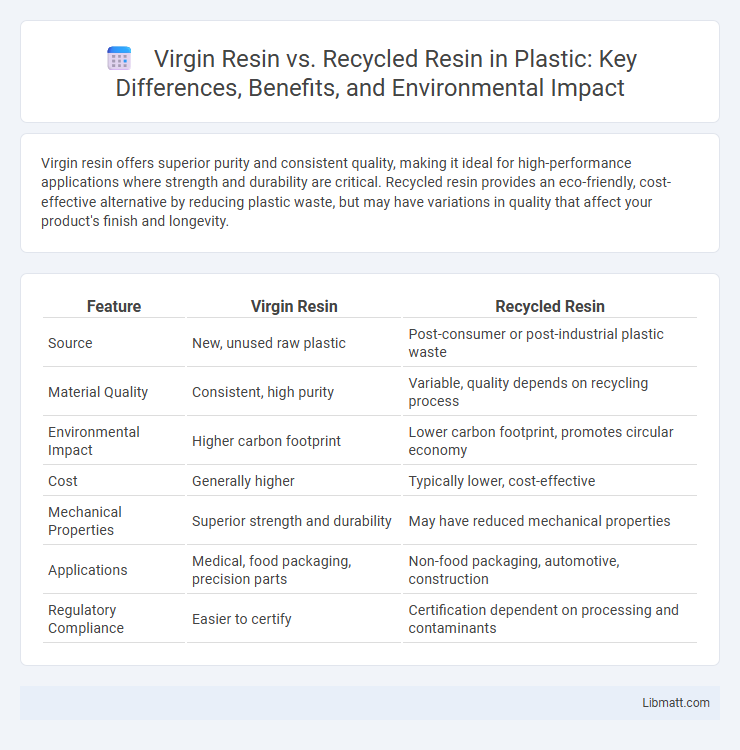
Virgin resin offers superior purity and consistent quality, making it ideal for high-performance applications where strength and durability are critical. Recycled resin provides an eco-friendly, cost-effective alternative by reducing plastic waste, but may have variations in quality that affect your product's finish and longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Virgin Resin | Recycled Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Source | New, unused raw plastic | Post-consumer or post-industrial plastic waste |
| Material Quality | Consistent, high purity | Variable, quality depends on recycling process |
| Environmental Impact | Higher carbon footprint | Lower carbon footprint, promotes circular economy |
| Cost | Generally higher | Typically lower, cost-effective |
| Mechanical Properties | Superior strength and durability | May have reduced mechanical properties |
| Applications | Medical, food packaging, precision parts | Non-food packaging, automotive, construction |
| Regulatory Compliance | Easier to certify | Certification dependent on processing and contaminants |
Introduction to Resin: Virgin vs Recycled
Virgin resin is a newly manufactured polymer made from raw petrochemical materials, offering high purity and consistent quality essential for demanding applications. Recycled resin, derived from reclaimed plastics, provides an eco-friendly alternative by reducing waste and conserving resources, often at a lower cost but with potential variability in performance. Your choice between virgin and recycled resin depends on the balance between quality requirements and sustainability goals in your project.
Defining Virgin Resin: Composition and Properties
Virgin resin is a polymer material created directly from petrochemical feedstocks, ensuring consistent purity and performance. Its composition consists of unprocessed monomers, resulting in superior mechanical strength, clarity, and resistance to contaminants compared to recycled resin. These properties make virgin resin ideal for applications demanding strict quality control, such as medical devices and food packaging.
Understanding Recycled Resin: Sources and Types
Recycled resin originates from post-consumer and post-industrial plastic waste, including materials like PET bottles, HDPE containers, and polypropylene scrap. These resins undergo processes such as mechanical recycling, where plastics are shredded and re-melted, or chemical recycling, which breaks polymers down into monomers for repolymerization. Different types of recycled resin, including both rigid and flexible grades, offer varying performance attributes depending on their feedstock and recycling methods, influencing their suitability for diverse manufacturing applications.
Manufacturing Processes: Virgin Resin and Recycled Resin
Virgin resin manufacturing involves polymerizing raw petrochemical feedstocks through processes like extrusion and pelletization to produce pure, high-quality plastic pellets. Recycled resin production includes collecting, sorting, cleaning, and reprocessing post-consumer or post-industrial plastic waste using techniques such as mechanical grinding, melting, and pelletizing to create reusable resin pellets. Both processes require precise control to ensure resin consistency, but recycled resin manufacturing incorporates additional quality checks to address contaminants and maintain material performance.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Virgin resin production consumes more energy and generates higher carbon emissions compared to recycled resin, contributing significantly to environmental pollution. Recycled resin reduces waste sent to landfills and lowers the demand for fossil fuels, promoting a circular economy and conserving natural resources. Choosing recycled resin for Your products can substantially minimize Your environmental footprint and support sustainable manufacturing practices.
Performance and Quality Differences
Virgin resin offers superior performance and consistent quality due to its pure polymer composition, resulting in enhanced strength, clarity, and durability in end products. Recycled resin often exhibits variability in mechanical properties and may contain impurities, leading to reduced tensile strength and potential discoloration or odor. Manufacturers frequently prefer virgin resin for high-precision applications, while recycled resin suits non-critical uses where environmental impact is prioritized.
Cost Analysis: Virgin vs Recycled Resin
Virgin resin typically incurs higher production costs due to raw material extraction and processing, resulting in increased pricing compared to recycled resin. Recycled resin benefits from lower manufacturing expenses by reusing plastic waste, leading to more cost-effective pricing and reduced environmental impact. Market trends show growing demand for recycled resin to optimize both economic savings and sustainability objectives in plastic production.
Applications and Industry Usage
Virgin resin is widely used in high-performance applications such as automotive parts, medical devices, and food packaging due to its consistent purity and mechanical properties. Recycled resin finds extensive use in industries like consumer goods, construction materials, and textiles where sustainability and cost-effectiveness are prioritized. Both types of resin serve critical roles, with virgin resin favored for strict regulatory compliance and recycled resin driving circular economy initiatives.
Regulatory Considerations and Certifications
Regulatory considerations for virgin resin typically emphasize compliance with strict purity and safety standards such as FDA food contact approvals and REACH regulations, ensuring consistent quality for sensitive applications. Recycled resin must meet additional certifications like the Global Recycled Standard (GRS) and OEKO-TEX to verify its environmental impact and contaminant control, reflecting a growing demand for sustainability. Your choice between virgin and recycled resin influences compliance complexity and certification requirements, impacting product labeling and market acceptance.
Future Trends in Resin Usage
Future trends in resin usage are shifting towards increased adoption of recycled resin due to rising environmental regulations and consumer demand for sustainable products. Virgin resin still dominates in high-performance applications requiring consistent quality and structural integrity. Your choice between virgin and recycled resin will increasingly be influenced by advances in recycling technology improving the properties and availability of recycled materials.
Virgin Resin vs Recycled Resin Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com