The ejector plate pushes the molded part out of the mold cavity after cooling, while the stripper plate helps remove the part by stripping it off the core or insert during the ejection phase. Understanding the difference between these components can enhance Your injection molding process efficiency and part quality.
Table of Comparison
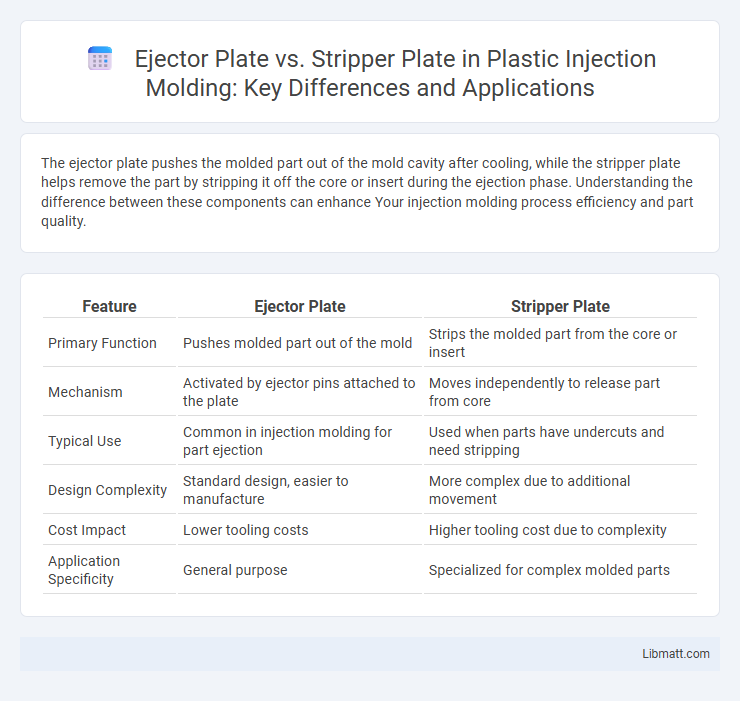
| Feature | Ejector Plate | Stripper Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Pushes molded part out of the mold | Strips the molded part from the core or insert |
| Mechanism | Activated by ejector pins attached to the plate | Moves independently to release part from core |
| Typical Use | Common in injection molding for part ejection | Used when parts have undercuts and need stripping |
| Design Complexity | Standard design, easier to manufacture | More complex due to additional movement |
| Cost Impact | Lower tooling costs | Higher tooling cost due to complexity |
| Application Specificity | General purpose | Specialized for complex molded parts |
Introduction to Ejector Plate and Stripper Plate
Ejector plates and stripper plates are essential components in injection molding, designed to aid in the removal of molded parts from the mold cavity. Ejector plates push the finished product out by moving ejector pins, while stripper plates function by stripping or peeling the molded part off the core to prevent damage. Effective use of these plates improves cycle times and ensures part integrity by facilitating smooth ejection processes.
Key Functions in Injection Molding
Ejector plates in injection molding primarily facilitate the removal of the molded part from the mold by pushing ejector pins forward, ensuring smooth and precise ejection without damaging the product. Stripper plates serve to strip or peel off molded parts that adhere to the core or cavity surfaces, particularly useful for thin-walled or intricate components. Both components optimize cycle time and maintain product quality by preventing sticking and ensuring consistent part release.
Design Differences: Ejector vs Stripper Plates
Ejector plates use pins or rods to push the finished part out of the mold, providing precise ejection with minimal part damage. Stripper plates, however, rely on a larger, solid plate to strip the part away from the core or cavity, often used for more complex or delicate shapes. Understanding these design differences helps optimize your injection molding process for efficiency and part quality.
Working Principle of Ejector Plates
Ejector plates operate by pushing the molded part off the core pin after the molding cycle, using ejector pins connected to the plate driven by hydraulic or mechanical means. This precise and controlled movement ensures efficient and damage-free removal of delicate or complex parts from the mold cavity. Understanding the working principle of ejector plates helps you optimize mold design for faster cycle times and improved part quality compared to stripper plates, which typically rely on a different stripping action.
Working Principle of Stripper Plates
Stripper plates function by holding the workpiece securely against the die during the return stroke, preventing it from sticking to the punch and ensuring smooth ejection. They work through a mechanical or hydraulic system that applies uniform pressure as the punch retracts, stripping the material off the punch face. Understanding the working principle of stripper plates helps optimize your stamping or forming process by reducing cycle time and minimizing damage to the workpiece.
Advantages of Ejector Plates
Ejector plates offer precise control and reliable ejection of molded parts, reducing cycle times and minimizing part damage compared to stripper plates. Their design allows for uniform force distribution, which enhances the longevity of molds and maintains consistent product quality. You benefit from improved efficiency and reduced maintenance costs when choosing ejector plates in injection molding applications.
Advantages of Stripper Plates
Stripper plates offer greater durability and lower maintenance compared to ejector plates, making them ideal for high-volume manufacturing processes. They provide improved part ejection consistency by stripping the part off the core simultaneously, reducing the risk of part deformation or damage. Your production efficiency benefits from the simplicity and reliability of stripper plates, especially in applications requiring precise and clean stripping action.
Applications: When to Use Each Type
Ejector plates are ideal for applications requiring fast, repetitive ejection of molded parts with minimal force, commonly used in high-volume plastic injection molding of thin-walled components. Stripper plates excel in scenarios involving delicate or complex parts that need uniform stripping to avoid deformation, typical in rubber molding or when substrates have intricate geometries. Selecting between ejector and stripper plates depends on part design, material type, and production speed requirements to ensure optimal ejection efficiency and product integrity.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Ejector plates often face issues such as misalignment, wear, and insufficient force, leading to incomplete part ejection and damage to molded components. Stripper plates commonly experience problems like sticking due to accumulated resin, improper clearance causing excessive wear, and timing discrepancies resulting in cycle delays. Addressing these issues requires regular maintenance, precise alignment checks, and timely lubrication to ensure optimal mold release and prolong equipment lifespan.
Choosing the Right Ejection System for Your Mold
Choosing the right ejection system for your mold involves understanding the key differences between ejector plates and stripper plates. An ejector plate provides precise, individual pin ejection ideal for delicate or complex parts, while a stripper plate offers uniform, simultaneous ejection suitable for parts with larger surface areas. Your selection should be based on part geometry, material type, and cycle time requirements to optimize mold performance and production efficiency.
Ejector plate vs stripper plate Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com