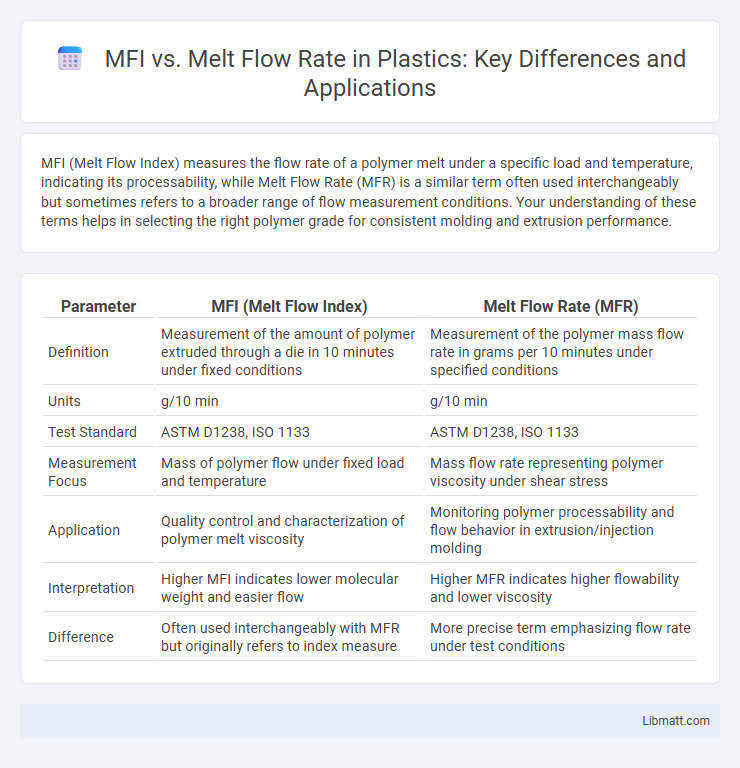
MFI (Melt Flow Index) measures the flow rate of a polymer melt under a specific load and temperature, indicating its processability, while Melt Flow Rate (MFR) is a similar term often used interchangeably but sometimes refers to a broader range of flow measurement conditions. Your understanding of these terms helps in selecting the right polymer grade for consistent molding and extrusion performance.
Table of Comparison
| Parameter | MFI (Melt Flow Index) | Melt Flow Rate (MFR) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measurement of the amount of polymer extruded through a die in 10 minutes under fixed conditions | Measurement of the polymer mass flow rate in grams per 10 minutes under specified conditions |
| Units | g/10 min | g/10 min |
| Test Standard | ASTM D1238, ISO 1133 | ASTM D1238, ISO 1133 |
| Measurement Focus | Mass of polymer flow under fixed load and temperature | Mass flow rate representing polymer viscosity under shear stress |
| Application | Quality control and characterization of polymer melt viscosity | Monitoring polymer processability and flow behavior in extrusion/injection molding |
| Interpretation | Higher MFI indicates lower molecular weight and easier flow | Higher MFR indicates higher flowability and lower viscosity |
| Difference | Often used interchangeably with MFR but originally refers to index measure | More precise term emphasizing flow rate under test conditions |
Introduction to MFI and Melt Flow Rate
MFI (Melt Flow Index) and Melt Flow Rate both measure the flow characteristics of thermoplastic polymers under specific conditions, serving as critical indicators for processing behavior and quality control. MFI quantifies the amount of polymer that flows through a die under a standardized load and temperature in ten minutes, expressed in grams per 10 minutes. Melt Flow Rate, often used interchangeably with MFI, emphasizes the polymer's viscosity and ease of flow during molding or extrusion, impacting product consistency and manufacturing efficiency.
Defining MFI (Melt Flow Index)
MFI (Melt Flow Index) measures the ease of flow of molten thermoplastic polymers through a standardized die under specified conditions, indicating polymer viscosity. It is expressed in grams per 10 minutes and serves as a key quality parameter in polymer processing to predict material behavior during extrusion or molding. This index helps manufacturers select appropriate polymers based on flow characteristics for specific applications.
