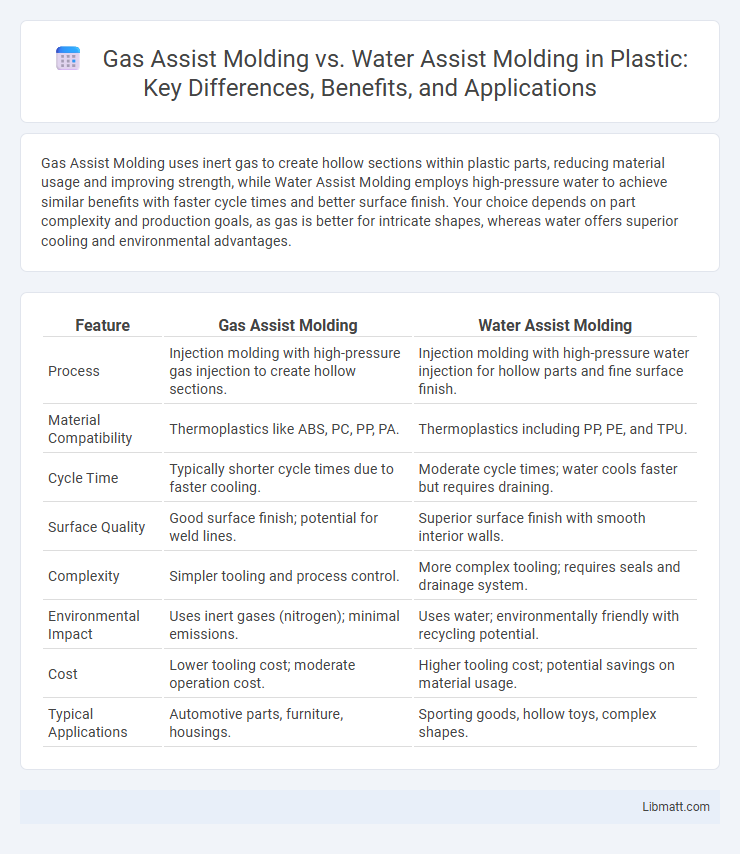
Gas Assist Molding uses inert gas to create hollow sections within plastic parts, reducing material usage and improving strength, while Water Assist Molding employs high-pressure water to achieve similar benefits with faster cycle times and better surface finish. Your choice depends on part complexity and production goals, as gas is better for intricate shapes, whereas water offers superior cooling and environmental advantages.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gas Assist Molding | Water Assist Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Injection molding with high-pressure gas injection to create hollow sections. | Injection molding with high-pressure water injection for hollow parts and fine surface finish. |
| Material Compatibility | Thermoplastics like ABS, PC, PP, PA. | Thermoplastics including PP, PE, and TPU. |
| Cycle Time | Typically shorter cycle times due to faster cooling. | Moderate cycle times; water cools faster but requires draining. |
| Surface Quality | Good surface finish; potential for weld lines. | Superior surface finish with smooth interior walls. |
| Complexity | Simpler tooling and process control. | More complex tooling; requires seals and drainage system. |
| Environmental Impact | Uses inert gases (nitrogen); minimal emissions. | Uses water; environmentally friendly with recycling potential. |
| Cost | Lower tooling cost; moderate operation cost. | Higher tooling cost; potential savings on material usage. |
| Typical Applications | Automotive parts, furniture, housings. | Sporting goods, hollow toys, complex shapes. |
Introduction to Gas Assist and Water Assist Molding
Gas Assist Molding uses pressurized nitrogen gas to hollow out thick plastic sections, reducing material usage and improving part strength and dimensional accuracy. Water Assist Molding employs high-pressure water to create hollow cavities within plastic parts, resulting in enhanced cooling rates and reduced cycle times compared to conventional molding. Understanding the differences in these techniques empowers you to select the optimal process for producing lightweight, durable plastic components with intricate designs.
