Heat stabilized nylon offers enhanced resistance to thermal degradation and maintains mechanical properties at elevated temperatures compared to standard nylon, making it ideal for applications involving prolonged heat exposure. Your choice between these materials should consider the operating environment, as heat stabilized nylon provides greater durability and dimensional stability under heat stress.
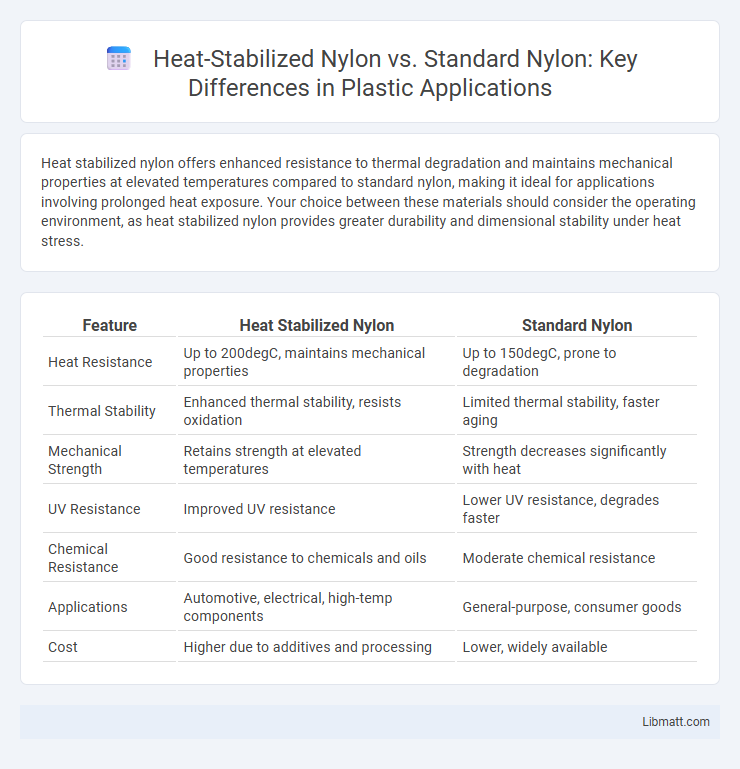
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Heat Stabilized Nylon | Standard Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Up to 200degC, maintains mechanical properties | Up to 150degC, prone to degradation |
| Thermal Stability | Enhanced thermal stability, resists oxidation | Limited thermal stability, faster aging |
| Mechanical Strength | Retains strength at elevated temperatures | Strength decreases significantly with heat |
| UV Resistance | Improved UV resistance | Lower UV resistance, degrades faster |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to chemicals and oils | Moderate chemical resistance |
| Applications | Automotive, electrical, high-temp components | General-purpose, consumer goods |
| Cost | Higher due to additives and processing | Lower, widely available |
Overview of Nylon Materials
Heat stabilized nylon features enhanced thermal resistance, allowing it to maintain strength and flexibility at elevated temperatures up to 150degC, compared to standard nylon which begins to degrade around 100degC. The heat stabilization process reduces moisture absorption and dimensional changes, improving durability in high-heat environments such as automotive engine components and electrical connectors. Standard nylon offers good mechanical properties and chemical resistance but may suffer from thermal deformation and reduced lifespan in continuous heat exposure applications.
What is Standard Nylon?
Standard nylon, often referred to as Nylon 6 or Nylon 6,6, is a synthetic polymer known for its strength, flexibility, and resistance to abrasion and chemicals. It is widely used in textiles, automotive parts, and industrial components due to its durability and lightweight properties. However, standard nylon tends to degrade when exposed to heat, causing deformation or loss of mechanical integrity in high-temperature applications.
What is Heat Stabilized Nylon?
Heat Stabilized Nylon is a type of nylon resin engineered to resist thermal degradation and maintain mechanical properties under elevated temperatures, typically up to 180degC. It incorporates stabilizers that enhance its heat deflection temperature and reduce discoloration during prolonged heat exposure. Compared to standard nylon, Heat Stabilized Nylon offers superior dimensional stability and durability in high-temperature applications such as automotive engine components and electrical housings.
Key Differences Between Heat Stabilized and Standard Nylon
Heat stabilized nylon features enhanced thermal resistance, allowing it to maintain structural integrity and mechanical properties at elevated temperatures up to 200degC, compared to standard nylon which typically degrades above 120degC. The chemical formulation of heat stabilized nylon reduces hydrolytic degradation and oxidative wear, resulting in superior durability in high-heat environments such as automotive engine components and electrical connectors. Standard nylon is more susceptible to thermal deformation and color changes under heat stress, making heat stabilized variants preferable for applications requiring prolonged exposure to heat and demanding mechanical performance.
Thermal Stability and Performance
Heat stabilized nylon offers significantly enhanced thermal stability compared to standard nylon, maintaining strength and dimensional integrity at elevated temperatures up to 200degC. This improvement in thermal performance makes heat stabilized nylon ideal for applications requiring resistance to heat-induced deformation and prolonged exposure to high temperatures. Your choice of heat stabilized nylon ensures reliable performance in demanding thermal environments where standard nylon would typically degrade or lose mechanical properties.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Heat stabilized nylon exhibits significantly improved mechanical properties compared to standard nylon, including enhanced tensile strength, higher impact resistance, and better dimensional stability under elevated temperatures. Your applications benefit from reduced deformation and increased durability when using heat stabilized nylon in demanding environments. This makes it an ideal choice for components requiring consistent performance and longevity in thermal stress conditions.
Chemical Resistance and Environmental Factors
Heat stabilized nylon exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to standard nylon, effectively withstanding exposure to oils, solvents, and hydrocarbons without significant degradation. It resists hydrolysis and oxidative aging better, maintaining mechanical properties in high-temperature and humid environments. Environmental factors such as UV exposure and moisture absorption impact standard nylon more severely, leading to faster mechanical weakening and dimensional changes.
Common Applications of Each Nylon Type
Heat stabilized nylon is commonly used in automotive components, electrical connectors, and industrial machinery where high thermal resistance and dimensional stability under heat are crucial. Standard nylon finds applications in textiles, packaging films, and consumer goods, benefiting from its flexibility, abrasion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. The choice between heat stabilized and standard nylon depends on the specific performance requirements related to temperature exposure and mechanical stress.
Cost Considerations and Availability
Heat stabilized nylon generally incurs higher costs due to specialized additives and processing techniques that enhance thermal resistance, making it less budget-friendly compared to standard nylon. Availability of heat stabilized nylon tends to be more limited as it is produced in smaller quantities and targeted toward specific industrial applications requiring elevated temperature performance. Standard nylon benefits from widespread production and diverse suppliers, resulting in lower prices and greater availability for general manufacturing needs.
Choosing the Right Nylon for Your Needs
Heat stabilized nylon offers enhanced thermal resistance and dimensional stability, making it ideal for applications involving high temperatures or prolonged heat exposure. Standard nylon provides excellent strength, flexibility, and chemical resistance for general-purpose uses where heat is not a critical factor. Selecting the appropriate nylon depends on balancing temperature requirements with mechanical performance to ensure durability and functionality in your specific environment.
Heat Stabilized Nylon vs Standard Nylon Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com