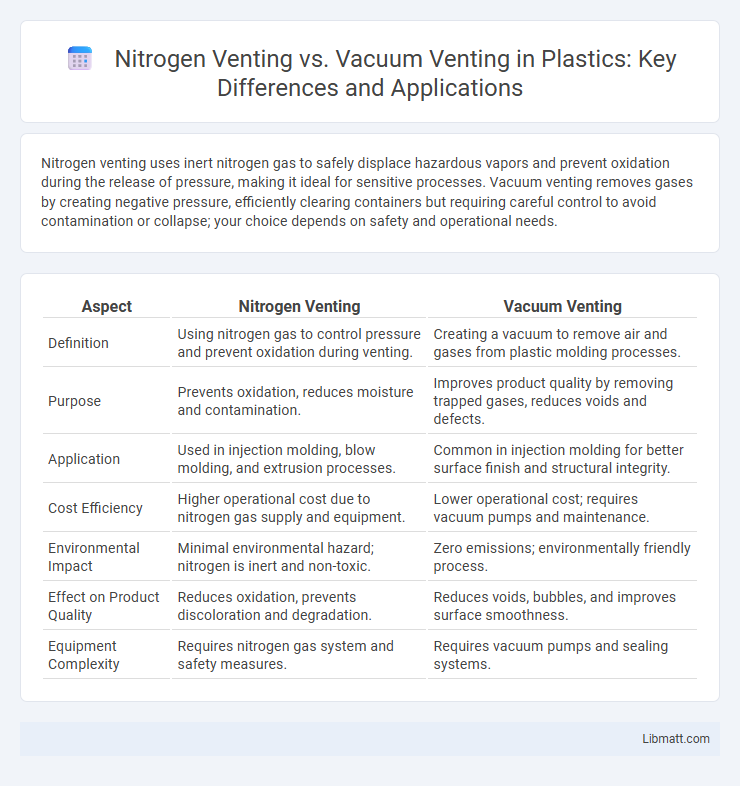
Nitrogen venting uses inert nitrogen gas to safely displace hazardous vapors and prevent oxidation during the release of pressure, making it ideal for sensitive processes. Vacuum venting removes gases by creating negative pressure, efficiently clearing containers but requiring careful control to avoid contamination or collapse; your choice depends on safety and operational needs.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Nitrogen Venting | Vacuum Venting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Using nitrogen gas to control pressure and prevent oxidation during venting. | Creating a vacuum to remove air and gases from plastic molding processes. |
| Purpose | Prevents oxidation, reduces moisture and contamination. | Improves product quality by removing trapped gases, reduces voids and defects. |
| Application | Used in injection molding, blow molding, and extrusion processes. | Common in injection molding for better surface finish and structural integrity. |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher operational cost due to nitrogen gas supply and equipment. | Lower operational cost; requires vacuum pumps and maintenance. |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal environmental hazard; nitrogen is inert and non-toxic. | Zero emissions; environmentally friendly process. |
| Effect on Product Quality | Reduces oxidation, prevents discoloration and degradation. | Reduces voids, bubbles, and improves surface smoothness. |
| Equipment Complexity | Requires nitrogen gas system and safety measures. | Requires vacuum pumps and sealing systems. |
Understanding Nitrogen Venting and Vacuum Venting
Nitrogen venting utilizes inert nitrogen gas to safely release pressure, preventing oxidation and contamination in industrial processes. Vacuum venting involves reducing pressure within a system by drawing air or gases out, often used to avoid overpressure or maintain controlled environments. Understanding the operational differences and applications of nitrogen venting versus vacuum venting is critical for selecting appropriate pressure management techniques in chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processing industries.
Key Principles of Gas Venting Methods
Nitrogen venting relies on inert gas displacement to safely remove hazardous gases by introducing nitrogen, which prevents combustion and contamination during gas release. Vacuum venting uses reduced pressure to extract gases, ensuring controlled removal without introducing additional gases, ideal for sensitive environments. Your choice between nitrogen venting and vacuum venting depends on factors like safety requirements, gas properties, and process control priorities.
How Nitrogen Venting Works
Nitrogen venting works by introducing inert nitrogen gas into tanks or vessels to displace volatile or flammable gases, preventing the ingress of oxygen and reducing the risk of explosions. This process maintains a positive pressure, minimizing contamination and oxidation while ensuring safe storage of sensitive materials. Nitrogen vent systems are commonly used in chemical, pharmaceutical, and petroleum industries to enhance safety and product stability.
How Vacuum Venting Operates
Vacuum venting operates by creating a negative pressure environment inside a tank or vessel, allowing external air pressure to enter and equalize the internal pressure as liquids are withdrawn or vapors condense. This process prevents structural damage caused by vacuum conditions, such as tank collapse, and ensures safe handling of volatile substances. Understanding how vacuum venting functions helps you maintain optimal pressure control and protect your storage systems from vacuum-induced hazards.
Performance Comparison: Nitrogen vs Vacuum Venting
Nitrogen venting offers superior inerting performance by minimizing oxidation and moisture contamination during storage or processing, making it ideal for sensitive materials. Vacuum venting excels in preventing pressure build-up by efficiently removing gases, providing rapid response in dynamic systems. Performance-wise, nitrogen venting ensures enhanced safety and product quality, while vacuum venting maximizes pressure control and system stability in industrial applications.
Application Areas for Nitrogen Venting
Nitrogen venting is primarily utilized in chemical processing, food packaging, and pharmaceutical manufacturing to prevent oxidation and contamination by providing an inert atmosphere. It is essential in storage tanks and pipelines for flammable liquids, reducing the risk of fire or explosion by displacing oxygen. In electronics production, nitrogen venting protects sensitive components from moisture and particulate exposure during manufacturing and packaging.
Application Areas for Vacuum Venting
Vacuum venting is primarily applied in industries requiring safe evacuation of air or gases to prevent pressure imbalances, such as chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and food packaging. This method is essential in maintaining product integrity and preventing contamination during storage or transportation by ensuring a controlled environment. Your operations can benefit from vacuum venting by reducing the risk of container collapse and improving process safety in sensitive applications.
Safety Considerations in Gas Venting Processes
Nitrogen venting reduces the risk of fire and explosion by displacing oxygen with an inert gas, ensuring a safer environment during gas venting processes. Vacuum venting minimizes gas release into the atmosphere, lowering environmental hazards and potential exposure to harmful substances. Your choice between these methods should prioritize the specific safety requirements of the operation, considering factors such as flammability, toxicity, and pressure control.
Environmental Impact: Nitrogen vs Vacuum Venting
Nitrogen venting releases inert nitrogen gas into the atmosphere, which is non-toxic but contributes to greenhouse gas accumulation and resource consumption during production. Vacuum venting minimizes gas emissions by using reduced pressure to control system pressure, resulting in lower environmental impact due to decreased venting volume and energy efficiency. Choosing vacuum venting over nitrogen venting can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve sustainability in industrial processes.
Choosing the Right Venting Method for Your Needs
Nitrogen venting provides an inert atmosphere that prevents oxidation and contamination, ideal for sensitive chemical processes and storage of reactive substances. Vacuum venting effectively removes gases and vapors, reducing pressure and preventing vapor lock in systems such as fuel tanks and reactors. Selecting the right venting method depends on the specific operational requirements, including the nature of the stored product, safety considerations, and environmental regulations.
Nitrogen venting vs vacuum venting Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com