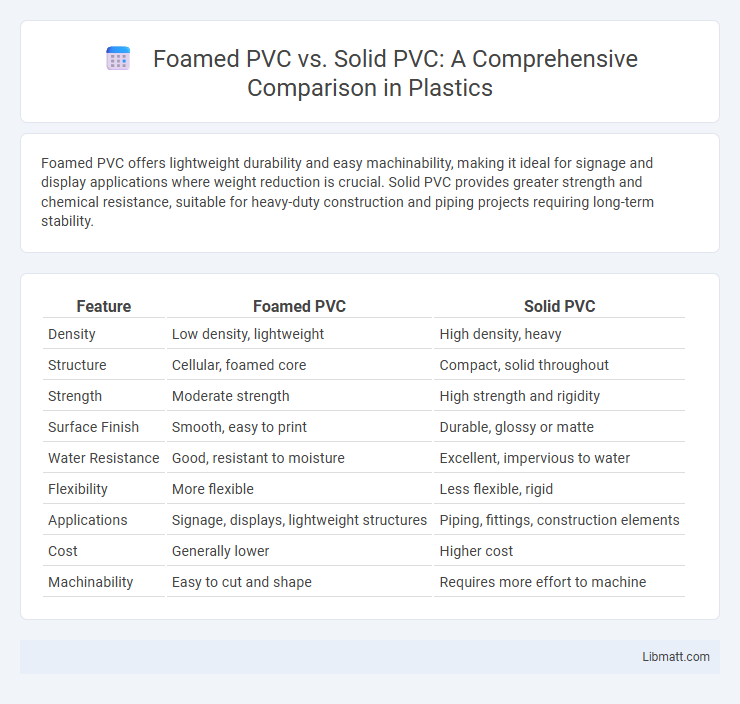
Foamed PVC offers lightweight durability and easy machinability, making it ideal for signage and display applications where weight reduction is crucial. Solid PVC provides greater strength and chemical resistance, suitable for heavy-duty construction and piping projects requiring long-term stability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Foamed PVC | Solid PVC |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low density, lightweight | High density, heavy |
| Structure | Cellular, foamed core | Compact, solid throughout |
| Strength | Moderate strength | High strength and rigidity |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, easy to print | Durable, glossy or matte |
| Water Resistance | Good, resistant to moisture | Excellent, impervious to water |
| Flexibility | More flexible | Less flexible, rigid |
| Applications | Signage, displays, lightweight structures | Piping, fittings, construction elements |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher cost |
| Machinability | Easy to cut and shape | Requires more effort to machine |
Introduction to Foamed PVC and Solid PVC
Foamed PVC is a lightweight, rigid material with a cellular core that provides excellent insulation and durability, making it ideal for signage, displays, and construction applications. Solid PVC, on the other hand, is a dense, non-porous plastic known for its high strength, chemical resistance, and versatility in piping, window frames, and marine uses. Your choice between foamed PVC and solid PVC depends on factors such as weight requirements, structural needs, and environmental exposure.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Foamed PVC consists of a cellular core created by expanding the PVC material during manufacturing, resulting in a lightweight, rigid foam sheet with closed cells. Solid PVC, made from pure polyvinyl chloride resin, undergoes extrusion or calendaring without expansion, producing a dense, homogenous material with consistent thickness. The manufacturing process of foamed PVC involves chemical or physical blowing agents to create the foam structure, whereas solid PVC relies on compact molding or extrusion techniques for uniform density and strength.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Foamed PVC offers a lightweight, rigid structure with excellent impact resistance and thermal insulation, making it ideal for signage and displays. Solid PVC, on the other hand, provides superior density, durability, and chemical resistance, suited for piping and construction applications. Understanding these key physical properties helps you select the right material for strength, weight, and environmental exposure requirements.
Weight and Density Differences
Foamed PVC is significantly lighter than solid PVC due to its cellular structure, which reduces its density to typically between 0.4 and 0.9 g/cm3, compared to solid PVC's density of about 1.3 to 1.45 g/cm3. This weight difference makes foamed PVC ideal for applications requiring easy handling and reduced load, such as signage and displays. Solid PVC's higher density provides greater strength and durability for structural uses, where weight is less critical.
Strength and Durability Factors
Foamed PVC offers lightweight properties with moderate strength, making it suitable for applications requiring easy handling but less impact resistance. Solid PVC provides superior strength and durability, with high resistance to wear, chemicals, and environmental stress, ideal for heavy-duty or structural uses. The dense composition of solid PVC contributes to its enhanced mechanical performance compared to the cellular structure of foamed PVC.
Applications in Various Industries
Foamed PVC offers lightweight, durable, and cost-effective properties ideal for signage, construction, and exhibition displays, while Solid PVC provides superior strength and chemical resistance essential in plumbing, electrical insulation, and industrial manufacturing. The choice between Foamed PVC and Solid PVC depends on your specific application requirements, balancing weight, rigidity, and exposure to environmental factors. Industries like automotive, advertising, and healthcare benefit from tailored PVC solutions to optimize performance and longevity.
Installation and Workability
Foamed PVC is lighter and easier to cut, drill, and shape, making installation faster and less labor-intensive compared to solid PVC. Its reduced density enhances workability for creative projects, especially in signage and displays where intricate designs are required. Solid PVC offers superior rigidity and strength, but its heavier weight and tougher surface demand more effort during cutting and fitting processes.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Foamed PVC offers a cost-effective alternative to solid PVC, generally priced 20-30% lower due to its reduced material density and manufacturing process. Solid PVC is widely available and preferred for applications requiring higher strength and durability, but it typically commands a higher price point. Both materials are readily accessible through industrial suppliers, with foamed PVC often stocked in thicker sheets for signage and displays, while solid PVC is more common in plumbing and construction markets.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Foamed PVC generates less waste during production due to its lightweight and efficient use of raw materials, making it more sustainable compared to solid PVC, which requires more resources and energy to manufacture. Both materials are recyclable, but solid PVC often offers a longer lifespan, reducing the frequency of replacement and associated environmental impact. By choosing foamed PVC, you can reduce transportation emissions and material consumption, contributing to lower carbon footprints in your projects.
Choosing the Right PVC for Your Project
Foamed PVC offers lightweight durability and flexibility, making it ideal for signage, displays, and projects requiring easy cutting and shaping, while Solid PVC provides superior strength and rigidity, suited for structural applications and outdoor use. Your project's specific needs for weight, strength, and finish will determine whether Foamed or Solid PVC is the right material. Consider factors like impact resistance, weather tolerance, and cost efficiency to select the optimal PVC type that fits your design and performance requirements.
Foamed PVC vs Solid PVC Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com