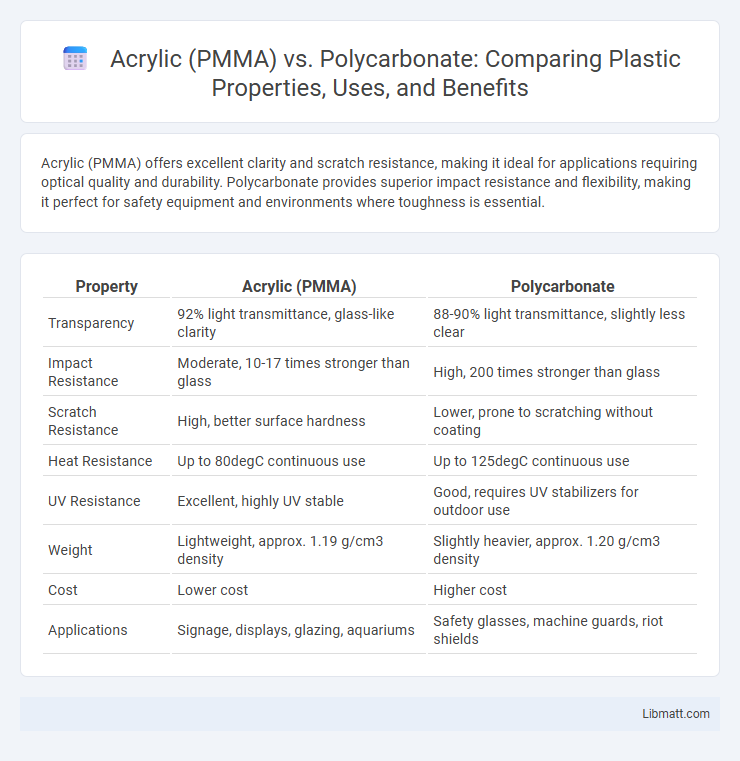
Acrylic (PMMA) offers excellent clarity and scratch resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring optical quality and durability. Polycarbonate provides superior impact resistance and flexibility, making it perfect for safety equipment and environments where toughness is essential.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Acrylic (PMMA) | Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | 92% light transmittance, glass-like clarity | 88-90% light transmittance, slightly less clear |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate, 10-17 times stronger than glass | High, 200 times stronger than glass |
| Scratch Resistance | High, better surface hardness | Lower, prone to scratching without coating |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 80degC continuous use | Up to 125degC continuous use |
| UV Resistance | Excellent, highly UV stable | Good, requires UV stabilizers for outdoor use |
| Weight | Lightweight, approx. 1.19 g/cm3 density | Slightly heavier, approx. 1.20 g/cm3 density |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Applications | Signage, displays, glazing, aquariums | Safety glasses, machine guards, riot shields |
Introduction to Acrylic (PMMA) and Polycarbonate
Acrylic (PMMA) is a lightweight, transparent thermoplastic known for its excellent optical clarity, weather resistance, and UV stability, making it ideal for applications such as windows, signage, and displays. Polycarbonate is a highly impact-resistant, durable plastic with superior toughness, often used in safety goggles, automotive components, and electronic housings. You can choose between Acrylic and Polycarbonate based on your need for clarity and scratch resistance versus impact strength and flexibility.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Acrylic (PMMA) is a thermoplastic polymer composed of methyl methacrylate monomers, forming a linear chain structure that provides hardness and clarity. Polycarbonate consists of carbonate groups linked by bisphenol A units, resulting in a polymer with a more complex, branched molecular structure that offers superior impact resistance. The chemical composition of PMMA leads to high optical clarity and UV resistance, while polycarbonate's structure imparts toughness and heat resistance.
Strength and Impact Resistance Comparison
Polycarbonate exhibits superior impact resistance, with a tensile strength around 70 MPa and the ability to withstand impacts up to 900 J/m, making it ideal for applications demanding high durability. Acrylic (PMMA), while offering higher scratch resistance and clarity, has a tensile strength near 65 MPa but lower impact resistance, typically around 20 J/m. For environments requiring robust strength and exceptional impact resistance, polycarbonate is the preferred choice over acrylic.
Optical Clarity and Light Transmission
Acrylic (PMMA) offers superior optical clarity and higher light transmission rates, often exceeding 92%, making it ideal for applications requiring clear, bright visuals. Polycarbonate, while slightly less transparent with around 88-90% light transmission, provides greater impact resistance and durability. Your choice depends on whether optical purity or toughness is the priority for the intended use.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Acrylic (PMMA) typically weighs about 1.18 g/cm3, making it lighter than polycarbonate, which has a density around 1.20 g/cm3. Polycarbonate exhibits superior flexibility and impact resistance, with the ability to withstand higher stress and deformation before cracking, unlike the more brittle acrylic. The enhanced flexibility of polycarbonate is ideal for applications requiring durability and resilience, whereas acrylic's lighter weight benefits uses prioritizing ease of handling and aesthetic clarity.
Weather and UV Resistance Performance
Acrylic (PMMA) demonstrates superior weather and UV resistance compared to polycarbonate, maintaining clarity and structural integrity over extended outdoor exposure without yellowing or becoming brittle. Polycarbonate tends to degrade faster under UV radiation, often requiring protective coatings to enhance its durability against sun damage and weathering. This makes acrylic the preferred choice for applications demanding long-term transparency and outdoor stability.
Thermal Properties: Temperature Tolerance
Acrylic (PMMA) offers a temperature tolerance typically up to 80degC (176degF), making it suitable for applications with moderate heat exposure. In contrast, polycarbonate exhibits superior thermal properties, withstanding temperatures up to 130degC (266degF), providing enhanced durability in high-temperature environments. Your choice between these materials should consider the specific thermal demands of your project to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Workability and Fabrication Techniques
Acrylic (PMMA) offers excellent workability with ease of cutting, drilling, and thermoforming, making it ideal for detailed fabrication projects requiring precision and clarity. Polycarbonate provides superior impact resistance and can be fabricated using similar techniques but requires specialized tools due to its toughness and tendency to melt if overheated. Your choice between the two depends on balancing ease of fabrication with durability and application-specific requirements.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Acrylic (PMMA) generally offers a lower initial cost compared to polycarbonate, making it a budget-friendly option for applications requiring clear, lightweight materials. However, polycarbonate's superior impact resistance and durability often translate into longer service life and reduced replacement expenses, providing better long-term economic value. Your choice should weigh upfront material costs against maintenance and lifecycle expenses to optimize overall budget efficiency.
Common Applications and Industry Uses
Acrylic (PMMA) is widely used in retail displays, signage, and automotive tail lights due to its excellent clarity and UV resistance, making it ideal for aesthetic and outdoor applications. Polycarbonate is favored in bulletproof windows, eyewear lenses, and electronic housings because of its superior impact resistance and toughness. Your choice between these materials depends on whether optical clarity or durability is the priority for your specific industrial application.
Acrylic (PMMA) vs Polycarbonate Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com