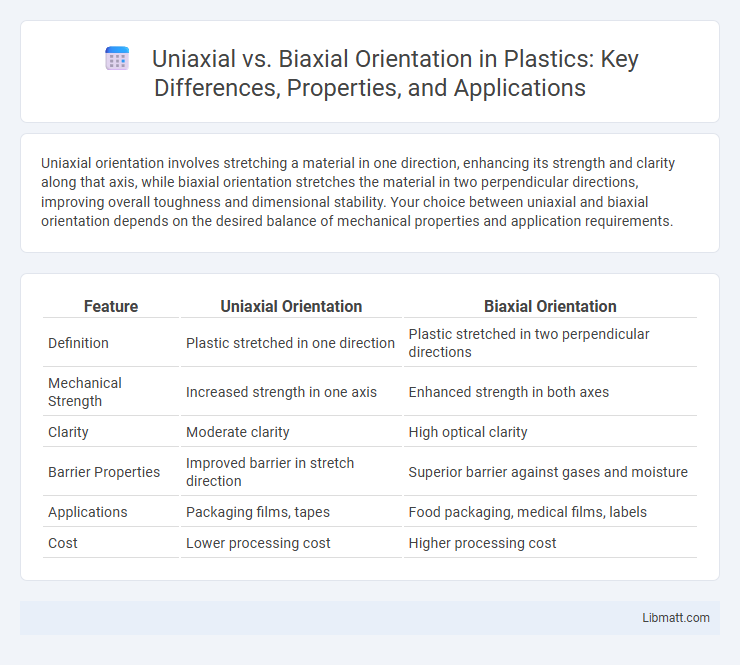
Uniaxial orientation involves stretching a material in one direction, enhancing its strength and clarity along that axis, while biaxial orientation stretches the material in two perpendicular directions, improving overall toughness and dimensional stability. Your choice between uniaxial and biaxial orientation depends on the desired balance of mechanical properties and application requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Uniaxial Orientation | Biaxial Orientation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Plastic stretched in one direction | Plastic stretched in two perpendicular directions |
| Mechanical Strength | Increased strength in one axis | Enhanced strength in both axes |
| Clarity | Moderate clarity | High optical clarity |
| Barrier Properties | Improved barrier in stretch direction | Superior barrier against gases and moisture |
| Applications | Packaging films, tapes | Food packaging, medical films, labels |
| Cost | Lower processing cost | Higher processing cost |
Introduction to Material Orientation
Material orientation in polymer films significantly impacts their mechanical and barrier properties, with uniaxial orientation involving stretching in a single direction and biaxial orientation stretching in two perpendicular directions. Uniaxially oriented films exhibit enhanced tensile strength and stiffness along the stretch axis, making them ideal for applications requiring directional strength. Biaxially oriented films provide balanced strength, improved clarity, and better dimensional stability, widely used in packaging and industrial applications where multidirectional durability is essential.
Defining Uniaxial and Biaxial Orientation
Uniaxial orientation refers to the alignment of polymer molecules along a single axis, enhancing tensile strength and clarity in that specific direction. Biaxial orientation involves stretching the polymer film in both the machine and transverse directions, resulting in improved dimensional stability, strength, and barrier properties. Understanding the differences in molecular alignment helps optimize material performance for packaging, films, and industrial applications.
Manufacturing Processes Involved
Uniaxial orientation involves stretching a polymer film or sheet in one direction, typically during processes like roll stretching or tenter frame operations, enhancing tensile strength along the stretch axis. Biaxial orientation stretches the material in two perpendicular directions, often achieved through sequential or simultaneous stretching using tenter frames or double bubble processes, improving overall mechanical properties and dimensional stability. These manufacturing techniques control molecular alignment to tailor the film's strength, clarity, and barrier performance for applications in packaging and industrial uses.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Uniaxial orientation enhances tensile strength and stiffness primarily along a single axis, resulting in improved dimensional stability and resistance to elongation in that direction. Biaxial orientation provides balanced mechanical properties, offering high tensile strength, impact resistance, and improved barrier properties uniformly along both machine and transverse directions. The biaxial process typically yields films or sheets with superior toughness and flexibility compared to uniaxially oriented materials, making it ideal for applications requiring multidirectional strength.
Optical Characteristics and Applications
Uniaxial orientation enhances clarity and gloss by aligning polymer molecules in a single direction, optimizing optical characteristics for applications like packaging films and display screens. Biaxial orientation improves light diffusion and strength by stretching materials in two perpendicular directions, making it ideal for products such as photographic films and flexible electronics. Understanding these orientation techniques helps tailor your materials for specific optical performance and durability requirements.
Thermal Stability and Performance
Uniaxial orientation aligns polymer chains in a single direction, enhancing tensile strength and thermal stability along that axis but offering limited multidirectional performance. Biaxial orientation stretches polymers in two perpendicular directions, resulting in balanced thermal resistance and improved dimensional stability under heat due to uniform stress distribution. The biaxial process typically leads to superior overall performance in applications requiring consistent thermal stability and mechanical strength across multiple directions.
Common Polymers and Their Orientation
Common polymers like polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polypropylene are frequently processed using uniaxial or biaxial orientation techniques to enhance mechanical properties. Uniaxial orientation aligns polymer chains in one direction, often improving tensile strength along that axis, while biaxial orientation stretches polymers in two perpendicular directions, resulting in superior dimensional stability and barrier properties. Your choice between uniaxial and biaxial orientation depends on the desired application-specific characteristics, such as flexibility or resistance to stress.
Industrial Applications: Uniaxial vs Biaxial
Uniaxial orientation is commonly utilized in applications requiring high tensile strength and stiffness in one direction, such as plastic strapping and industrial film packaging. Biaxial orientation enhances mechanical properties uniformly in two perpendicular directions, making it ideal for flexible packaging films, automotive parts, and electrical insulation materials. Industrial processes often select biaxial orientation for improved clarity, barrier properties, and puncture resistance, critical in food packaging and medical device manufacturing.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Method
Uniaxial orientation offers enhanced tensile strength and stiffness along a single direction, making it ideal for applications requiring directional durability, but it may lack uniform properties across other axes. Biaxial orientation improves overall strength, clarity, and barrier properties by stretching the material in two perpendicular directions, providing balanced performance but often at a higher manufacturing cost. Your choice between uniaxial and biaxial orientation should consider the specific mechanical requirements and cost-effectiveness for the intended application.
Future Trends in Material Orientation
Future trends in material orientation focus on enhancing performance through advanced uniaxial and biaxial orientation techniques, enabling improved tensile strength, clarity, and barrier properties for packaging and industrial applications. Innovations such as nanocomposite integration and machine learning-driven process optimization aim to tailor orientation angles precisely, increasing material efficiency and sustainability. Research into hybrid orientation methods promises the development of multifunctional films with customizable mechanical and optical properties for next-generation materials.
Uniaxial vs Biaxial Orientation Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com