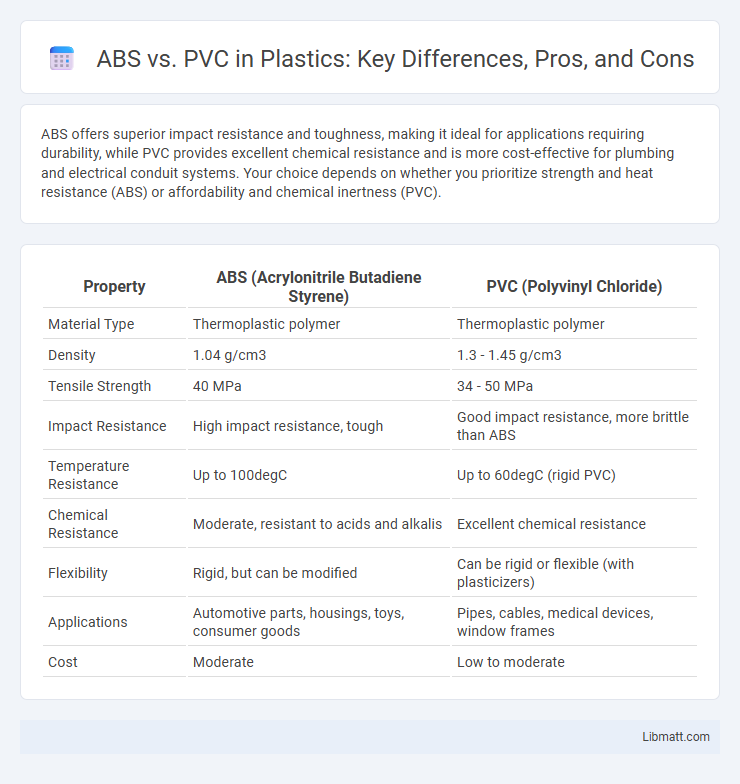
ABS offers superior impact resistance and toughness, making it ideal for applications requiring durability, while PVC provides excellent chemical resistance and is more cost-effective for plumbing and electrical conduit systems. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize strength and heat resistance (ABS) or affordability and chemical inertness (PVC).
Table of Comparison
| Property | ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) | PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoplastic polymer | Thermoplastic polymer |
| Density | 1.04 g/cm3 | 1.3 - 1.45 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 40 MPa | 34 - 50 MPa |
| Impact Resistance | High impact resistance, tough | Good impact resistance, more brittle than ABS |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 100degC | Up to 60degC (rigid PVC) |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate, resistant to acids and alkalis | Excellent chemical resistance |
| Flexibility | Rigid, but can be modified | Can be rigid or flexible (with plasticizers) |
| Applications | Automotive parts, housings, toys, consumer goods | Pipes, cables, medical devices, window frames |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
Introduction to ABS and PVC
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a thermoplastic polymer known for its impact resistance, toughness, and ease of machining, commonly used in automotive parts, consumer goods, and piping systems. PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is a versatile plastic widely utilized in construction, electrical cables, and medical devices due to its chemical resistance, durability, and low cost. Both ABS and PVC offer unique properties tailored for specific industrial and commercial applications, emphasizing the importance of material selection based on environmental exposure and mechanical requirements.
What is ABS?
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is a durable thermoplastic polymer known for its impact resistance, toughness, and lightweight properties, commonly used in automotive parts, consumer electronics, and plumbing fittings. Its molecular structure combines acrylonitrile for chemical resistance, butadiene for toughness, and styrene for rigidity and glossy finish. When choosing materials for your project, ABS offers enhanced durability and heat resistance compared to many alternatives.
What is PVC?
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is a versatile thermoplastic polymer widely used in construction, plumbing, and electrical insulation due to its durability, corrosion resistance, and affordability. Its chemical composition allows it to be rigid or flexible, making it suitable for pipes, window frames, and wiring insulation. PVC's resistance to chemicals, fire, and weathering makes it a preferred material for numerous industrial and commercial applications.
Key Differences Between ABS and PVC
ABS and PVC differ primarily in their chemical composition and applications, with ABS being a thermoplastic polymer known for impact resistance and toughness, commonly used in automotive parts and toys, while PVC offers superior chemical resistance and durability, ideal for piping and construction materials. ABS has a higher temperature tolerance, making it suitable for applications involving heat, whereas PVC excels in exposure to moisture and corrosive environments. Your choice between ABS and PVC should be guided by specific project needs regarding mechanical strength, temperature resilience, and environmental exposure.
Physical Properties Comparison
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) exhibits higher impact resistance and better toughness compared to PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), making it suitable for applications requiring durability. PVC offers greater chemical resistance and superior weatherability, retaining its properties under exposure to UV light and moisture. The density of ABS ranges from 1.04 to 1.06 g/cm3, while PVC is denser at approximately 1.3 to 1.45 g/cm3, influencing weight considerations in product design.
Common Applications of ABS
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is widely used in automotive components, consumer electronics housings, and household appliances due to its high impact resistance and toughness. Its applications include LEGO bricks, piping systems, and protective gear, where durability and heat resistance are essential. ABS's ease of molding and strong mechanical properties make it preferred over PVC in products requiring enhanced structural integrity and surface finish.
Common Applications of PVC
PVC is widely used in construction for plumbing pipes, electrical cable insulation, and window frames due to its durability and resistance to corrosion. Its flexibility and waterproof properties make it ideal for irrigation systems and sewage pipelines. PVC also finds applications in medical devices and packaging because of its chemical stability and ease of sterilization.
Cost and Availability
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) typically costs more than PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) due to its higher impact resistance and durability, making it suitable for demanding applications. PVC is widely available and generally less expensive, favored for plumbing and electrical conduit projects because of its affordability and ease of installation. Both materials are readily accessible in most hardware stores, but PVC's greater market presence often leads to lower prices and faster procurement times.
Environmental Impact and Safety
ABS plastic is less environmentally friendly due to its non-biodegradable properties and the release of toxic fumes when burned, posing significant safety risks. PVC contains chlorine, which can release harmful dioxins during production and disposal, contributing to environmental pollution and potential health hazards. Both materials require careful handling and recycling processes to mitigate their environmental impact and ensure user safety.
Which Material Should You Choose?
Choosing between ABS and PVC depends on your project requirements and environmental conditions. ABS offers superior impact resistance and toughness, making it ideal for applications requiring durability, while PVC provides excellent chemical resistance and better weatherability for outdoor use. Your decision should factor in these material strengths along with cost, installation ease, and specific regulatory standards for plumbing or construction.
ABS vs PVC Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com