Polyolefin offers superior chemical resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for packaging and automotive applications, while polystyrene provides excellent rigidity and insulation properties, commonly used in disposable containers and insulation panels. Choosing between polyolefin and polystyrene depends on your specific needs for durability, thermal resistance, and environmental impact.
Table of Comparison
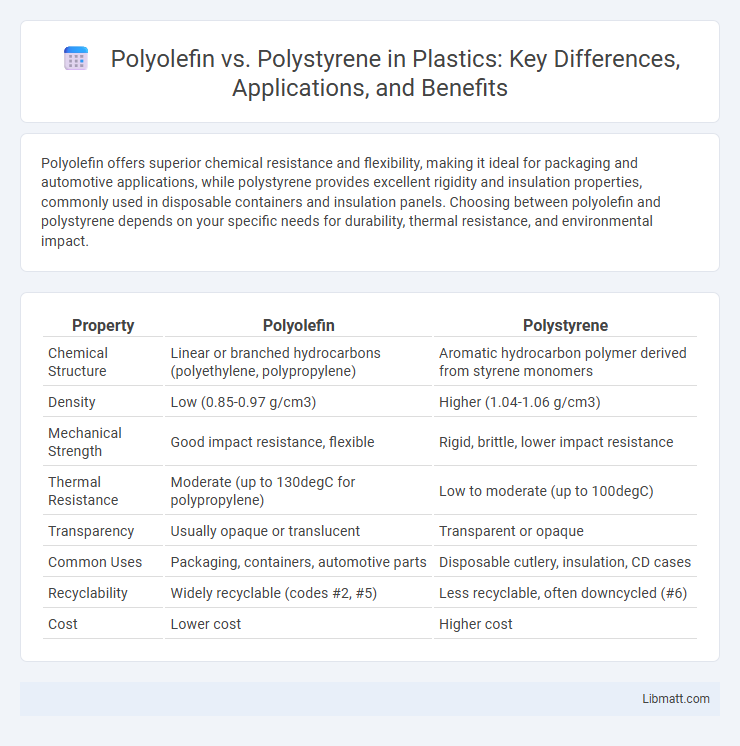
| Property | Polyolefin | Polystyrene |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Linear or branched hydrocarbons (polyethylene, polypropylene) | Aromatic hydrocarbon polymer derived from styrene monomers |
| Density | Low (0.85-0.97 g/cm3) | Higher (1.04-1.06 g/cm3) |
| Mechanical Strength | Good impact resistance, flexible | Rigid, brittle, lower impact resistance |
| Thermal Resistance | Moderate (up to 130degC for polypropylene) | Low to moderate (up to 100degC) |
| Transparency | Usually opaque or translucent | Transparent or opaque |
| Common Uses | Packaging, containers, automotive parts | Disposable cutlery, insulation, CD cases |
| Recyclability | Widely recyclable (codes #2, #5) | Less recyclable, often downcycled (#6) |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Polyolefin and Polystyrene
Polyolefin and polystyrene are two widely used thermoplastics distinguished by their chemical structure and applications. Polyolefins, including polyethylene and polypropylene, are valued for their durability, flexibility, and chemical resistance, making them ideal for packaging, automotive components, and consumer goods. Polystyrene, known for its rigidity and clarity, is commonly used in insulation, disposable cutlery, and packaging materials, offering cost-effective solutions where stiffness and thermal insulation are required.
Chemical Structure Comparison
Polyolefins consist of long hydrocarbon chains with repeating units of ethylene or propylene, characterized by their simple, non-polar carbon-carbon backbone, which provides excellent chemical resistance and flexibility. In contrast, polystyrene is a polymer made from styrene monomers containing an aromatic benzene ring attached to the carbon backbone, resulting in a rigid and brittle structure with different thermal and mechanical properties. Understanding these chemical structure differences helps you select the appropriate material for your specific application based on performance requirements and environmental stability.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Polyolefin exhibits superior flexibility, impact resistance, and chemical stability compared to polystyrene, which is typically rigid and brittle under stress. The tensile strength of polyolefin ranges from 20 to 40 MPa, while polystyrene generally shows lower strength around 30 MPa but higher hardness and dimensional stability. Polyolefin's lower density (0.90-0.97 g/cm3) enables enhanced durability and shock absorption, whereas polystyrene (1.04-1.06 g/cm3) excels in rigidity and thermal insulation properties.
Manufacturing Processes
Polyolefin manufacturing primarily involves polymerization of olefins such as ethylene and propylene through processes like Ziegler-Natta or metallocene catalysis, yielding materials like polyethylene and polypropylene. Polystyrene production relies on the polymerization of styrene monomers using suspension, bulk, or emulsion polymerization techniques to create either general-purpose or high-impact polystyrene. The choice of polymerization method directly affects product properties, processing conditions, and end-use applications for both polyolefins and polystyrene.
Common Applications
Polyolefins such as polyethylene and polypropylene are widely used in packaging materials, automotive parts, and consumer goods due to their excellent chemical resistance and flexibility. Polystyrene is commonly found in disposable cutlery, insulation panels, and product packaging like foam peanuts, benefiting from its rigidity and insulating properties. Both materials serve crucial roles in manufacturing, with polyolefins preferred for durability and polystyrene favored for lightweight protection.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Polyolefin, primarily composed of polyethylene and polypropylene, offers significant environmental benefits due to its high recyclability and lower carbon footprint compared to polystyrene, which is known for its limited recyclability and persistence in ecosystems. Polyolefin recycling processes are well-established, resulting in reduced landfill waste and energy consumption, whereas polystyrene often ends up in landfills or the ocean, contributing to long-lasting pollution. The environmental impact of polystyrene is exacerbated by its slow degradation rate and the release of toxic chemicals, making polyolefin a more sustainable choice in packaging and consumer products.
Cost Analysis
Polyolefin generally offers a lower cost profile compared to polystyrene due to its widespread availability and simpler polymerization process. Polystyrene, while often more expensive, provides enhanced rigidity and clarity that can justify higher costs in specific applications such as packaging and insulation. Cost efficiency in choosing between polyolefin and polystyrene largely depends on the required material properties and production volume, with polyolefins favored for cost-sensitive, high-volume manufacturing.
Performance in Packaging Solutions
Polyolefin offers superior flexibility, impact resistance, and moisture barrier properties, making it ideal for versatile packaging applications. Polystyrene provides excellent rigidity, clarity, and thermal insulation, often used in protective packaging and food containers. Polyolefin's recyclability and chemical resistance enhance its sustainability profile compared to polystyrene's more limited recyclability and brittleness.
Durability and Lifespan
Polyolefin offers superior durability and a longer lifespan compared to polystyrene due to its resistance to UV radiation, chemicals, and physical impact. Polystyrene tends to degrade faster when exposed to environmental stressors, making it less ideal for long-term applications. Choosing polyolefin ensures your products maintain structural integrity over extended periods, especially in demanding conditions.
Choosing Between Polyolefin and Polystyrene
Choosing between polyolefin and polystyrene depends on the application's requirements for flexibility, chemical resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Polyolefin, including polyethylene and polypropylene, offers superior impact resistance, chemical inertness, and is widely used in packaging and automotive parts. Polystyrene provides excellent rigidity and clarity, making it ideal for disposable cutlery, containers, and insulation, but it is more brittle and less resistant to heat and chemicals compared to polyolefin.
Polyolefin vs polystyrene Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com