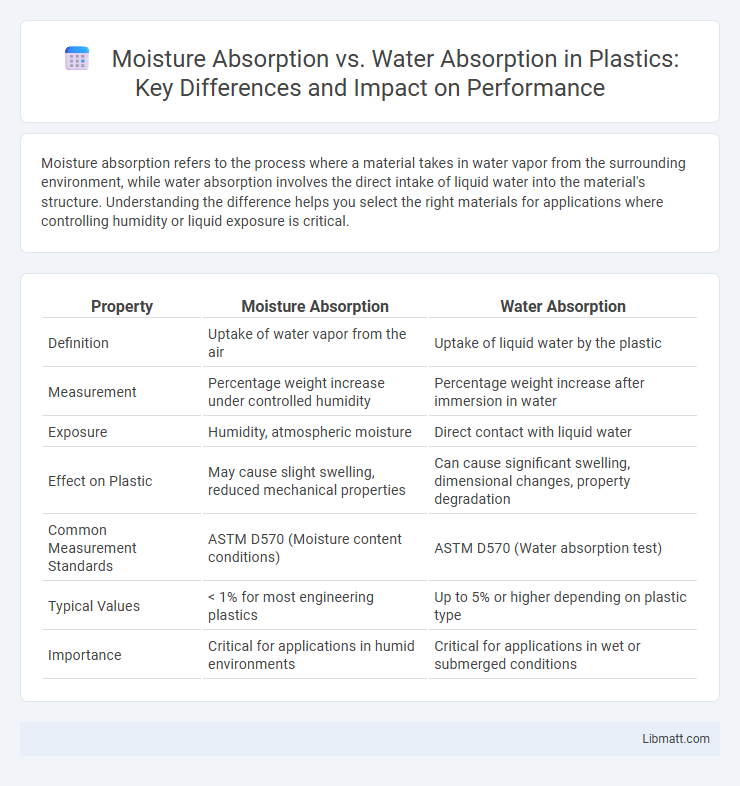
Moisture absorption refers to the process where a material takes in water vapor from the surrounding environment, while water absorption involves the direct intake of liquid water into the material's structure. Understanding the difference helps you select the right materials for applications where controlling humidity or liquid exposure is critical.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Moisture Absorption | Water Absorption |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uptake of water vapor from the air | Uptake of liquid water by the plastic |
| Measurement | Percentage weight increase under controlled humidity | Percentage weight increase after immersion in water |
| Exposure | Humidity, atmospheric moisture | Direct contact with liquid water |
| Effect on Plastic | May cause slight swelling, reduced mechanical properties | Can cause significant swelling, dimensional changes, property degradation |
| Common Measurement Standards | ASTM D570 (Moisture content conditions) | ASTM D570 (Water absorption test) |
| Typical Values | < 1% for most engineering plastics | Up to 5% or higher depending on plastic type |
| Importance | Critical for applications in humid environments | Critical for applications in wet or submerged conditions |
Understanding Moisture Absorption
Moisture absorption refers to the ability of a material to uptake water vapor from the surrounding environment, influencing properties such as dimensional stability and mechanical strength. Unlike water absorption, which measures liquid water uptake, moisture absorption impacts processes like corrosion, mold growth, and thermal insulation performance. Accurate assessment of moisture absorption is critical in industries like textiles, polymers, and building materials to ensure product durability and functionality.
Defining Water Absorption
Water absorption refers to the process by which a material, typically porous, takes in water molecules through its surface or internal structure, leading to increased weight and potential changes in physical properties. Unlike moisture absorption, which includes uptake from vapor or humidity in the air, water absorption specifically involves the direct intake of liquid water. Accurate measurement of water absorption is crucial in materials science, impacting durability, structural integrity, and application suitability in construction, textiles, and polymers.
Key Differences Between Moisture and Water Absorption
Moisture absorption refers to the uptake of water vapor from the atmosphere by a material, typically measured as a percentage weight increase under controlled humidity conditions, whereas water absorption involves the material's capacity to soak up liquid water when fully immersed. Moisture absorption affects the material's dimensional stability and electrical properties, often occurring at the surface and within the microstructure, while water absorption influences the material's bulk mechanical strength and durability due to liquid penetration. Key differences lie in the state of water absorbed (vapor vs. liquid), measurement methods, and the impact on material performance in various environmental conditions.
Mechanisms of Moisture Absorption
Moisture absorption involves the uptake of water vapor from the surrounding atmosphere into a material's surface and subsurface layers through processes like adsorption and diffusion. Adsorption occurs when water molecules adhere to the material's surface, forming a thin film, while diffusion allows these molecules to penetrate deeper into the material's porous structure. This mechanism differs significantly from water absorption, which typically involves liquid water permeating the material, often leading to swelling or physical changes in properties.
Mechanisms of Water Absorption
Water absorption involves the penetration of liquid water into a material's bulk through capillary action, diffusion, or permeation, leading to swelling or degradation. Moisture absorption primarily refers to the uptake of water vapor from the environment, which occurs via adsorption or absorption at the surface or within microvoids. Understanding these mechanisms helps you select materials with appropriate resistance to water damage in applications like coatings, composites, or textiles.
Factors Influencing Moisture Absorption
Factors influencing moisture absorption include temperature, humidity levels, and material porosity, which collectively determine how much moisture a substance can retain. The molecular structure and chemical composition of materials, such as hydrophilic or hydrophobic properties, significantly impact their moisture absorption capacity. Environmental exposure duration and surface area also play crucial roles in the rate and extent of moisture uptake by materials.
Factors Influencing Water Absorption
Water absorption in materials is influenced by factors such as porosity, surface tension, and the hydrophilic nature of the material's molecular structure. Temperature and exposure duration also play critical roles in determining the rate and extent of water uptake. Understanding these factors helps you select materials with optimal performance for moisture-sensitive applications.
Applications in Material Science
Moisture absorption refers to the uptake of water vapor by materials, critical in evaluating polymers, textiles, and composites for durability and dimensional stability under humid conditions. Water absorption measures the amount of liquid water a material can take in, significantly impacting coatings, ceramics, and construction materials where resistance to liquid water penetration ensures performance and longevity. Understanding the differences between moisture and water absorption helps optimize material selection and treatment processes to enhance Your product's reliability in diverse environmental applications.
Impact on Product Performance
Moisture absorption affects product performance by causing dimensional changes, reduced mechanical strength, and potential chemical degradation, particularly in polymers and composites. Water absorption, a subset of moisture uptake, leads to swelling, loss of adhesion, and increased risk of microbial growth, severely impacting durability. Controlling both types of absorption is crucial for maintaining integrity, longevity, and functionality in manufacturing and packaging applications.
Testing Methods and Standards
Moisture absorption and water absorption testing methods differ primarily in scope and conditions, with moisture absorption typically measured using ASTM D570 and ISO 62 standards that assess the material's ability to absorb water vapor under controlled humidity and temperature. Water absorption tests involve immersing samples in liquid water for a specified period, adhering to standards like ASTM D570, which defines the water uptake percentage by weight after immersion. Your choice of testing method should align with the application environment to accurately evaluate material performance in moisture or water exposure scenarios.
Moisture Absorption vs Water Absorption Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com