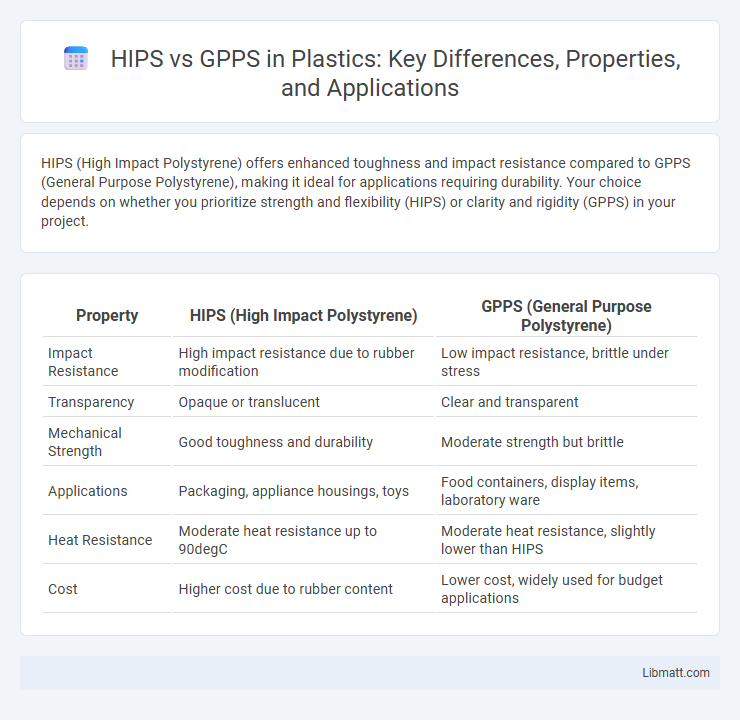
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) offers enhanced toughness and impact resistance compared to GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene), making it ideal for applications requiring durability. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize strength and flexibility (HIPS) or clarity and rigidity (GPPS) in your project.
Table of Comparison
| Property | HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) | GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene) |
|---|---|---|
| Impact Resistance | High impact resistance due to rubber modification | Low impact resistance, brittle under stress |
| Transparency | Opaque or translucent | Clear and transparent |
| Mechanical Strength | Good toughness and durability | Moderate strength but brittle |
| Applications | Packaging, appliance housings, toys | Food containers, display items, laboratory ware |
| Heat Resistance | Moderate heat resistance up to 90degC | Moderate heat resistance, slightly lower than HIPS |
| Cost | Higher cost due to rubber content | Lower cost, widely used for budget applications |
Introduction to HIPS and GPPS
High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) is a rubber-modified polystyrene known for its enhanced impact resistance and toughness, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and flexibility. General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS) is a clear, rigid, and brittle polymer widely used for packaging, disposable cutlery, and model kits due to its excellent clarity and ease of processing. Both HIPS and GPPS are styrene-based polymers but differ significantly in mechanical properties and typical use cases.
Chemical Composition: HIPS vs GPPS
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) contains butadiene rubber dispersed within the polystyrene matrix, enhancing its impact resistance and toughness. GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene) is a rigid, transparent polymer composed primarily of styrene monomer without rubber additives, resulting in higher clarity but lower impact strength. Your choice between HIPS and GPPS depends on whether chemical composition prioritizes durability or optical clarity for your application.
Physical Properties Comparison
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) offers greater impact resistance and toughness, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and shock absorption. GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene) provides higher rigidity, clarity, and dimensional stability but is more brittle under stress. Your choice depends on whether impact strength or optical clarity is more critical for your product's physical performance.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) offers superior impact resistance and toughness compared to GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene), making it ideal for applications requiring enhanced mechanical strength. GPPS provides good rigidity and dimensional stability but lacks the durability under stress that HIPS delivers, especially in environments prone to physical impact. Choosing HIPS ensures your products maintain structural integrity and longevity where mechanical durability is critical.
Processing and Manufacturing Differences
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) offers superior impact resistance due to its rubber-modified structure, making it easier to mold into complex shapes during injection molding and thermoforming processes. GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene) provides higher clarity and stiffness but is more brittle, requiring careful temperature control to avoid defects like warping or cracking during extrusion and molding. Manufacturing with HIPS typically involves slower cooling rates to enhance toughness, whereas GPPS processing benefits from faster cooling to maintain dimensional stability and surface finish quality.
Applications of HIPS
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) is widely used in packaging, especially for food containers, medical trays, and consumer electronics housings due to its toughness and impact resistance. It excels in applications requiring easy molding and cost-effective production while maintaining good surface finish and durability. Your projects involving shock absorption or protective casing benefit significantly from HIPS's mechanical strength and flexibility.
Applications of GPPS
GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene) is widely used in packaging, disposable cutlery, and refrigerator liners due to its clarity, rigidity, and ease of molding. It serves in producing laboratory equipment, CD cases, and toys, where transparency and surface finish are critical. The material's low cost and good dimensional stability make it ideal for consumer goods and household appliances.
Cost and Economic Considerations
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) generally offers a lower cost per kilogram compared to GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene), making it a more economical choice for applications requiring enhanced toughness. The manufacturing process for HIPS involves rubber modification, which slightly increases production costs but results in better impact resistance, potentially reducing expenses related to product defects or replacements. For large-scale production, the overall cost-effectiveness of HIPS often outweighs the marginally higher price due to improved durability and longer product lifespan.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene) typically has a lower environmental impact due to its energy-efficient production process and better recyclability compared to GPPS (General Purpose Polystyrene), which tends to be more brittle and less recyclable. HIPS's enhanced durability means less frequent replacement, reducing waste generation and supporting circular economy goals. Choosing HIPS can help your project benefit from improved sustainability through easier recycling and reduced environmental footprint.
Choosing Between HIPS and GPPS: Key Factors
When choosing between High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) and General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS), consider impact resistance and clarity as primary factors. HIPS offers superior toughness and durability, making it ideal for applications requiring shock absorption, while GPPS provides excellent optical clarity suitable for display cases and food packaging. Cost and processing requirements also influence selection, with GPPS typically being more brittle and cheaper, and HIPS requiring more robust molding conditions.
HIPS vs GPPS Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com