Nylon offers excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under stress, while Acetal provides superior stiffness, low friction, and dimensional stability, perfect for precision parts and smooth operation. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize toughness and impact resistance (Nylon) or rigidity and minimal wear (Acetal).
Table of Comparison
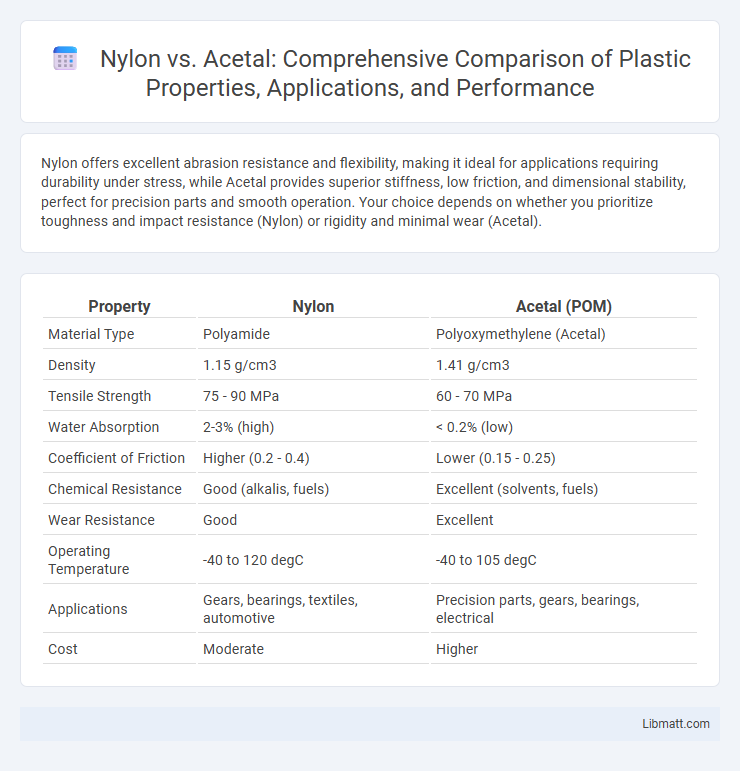
| Property | Nylon | Acetal (POM) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polyamide | Polyoxymethylene (Acetal) |
| Density | 1.15 g/cm3 | 1.41 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 75 - 90 MPa | 60 - 70 MPa |
| Water Absorption | 2-3% (high) | < 0.2% (low) |
| Coefficient of Friction | Higher (0.2 - 0.4) | Lower (0.15 - 0.25) |
| Chemical Resistance | Good (alkalis, fuels) | Excellent (solvents, fuels) |
| Wear Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Operating Temperature | -40 to 120 degC | -40 to 105 degC |
| Applications | Gears, bearings, textiles, automotive | Precision parts, gears, bearings, electrical |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Introduction to Nylon and Acetal
Nylon and Acetal are engineering thermoplastics known for their strength, durability, and resistance to wear and chemicals. Nylon offers excellent flexibility and impact resistance, making it ideal for applications like gears, bearings, and textiles, while Acetal provides superior stiffness and low friction, commonly used in precision parts and automotive components. Your choice between Nylon and Acetal depends on specific mechanical requirements and environmental factors in your project.
Overview of Material Properties
Nylon exhibits high tensile strength, excellent abrasion resistance, and good chemical stability, making it ideal for wear-intensive applications. Acetal offers superior stiffness, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability under varying temperatures, preferred for precision mechanical components. Both materials provide strong mechanical performance, but Nylon excels in impact resistance while Acetal delivers better creep resistance and moisture resistance.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Nylon exhibits superior tensile strength and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring impact resistance and durability under dynamic loads. Acetal offers high stiffness, excellent dimensional stability, and lower friction, which benefits precision parts subjected to repetitive motion. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize toughness and elasticity with Nylon or rigidity and wear resistance with Acetal.
Wear and Friction Performance
Nylon exhibits excellent wear resistance and low friction properties, making it ideal for applications involving continuous sliding and heavy loads. Acetal offers superior dimensional stability with consistent low friction coefficients, ensuring minimal wear in precision parts such as gears and bearings. Both materials provide durable performance, but nylon's natural lubricity gives it an edge in dynamic, high-wear environments.
Chemical Resistance Differences
Nylon exhibits strong resistance to oils, fuels, and some chemicals but is prone to degradation when exposed to strong acids and bases, absorbing moisture that can affect its mechanical properties. Acetal, also known as polyoxymethylene (POM), offers superior chemical resistance to solvents, fuels, and dilute acids, while maintaining low moisture absorption and excellent dimensional stability. This makes acetal more suitable than nylon for applications requiring sustained exposure to harsh chemicals and damp environments.
Moisture Absorption and Stability
Nylon exhibits higher moisture absorption, which can lead to dimensional changes and reduced stability in humid environments. Acetal maintains superior dimensional stability due to its low moisture absorption, making it ideal for applications requiring consistent mechanical properties. Your choice between nylon and acetal should consider the environmental conditions and the need for moisture resistance.
Temperature Tolerance and Performance
Nylon exhibits a temperature tolerance typically ranging from -40degC to 120degC, making it suitable for moderate heat applications, while Acetal withstands higher continuous operating temperatures up to 105degC and short-term exposures near 130degC. Acetal offers superior dimensional stability and mechanical performance under thermal stress, maintaining strength and rigidity where Nylon may soften or absorb moisture, affecting its properties. In high-temperature environments demanding precision and wear resistance, Acetal often outperforms Nylon due to its lower moisture absorption and better thermal endurance.
Typical Applications for Nylon vs Acetal
Nylon is commonly used in automotive parts, electrical components, and consumer goods due to its excellent wear resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for gears, bushings, and connectors. Acetal, known for its high stiffness, low friction, and dimensional stability, is frequently applied in precision mechanical parts, such as bearings, valve components, and conveyor system parts. Understanding these typical applications helps you select the right material based on performance requirements and environmental conditions.
Cost Analysis and Availability
Nylon generally offers a more cost-effective solution compared to Acetal, making it a preferred choice for budget-sensitive applications without compromising durability. Acetal tends to be pricier due to its superior dimensional stability and chemical resistance, but its consistent availability across industrial suppliers ensures fewer delays in procurement. Your choice should balance Nylon's affordability and widespread availability against Acetal's higher cost and specialized properties.
Choosing the Right Material: Key Considerations
Selecting between nylon and acetal hinges on factors like mechanical strength, moisture absorption, and chemical resistance. Nylon offers superior toughness and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for dynamic applications but absorbs moisture, which can affect dimensional stability. Acetal provides excellent stiffness, low friction, and minimal moisture uptake, preferred for precision parts requiring stable performance in humid environments.
Nylon vs Acetal Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com