UV stabilizers protect materials from degradation caused by ultraviolet light exposure, extending the lifespan of plastics and coatings. Antioxidants prevent oxidative damage by neutralizing free radicals, preserving your product's strength and color over time.
Table of Comparison
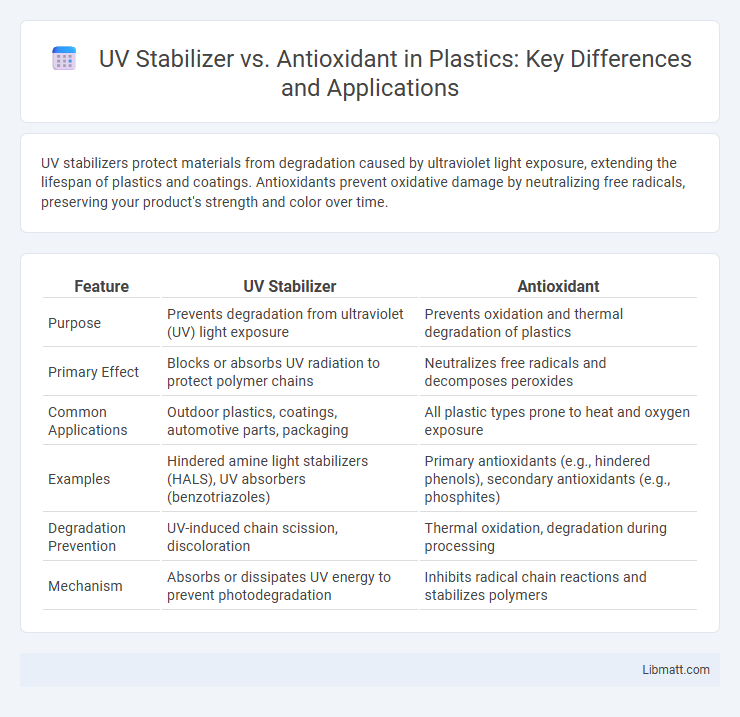
| Feature | UV Stabilizer | Antioxidant |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents degradation from ultraviolet (UV) light exposure | Prevents oxidation and thermal degradation of plastics |
| Primary Effect | Blocks or absorbs UV radiation to protect polymer chains | Neutralizes free radicals and decomposes peroxides |
| Common Applications | Outdoor plastics, coatings, automotive parts, packaging | All plastic types prone to heat and oxygen exposure |
| Examples | Hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS), UV absorbers (benzotriazoles) | Primary antioxidants (e.g., hindered phenols), secondary antioxidants (e.g., phosphites) |
| Degradation Prevention | UV-induced chain scission, discoloration | Thermal oxidation, degradation during processing |
| Mechanism | Absorbs or dissipates UV energy to prevent photodegradation | Inhibits radical chain reactions and stabilizes polymers |
Introduction to UV Stabilizers and Antioxidants
UV stabilizers protect materials by absorbing or blocking harmful ultraviolet radiation, preventing degradation caused by sunlight exposure. Antioxidants inhibit oxidation processes in polymers, metals, and other substances, extending the lifespan by reducing damage from oxygen and heat. Understanding the distinct roles of UV stabilizers and antioxidants helps you select the right additive for enhancing durability and performance in various applications.
Defining UV Stabilizers: Functions and Applications
UV stabilizers prevent polymer degradation by absorbing or reflecting harmful ultraviolet radiation, extending product lifespan in applications like automotive coatings, packaging, and outdoor textiles. These additives enhance material durability by reducing discoloration, cracking, and loss of mechanical properties caused by UV exposure. Your formulations benefit from UV stabilizers by maintaining aesthetic appeal and functional integrity under prolonged sunlight exposure.
Understanding Antioxidants in Polymer Industry
Antioxidants in the polymer industry prevent oxidative degradation by scavenging free radicals, thereby enhancing the durability and lifespan of plastics. UV stabilizers primarily absorb or block harmful ultraviolet radiation, protecting polymers from photodegradation and color fading. Effectively combining antioxidants with UV stabilizers ensures comprehensive protection against both thermal oxidation and UV-induced damage in polymer applications.
Key Differences Between UV Stabilizers and Antioxidants
UV stabilizers protect materials by absorbing or reflecting harmful ultraviolet radiation, preventing polymer degradation caused by sunlight exposure. Antioxidants inhibit oxidative degradation by neutralizing free radicals and preventing the breakdown of materials due to heat, oxygen, and processing stresses. The key difference lies in UV stabilizers targeting photo-oxidation from UV light, while antioxidants specifically combat thermal and oxidative degradation.
Mechanisms of Action: How UV Stabilizers Work
UV stabilizers protect polymers by absorbing harmful ultraviolet radiation and dissipating the energy as low-level heat, preventing polymer chain scission and degradation. They function primarily through mechanisms such as UV absorption, quenching excited states, and scavenging free radicals generated by UV exposure. Unlike antioxidants, which inhibit oxidative degradation by neutralizing free radicals, UV stabilizers specifically target and mitigate UV-induced damage to enhance material longevity.
Mechanisms of Action: Role of Antioxidants
Antioxidants protect materials by neutralizing free radicals generated during oxidation, effectively interrupting degradation pathways at a molecular level. They donate electrons to unstable molecules, stabilizing them and preventing chain reactions that cause discoloration, brittleness, or loss of mechanical properties. Unlike UV stabilizers, which absorb or block harmful ultraviolet radiation to prevent initial damage, antioxidants primarily combat oxidative stress, prolonging the lifespan of Your polymers and coatings.
Applications in Plastics and Polymers
UV stabilizers protect plastics and polymers from degradation caused by ultraviolet light exposure, enhancing the durability of outdoor applications such as automotive parts, agricultural films, and construction materials. Antioxidants prevent oxidative degradation during processing and service life, improving thermal stability and extending the lifespan of products like packaging films, molded components, and elastomers. Combining UV stabilizers and antioxidants provides comprehensive protection against environmental and thermal stresses, optimizing performance in polymers used for outdoor and high-temperature applications.
Factors Influencing the Choice Between UV Stabilizers and Antioxidants
Factors influencing the choice between UV stabilizers and antioxidants include the material's exposure conditions, such as sunlight intensity, temperature fluctuations, and oxygen presence. UV stabilizers are essential for protecting polymers from degradation due to ultraviolet radiation, while antioxidants primarily prevent oxidative breakdown caused by heat and oxygen during processing and service life. Your material's specific environmental stressors and application requirements will determine whether UV stabilizers, antioxidants, or a combination of both provide optimal durability and performance.
Benefits and Limitations of Each Additive
UV stabilizers protect materials from degradation caused by ultraviolet light, extending the lifespan of plastics and coatings by preventing color fading and surface cracking. Antioxidants hinder the oxidation process in polymers, preserving mechanical properties and preventing brittleness during processing and long-term use. Your choice depends on the specific environmental stressors; UV stabilizers excel in outdoor applications, while antioxidants are essential for thermal and oxidative stability.
Future Trends in Polymer Stabilization Technologies
Emerging trends in polymer stabilization technologies emphasize the integration of UV stabilizers and antioxidants to enhance material longevity under environmental stress. Advanced formulations combine hindered amine light stabilizers (HALS) with multifunctional antioxidants to provide synergistic protection against photo-oxidative degradation and thermal aging. Innovative polymer stabilization research focuses on nano-enabled additives and smart responsive systems to optimize UV and oxidative resistance in automotive, packaging, and construction polymers.
UV Stabilizer vs Antioxidant Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com