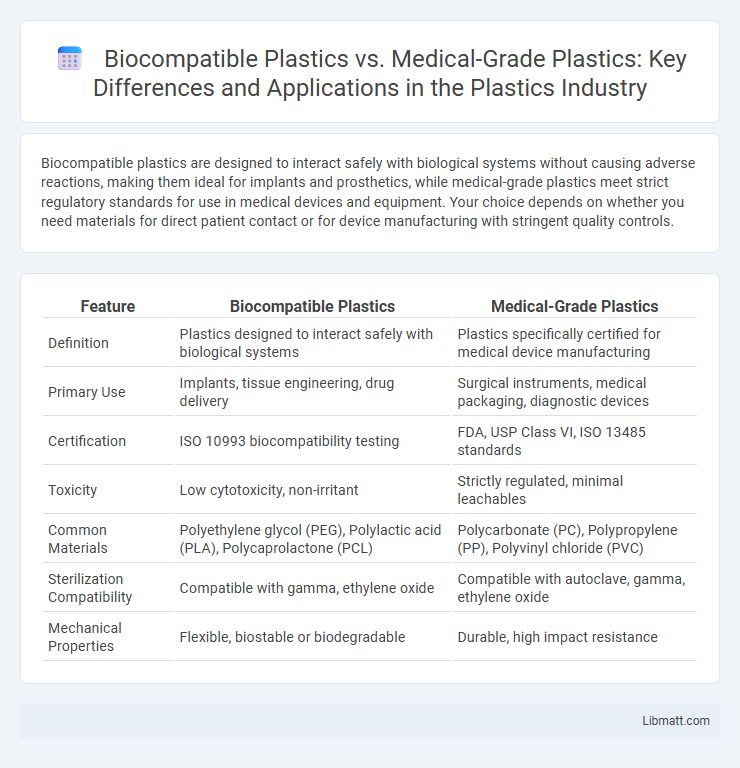
Biocompatible plastics are designed to interact safely with biological systems without causing adverse reactions, making them ideal for implants and prosthetics, while medical-grade plastics meet strict regulatory standards for use in medical devices and equipment. Your choice depends on whether you need materials for direct patient contact or for device manufacturing with stringent quality controls.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biocompatible Plastics | Medical-Grade Plastics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Plastics designed to interact safely with biological systems | Plastics specifically certified for medical device manufacturing |
| Primary Use | Implants, tissue engineering, drug delivery | Surgical instruments, medical packaging, diagnostic devices |
| Certification | ISO 10993 biocompatibility testing | FDA, USP Class VI, ISO 13485 standards |
| Toxicity | Low cytotoxicity, non-irritant | Strictly regulated, minimal leachables |
| Common Materials | Polyethylene glycol (PEG), Polylactic acid (PLA), Polycaprolactone (PCL) | Polycarbonate (PC), Polypropylene (PP), Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) |
| Sterilization Compatibility | Compatible with gamma, ethylene oxide | Compatible with autoclave, gamma, ethylene oxide |
| Mechanical Properties | Flexible, biostable or biodegradable | Durable, high impact resistance |
Introduction to Biocompatible and Medical-Grade Plastics
Biocompatible plastics are designed to interact safely with biological systems, minimizing adverse reactions when used in medical devices or implants. Medical-grade plastics meet stringent regulatory standards for purity, mechanical properties, and sterilization compatibility to ensure patient safety and efficacy. Understanding the distinctions helps you select the appropriate material for applications requiring both biocompatibility and regulatory compliance.
Defining Biocompatibility in Plastics
Biocompatibility in plastics refers to the material's ability to perform without causing adverse reactions when in contact with living tissue, crucial for medical applications. Medical-grade plastics are specifically formulated and tested to meet stringent regulatory standards ensuring safety, sterility, and non-toxicity for implants, devices, or drug delivery systems. Your choice of plastic must prioritize biocompatibility to ensure patient safety and regulatory compliance in healthcare environments.
What Makes a Plastic Medical-Grade?
Medical-grade plastics are specifically engineered to meet stringent regulatory standards for purity, biocompatibility, and mechanical performance, ensuring safety when in contact with human tissues or fluids. These plastics undergo rigorous testing for toxicity, sterilization compatibility, and resistance to chemical degradation, differentiating them from general biocompatible plastics that may not meet all medical requirements. Your choice of medical-grade plastic ensures reliable performance and compliance with healthcare industry regulations essential for medical device manufacturing.
Standards and Regulatory Requirements
Biocompatible plastics must comply with ISO 10993 standards, ensuring they are non-toxic and safe for contact with human tissue, while medical-grade plastics adhere to FDA regulations and ASTM standards for sterilization, mechanical properties, and chemical resistance. Your choice of plastic depends on the specific medical application and regulatory environment, as both categories demand rigorous testing to meet safety and performance criteria. Certifications like USP Class VI further differentiate medical-grade plastics by guaranteeing suitability for implantable devices and long-term medical use.
Common Applications in Healthcare
Biocompatible plastics, including materials like polyethylene and silicone, are widely used in implants, prosthetics, and wound dressings due to their compatibility with human tissues. Medical-grade plastics such as polycarbonate and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are preferred for manufacturing surgical instruments, diagnostic devices, and drug delivery systems because of their sterilization resistance and mechanical strength. Both categories meet stringent regulatory standards to ensure safety and efficacy in diverse healthcare applications.
Material Properties and Performance
Biocompatible plastics exhibit excellent compatibility with biological tissues, minimizing immune response and toxicity, making them ideal for implants and prosthetics. Medical-grade plastics combine strict regulatory compliance with superior mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and sterilization capability, ensuring safety and durability in medical devices. Your choice between these materials should consider specific performance requirements such as flexibility, biodegradability, and long-term interaction with the human body.
Compatibility with Sterilization Methods
Biocompatible plastics exhibit varying compatibility with sterilization methods such as autoclaving, gamma radiation, and ethylene oxide, depending on their chemical composition and thermal stability. Medical-grade plastics are specifically formulated to withstand rigorous sterilization processes while maintaining mechanical integrity and biocompatibility, making them suitable for repeated sterilization cycles in clinical environments. Understanding the material properties ensures optimal selection for devices requiring sterilization without compromising safety or functionality.
Safety, Allergies, and Toxicity Concerns
Biocompatible plastics are specifically designed to minimize adverse reactions, making them ideal for implants and prolonged body contact due to their high safety and low toxicity profiles. Medical-grade plastics undergo stringent testing to meet regulatory standards, ensuring reduced allergenic potential and toxicity suitable for surgical instruments and short-term patient use. Your choice should consider the intended application duration and sensitivity to prevent allergic reactions and ensure maximum patient safety.
Market Trends and Innovations
The market for biocompatible plastics is rapidly expanding due to increased demand for sustainable and environmentally friendly materials in the healthcare industry, with innovations focusing on bioresorbable polymers and advanced polymer blends. Medical-grade plastics continue to evolve through enhanced sterilization compatibility and improved mechanical properties, supporting their critical role in durable medical devices and implants. Your choice between these materials depends on balancing performance requirements with emerging regulatory standards and sustainability goals.
Future Outlook: Evolving Needs in Medical Plastics
Emerging advancements in biocompatible plastics are driving innovations to meet stricter safety and performance standards in medical applications. Medical-grade plastics are increasingly engineered for enhanced durability, sterilization resistance, and reduced environmental impact, addressing the evolving needs of healthcare providers. Your choice in materials will benefit from ongoing research focusing on sustainability and improved patient outcomes through next-generation polymer technologies.
Biocompatible Plastics vs Medical-Grade Plastics Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com