What is Melt Flow Rate?
Melt Flow Rate (MFR) measures the rate at which a thermoplastic polymer melts and flows through a specified die under controlled temperature and pressure, quantifying its viscosity and flow characteristics. It is expressed in grams per 10 minutes and helps determine the processability and quality of polymers during molding or extrusion. MFR is critical for selecting materials suitable for specific manufacturing processes, ensuring consistent material performance.
MFI vs Melt Flow Rate: Key Differences
MFI (Melt Flow Index) and Melt Flow Rate (MFR) both measure the flow properties of thermoplastic polymers under specific conditions but differ mainly in testing methods and units. MFI quantifies the mass of polymer extruded through a die in 10 minutes under a set temperature and load, typically reported in grams per 10 minutes, whereas MFR often refers to the volume or mass flow rate and can vary slightly depending on international standards. Understanding MFI vs Melt Flow Rate is crucial for selecting the right polymer grade for manufacturing processes like injection molding or extrusion, ensuring optimal material behavior and product quality.
Measurement Methods for MFI and Melt Flow Rate
MFI (Melt Flow Index) and Melt Flow Rate both measure the flow properties of thermoplastic polymers under heat, but MFI is determined by the mass of polymer extruded through a die in a set time, while Melt Flow Rate quantifies the volumetric flow using specific conditions defined by ASTM or ISO standards. MFI measurement involves applying a standard load on the polymer melt and recording the mass flow in grams per 10 minutes, whereas Melt Flow Rate uses a similar process but emphasizes the volume of material passing through the die per unit time. Your accurate polymer characterization depends on understanding these measurement nuances to predict processing behavior effectively.
Importance in Polymer Processing
MFI (Melt Flow Index) and Melt Flow Rate are critical parameters in polymer processing that measure the ease of flow of molten polymers, directly impacting manufacturing consistency and product quality. These values help you determine the optimal processing conditions, such as temperature and pressure, ensuring efficient molding, extrusion, and overall handling of thermoplastics. Accurate measurement of MFI vs Melt Flow Rate supports better selection of raw materials, enhancing the mechanical properties and performance of the final polymer products.
Factors Affecting MFI and Melt Flow Rate
MFI (Melt Flow Index) and Melt Flow Rate measure the ease of polymer flow under heat and pressure, influenced mainly by molecular weight, temperature, and applied load. Higher temperatures and lower molecular weights generally increase MFI by reducing polymer viscosity, while increased pressure enhances flow rate by forcing the melt through the die faster. Additives, polymer branching, and degradation also affect these values by altering the polymer's structural properties and flow behavior.
Applications in the Plastics Industry
MFI (Melt Flow Index) and Melt Flow Rate are critical parameters used to evaluate the flow properties of thermoplastic polymers during processing. These measurements directly influence the selection of materials for injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding, ensuring your products meet specific viscosity and flow requirements for optimal manufacturing performance. Understanding the MFI enables manufacturers to predict ease of processing and final mechanical properties of plastic components in various industrial applications.
Limitations and Challenges
MFI (Melt Flow Index) and Melt Flow Rate both measure the flow properties of thermoplastic polymers, but their limitations include sensitivity to testing conditions such as temperature and load, which can cause variability in results. Challenges arise due to MFI providing only a single-point measurement that may not represent the polymer's behavior under real processing conditions, while Melt Flow Rate requires precise calibration to ensure accuracy. You should consider these factors when interpreting flow data to avoid misjudging a material's processability or performance.
Conclusion: Choosing Between MFI and Melt Flow Rate
MFI (Melt Flow Index) and Melt Flow Rate both measure the flow properties of thermoplastics but differ in test conditions and units, with MFI expressed in grams per 10 minutes and Melt Flow Rate typically as grams per minute. Your choice depends on the specific polymer type, processing conditions, and industry standards to ensure accurate assessment of material behavior under heat and pressure. Selecting the right parameter improves quality control and optimizes manufacturing processes for better product performance.
MFI vs Melt Flow Rate Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com