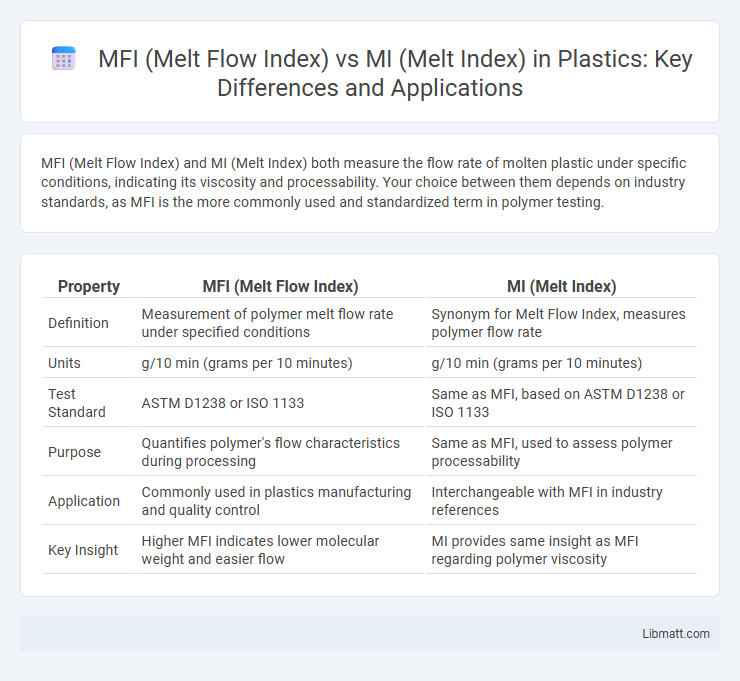
MFI (Melt Flow Index) and MI (Melt Index) both measure the flow rate of molten plastic under specific conditions, indicating its viscosity and processability. Your choice between them depends on industry standards, as MFI is the more commonly used and standardized term in polymer testing.
Table of Comparison
| Property | MFI (Melt Flow Index) | MI (Melt Index) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measurement of polymer melt flow rate under specified conditions | Synonym for Melt Flow Index, measures polymer flow rate |
| Units | g/10 min (grams per 10 minutes) | g/10 min (grams per 10 minutes) |
| Test Standard | ASTM D1238 or ISO 1133 | Same as MFI, based on ASTM D1238 or ISO 1133 |
| Purpose | Quantifies polymer's flow characteristics during processing | Same as MFI, used to assess polymer processability |
| Application | Commonly used in plastics manufacturing and quality control | Interchangeable with MFI in industry references |
| Key Insight | Higher MFI indicates lower molecular weight and easier flow | MI provides same insight as MFI regarding polymer viscosity |
Understanding Melt Flow Index (MFI) and Melt Index (MI)
Melt Flow Index (MFI) and Melt Index (MI) both measure the ease of flow of thermoplastic polymers under specific conditions, providing critical data for processing and quality control. These terms are often used interchangeably, as standardized test methods such as ASTM D1238 define them as the mass of polymer flowing through a capillary die at a set temperature and load, expressed in grams per 10 minutes. Understanding MFI or MI values allows manufacturers to predict material behavior during extrusion or molding processes, optimize processing parameters, and ensure consistent product performance.
Key Definitions: What Are MFI and MI?
MFI (Melt Flow Index) and MI (Melt Index) both measure the flow rate of melted thermoplastic polymers under specific conditions, indicating material viscosity and processability. MFI typically refers to the mass of polymer flowing through a die per 10 minutes, often expressed in grams per 10 minutes, while MI is a less precise term historically used interchangeably with MFI. Understanding these standardized measurements helps you evaluate polymer behavior during extrusion or molding for quality control and product consistency.
