providing a reliable method to authenticate documents and deter counterfeiting. Unlike plain paper, watermark paper enables quick visual verification by authorities, reducing the risk of forgery in sensitive documents such as certificates, legal papers, and currency. The unique translucency and customizability of watermarks serve as a robust anti-fraud measure, ensuring document integrity in high-security environments.
Common Uses for Watermark Paper
Watermark paper is commonly used for official documents, certificates, and currency to ensure authenticity and prevent counterfeiting. It is favored in legal agreements, diplomas, and high-value packaging where security and verification are paramount. In contrast, plain paper is typically used for everyday printing, note-taking, and general office correspondence due to its cost-effectiveness and versatility.
Cost Comparison: Watermark Paper vs Plain Paper
Watermark paper generally costs more than plain paper due to the specialized manufacturing process that embeds the watermark, enhancing security and authenticity. Plain paper is more economical and widely used for everyday printing tasks, making it the preferred choice for bulk printing needs. Your decision between watermark and plain paper should consider the balance between cost and the requirement for document verification or brand protection.
Durability and Quality Differences
Watermark paper offers enhanced durability compared to plain paper due to its thicker fibers and embedded designs that resist wear and tear. The quality of watermark paper ensures higher resistance to folding, tearing, and environmental damage, making it ideal for important documents. Your choice of paper impacts the longevity and professional appearance of printed materials, with watermark paper generally providing superior quality.
Environmental Impact of Watermark and Plain Paper
Watermark paper often requires additional production steps and specialized materials, which can increase its environmental footprint compared to plain paper. The use of watermarks may lead to higher water and energy consumption during manufacturing, as well as greater resource intensity in sourcing fibers. Your choice between watermark and plain paper can influence sustainability efforts, with plain paper generally offering a lower environmental impact due to simpler production processes.
Choosing the Right Paper for Your Needs
Watermark paper offers a subtle, embedded design that enhances authenticity and professional appearance, making it ideal for official documents and certificates. Plain paper provides versatile, cost-effective options for everyday printing, note-taking, or general use where branding is not essential. Assess your specific needs for security, presentation, and budget to select the most suitable paper type for your project.
watermark paper vs plain paper Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com