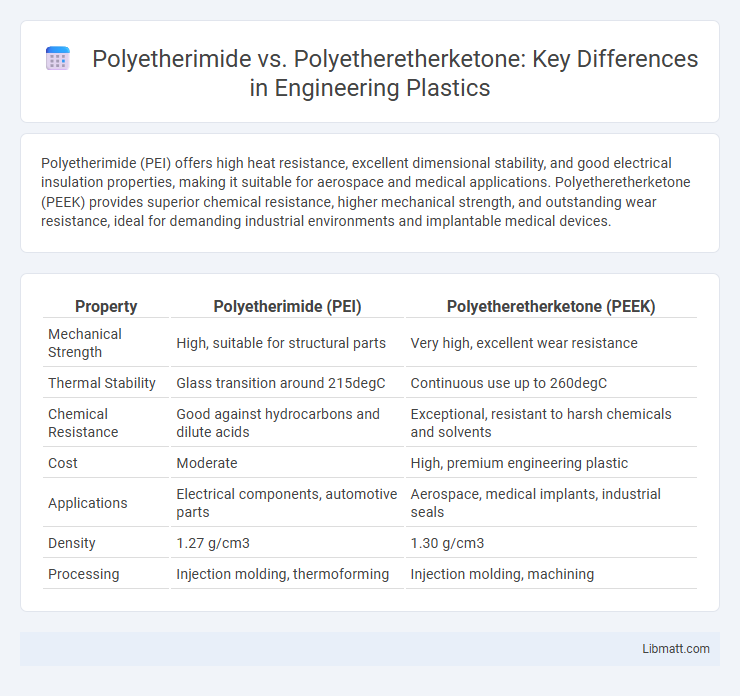
Polyetherimide (PEI) offers high heat resistance, excellent dimensional stability, and good electrical insulation properties, making it suitable for aerospace and medical applications. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) provides superior chemical resistance, higher mechanical strength, and outstanding wear resistance, ideal for demanding industrial environments and implantable medical devices.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyetherimide (PEI) | Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | High, suitable for structural parts | Very high, excellent wear resistance |
| Thermal Stability | Glass transition around 215degC | Continuous use up to 260degC |
| Chemical Resistance | Good against hydrocarbons and dilute acids | Exceptional, resistant to harsh chemicals and solvents |
| Cost | Moderate | High, premium engineering plastic |
| Applications | Electrical components, automotive parts | Aerospace, medical implants, industrial seals |
| Density | 1.27 g/cm3 | 1.30 g/cm3 |
| Processing | Injection molding, thermoforming | Injection molding, machining |
Introduction to Polyetherimide (PEI) and Polyetheretherketone (PEEK)
Polyetherimide (PEI) is a high-performance amorphous thermoplastic known for its excellent strength, thermal stability up to 170degC, and flame resistance, making it ideal for aerospace and medical applications. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) is a semi-crystalline polymer with exceptional mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and thermal stability exceeding 250degC, commonly used in automotive, electronics, and biomedical implants. Understanding the unique attributes of PEI and PEEK helps you select the optimal material based on temperature requirements and application-specific demands.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Polyetherimide (PEI) consists of repeating units featuring an imide group linked to aromatic rings, providing high thermal stability and rigidity. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) features ketone and ether linkages connecting aromatic rings, contributing to its exceptional mechanical properties and chemical resistance. The presence of imide groups in PEI results in higher glass transition temperatures, while PEEK's ketone groups enhance crystallinity and toughness.
Mechanical Properties Analysis
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) exhibits superior tensile strength and modulus compared to polyetherimide (PEI), making it highly suitable for high-stress applications. PEI offers better impact resistance and higher heat deflection temperature, enhancing its performance in thermal and mechanical cycling environments. Both polymers demonstrate excellent chemical resistance, but PEEK's crystallinity contributes to enhanced wear resistance and long-term mechanical stability.
Thermal Performance and Heat Resistance
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) exhibits superior thermal performance with a melting point around 343degC and continuous use temperature up to 260degC, making it ideal for high-heat environments. Polyetherimide (PEI) offers excellent heat resistance with a glass transition temperature near 217degC but has a lower maximum service temperature compared to PEEK. The thermal stability and mechanical strength of PEEK under prolonged high temperatures outperform PEI, making PEEK preferable for demanding aerospace and medical applications requiring extreme heat resistance.
Electrical and Dielectric Properties
Polyetherimide (PEI) offers excellent electrical insulation with a dielectric constant typically around 3.2 and a volume resistivity exceeding 10^15 ohm-cm, making it ideal for high-performance electronic applications. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) provides superior dielectric strength up to 17 kV/mm and maintains stable electrical properties at elevated temperatures, surpassing PEI in harsh environments. Your selection between PEI and PEEK should consider the specific electrical performance requirements and operating conditions of your device.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Stability
Polyetherimide (PEI) exhibits excellent chemical resistance against acids, bases, and hydrocarbons, maintaining its integrity in harsh environments, while Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) offers superior resistance to a broader range of aggressive chemicals, including strong oxidizing agents. Environmental stability in PEI supports high-temperature applications up to 170degC with good dimensional stability, whereas PEEK withstands continuous use at temperatures around 250degC, showing exceptional resistance to hydrolysis and radiation. Your choice between PEI and PEEK should consider the specific chemical exposure and temperature conditions in your application for optimal performance.
Processing and Manufacturability
Polyetherimide (PEI) offers easier processing with a lower melting point around 217degC, enabling faster manufacturing cycles and versatile molding techniques such as injection molding and thermoforming. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) requires higher processing temperatures, typically above 343degC, demanding specialized equipment and more precise thermal control to maintain material integrity. Your choice between PEI and PEEK should consider the available processing capabilities and the complexity of the intended application to optimize manufacturability.
Key Applications and Industry Uses
Polyetherimide (PEI) finds extensive use in aerospace, medical devices, and electrical components due to its excellent thermal stability and flame resistance, making it suitable for high-performance insulation and sterilizable parts. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) is preferred in automotive, aerospace, and chemical processing industries for its superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and ability to withstand extreme temperatures. Your choice between PEI and PEEK depends on specific application requirements such as thermal endurance, chemical exposure, and mechanical load.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Polyetherimide (PEI) generally offers a lower cost option compared to Polyetheretherketone (PEEK), making it more accessible for budget-sensitive applications while still delivering high performance. PEEK commands a premium price due to its superior chemical resistance and mechanical properties, which limits its market availability primarily to specialized industries like aerospace and medical devices. Your choice between PEI and PEEK will depend on balancing budget constraints with the specific material performance requirements and availability in your target market.
Selecting the Right Polymer: PEI vs PEEK
Choosing between Polyetherimide (PEI) and Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) depends on your application's thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical resistance requirements. PEI offers excellent flame retardancy and dimensional stability with a continuous use temperature up to 170degC, while PEEK surpasses PEI in high-temperature performance withstanding up to 250degC and superior chemical resistance in harsh environments. Evaluating these polymers based on their thermal endurance, mechanical properties, and exposure conditions ensures optimal material selection for reliable and long-lasting results.
Polyetherimide vs Polyetheretherketone Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com