Fundamental Principles of Gas Assist Molding
Gas Assist Molding involves injecting nitrogen gas into molten plastic to create hollow sections within molded parts, reducing material usage and improving strength-to-weight ratios. The gas pushes the molten plastic against the mold walls, forming complex shapes with consistent wall thickness and minimizing sink marks. This process enhances cycle times and part quality compared to conventional injection molding techniques.
Fundamentals of Water Assist Molding
Water Assist Molding (WAM) utilizes high-pressure water injected into the polymer melt during the molding process to create hollow sections and complex internal geometries, enhancing part strength and reducing weight. Unlike Gas Assist Molding, which uses nitrogen gas, WAM leverages water's incompressibility and superior heat capacity for faster cooling and more precise dimensional control. This fundamental difference allows Water Assist Molding to produce parts with improved surface finish, reduced cycle times, and greater design flexibility in thick-walled components.
Key Differences Between Gas and Water Assist Molding
Gas Assist Molding uses inert nitrogen gas to create hollow sections within plastic parts, improving material efficiency and reducing cycle times, while Water Assist Molding employs high-pressure water to achieve similar hollow structures with enhanced surface finish and shorter cooling times. Gas assist typically offers better control over complex geometries and thicker sections, whereas water assist excels in fast cooling and producing parts with smoother inner surfaces. The choice between gas and water assist molding depends on factors such as part design, cycle time requirements, and surface quality preferences.
Material Compatibility for Each Method
Gas Assist Molding is highly compatible with engineering plastics such as ABS, polypropylene, and nylon, allowing for complex hollow parts with uniform wall thickness. Water Assist Molding works best with materials like polyethylene and certain elastomers that tolerate higher moisture levels and offer superior surface finishes. Each method optimizes material flow and cooling differently, impacting the choice of polymer based on part design and functional requirements.
Applications and Industries Served
Gas Assist Molding excels in producing complex, hollow plastic parts used in automotive components, consumer electronics, and medical devices, offering lightweight strength and reduced material usage. Water Assist Molding is favored in industries such as packaging, household appliances, and toys for creating intricate internal channels with superior surface finish and reduced cycle times. Your choice between these technologies depends on the specific application requirements, including part geometry and industry standards.
Advantages of Gas Assist Molding
Gas Assist Molding offers advantages such as reduced cycle times, improved part strength, and enhanced surface finish due to the controlled injection of inert gas into the mold. It enables the production of lightweight yet rigid parts by creating hollow sections without sacrifice to structural integrity. This process also minimizes material usage, leading to cost savings and less warpage compared to Water Assist Molding.
Benefits of Water Assist Molding
Water Assist Molding offers improved cycle times and superior surface finish compared to traditional Gas Assist Molding, reducing scrap rates and enhancing product quality. The use of water as a cooling medium provides more uniform cooling, minimizing warpage and internal stresses in molded parts. Your manufacturing process benefits from lower tooling costs and increased design flexibility due to water's higher heat capacity and pressure control capabilities.
Limitations and Challenges of Both Methods
Gas Assist Molding faces limitations such as difficulty in achieving uniform gas flow in complex geometries and challenges with controlling gas penetration depth, which can lead to inconsistent wall thickness and surface defects. Water Assist Molding struggles with corrosion of mold components and the need for high-pressure water systems, increasing equipment costs and maintenance requirements. Both methods encounter challenges in optimizing process parameters to balance cycle time, material usage, and part quality while minimizing defects like sink marks and dimensional inaccuracies.
Selecting the Right Process for Your Project
Choosing between Gas Assist Molding and Water Assist Molding depends on part geometry, material properties, and desired surface finish. Gas Assist Molding excels in creating hollow sections with uniform wall thickness in thick parts, while Water Assist Molding offers superior cycle times and better surface quality for thinner, intricate components. Evaluating project requirements such as structural integrity, production speed, and cost efficiency ensures the optimal selection of the molding process.
Gas Assist Molding vs Water Assist Molding Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com