The Historical Context of MFI and MI
MFI (Melt Flow Index) and MI (Melt Index) trace their origins to standardized testing methods established in the mid-20th century to measure the flow properties of thermoplastic polymers. Initially, MI was widely used to describe the rate of polymer melt extruded through a die under specific conditions, while MFI evolved as a more precise and consistent parameter, aligning with ISO and ASTM standards for polymer characterization. Understanding the historical context of these terms helps clarify how modern polymer processing relies on MFI for accurate, repeatable assessments of melt viscosity and material behavior.
Differences Between MFI and MI
Melt Flow Index (MFI) and Melt Index (MI) are terms often used interchangeably but differ slightly in their testing standards and units. MFI measures the mass of polymer melt extruded through a capillary under a specified load and temperature over 10 minutes, expressed in grams per 10 minutes, while MI generally refers to a broader category of melt flow measurements that can include variations in testing conditions and units. The distinction lies primarily in standardization, where MFI is defined by ASTM D1238 and ISO 1133, ensuring consistent test parameters, whereas MI may encompass other methods or customized tests depending on industry or regulatory requirements.
Measuring Methods: How MFI and MI Are Tested
MFI (Melt Flow Index) and MI (Melt Index) both quantify the flow properties of thermoplastic polymers by measuring the mass of material extruded through a standardized die under prescribed temperature and load conditions. The test involves heating the polymer in a barrel to a specific temperature, then applying a fixed weight to push the molten polymer through a capillary, where the extrudate is collected and weighed over ten minutes for MFI or calculated for MI. While MFI is expressed in grams per 10 minutes, reflecting the polymer's ease of flow during processing, MI often represents the same parameter but may follow slightly different testing standards depending on region or polymer type.
Units of Measurement: MFI vs. MI
MFI (Melt Flow Index) and MI (Melt Index) both measure the flow rate of melted thermoplastic polymers but differ in unit expression and testing standards. MFI is typically expressed in grams per 10 minutes (g/10 min), reflecting the mass of polymer extruded under specific loads and temperatures according to ASTM D1238. MI, often used synonymously with MFI, may sometimes refer to variations in test conditions or regional standards but generally shares the same g/10 min unit, making them functionally equivalent in industry practice.
Importance in Polymer Industry
MFI (Melt Flow Index) and MI (Melt Index) are critical parameters in the polymer industry for assessing the flow properties of thermoplastic materials during processing. MFI measures the amount of polymer that can flow through a standardized die under specific temperature and pressure, directly influencing the ease of molding, extrusion, and overall product quality. Understanding Your material's MFI/MI helps optimize manufacturing conditions, ensuring consistent performance and meeting precise application requirements.
Applications: Where MFI and MI Are Used
MFI (Melt Flow Index) and MI (Melt Index) are widely used in the plastics industry to assess the flow properties of thermoplastic polymers during processing, such as extrusion and injection molding. MFI is commonly applied for quality control in manufacturing polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene, helping determine processability and material consistency. MI, often used interchangeably with MFI, supports material selection in product design and helps predict polymer behavior under specific temperature and load conditions for applications like packaging films, automotive parts, and consumer goods.
Advantages and Limitations of MFI/MI
Melt Flow Index (MFI) and Melt Index (MI) both measure the flow properties of thermoplastics, providing critical data for processing and quality control. MFI offers a quick and standardized method to assess polymer viscosity at specific temperatures and loads, helping optimize manufacturing parameters, but it does not capture the material's behavior under real processing conditions or its rheological complexity. Your choice between MFI and MI should consider that while both indicate melt flow characteristics, their limitations include sensitivity to test conditions and inability to fully predict final product performance.
Choosing the Right Index for Your Application
Melt Flow Index (MFI) and Melt Index (MI) both measure the flow properties of thermoplastic polymers, indicating their processability under specific conditions. MFI typically quantifies the mass of polymer extruded per 10 minutes under a set temperature and load, making it ideal for assessing material behavior during extrusion or molding processes. Choosing the right index depends on your application's temperature, load requirements, and desired precision in characterizing polymer flow to optimize manufacturing performance.
MFI (melt flow index) vs MI (melt index) Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com