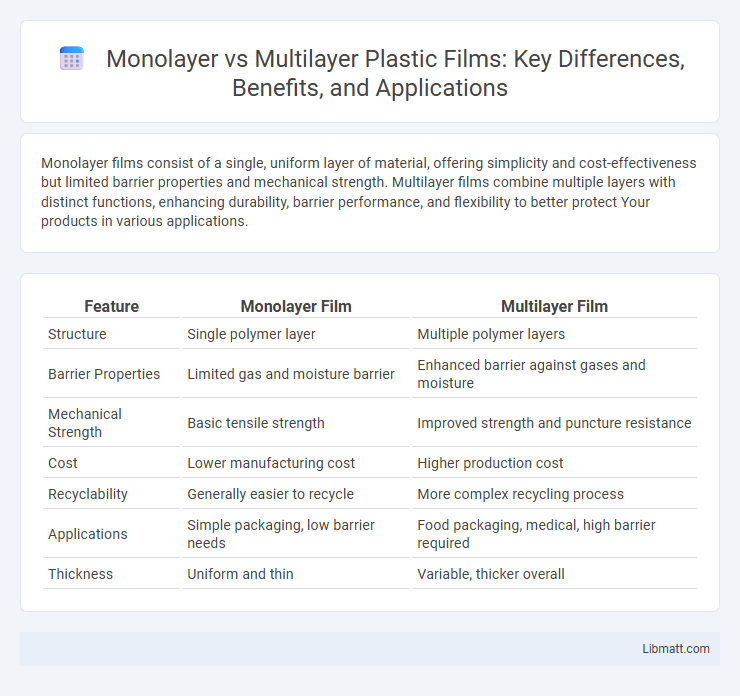
Monolayer films consist of a single, uniform layer of material, offering simplicity and cost-effectiveness but limited barrier properties and mechanical strength. Multilayer films combine multiple layers with distinct functions, enhancing durability, barrier performance, and flexibility to better protect Your products in various applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Monolayer Film | Multilayer Film |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Single polymer layer | Multiple polymer layers |
| Barrier Properties | Limited gas and moisture barrier | Enhanced barrier against gases and moisture |
| Mechanical Strength | Basic tensile strength | Improved strength and puncture resistance |
| Cost | Lower manufacturing cost | Higher production cost |
| Recyclability | Generally easier to recycle | More complex recycling process |
| Applications | Simple packaging, low barrier needs | Food packaging, medical, high barrier required |
| Thickness | Uniform and thin | Variable, thicker overall |
Introduction to Monolayer and Multilayer Films
Monolayer films consist of a single, uniform layer of material offering basic barrier properties ideal for simple packaging needs. Multilayer films combine two or more layers, each providing specific functionalities such as enhanced strength, moisture resistance, or oxygen barrier, improving overall performance. Your choice depends on the application requirements, with multilayer films delivering superior protection for complex packaging solutions.
Composition and Structure Differences
Monolayer films consist of a single layer of molecules or atoms arranged in a uniform structure, offering simplicity and minimal thickness. Multilayer films are composed of multiple stacked layers, each potentially having different material properties, enhancing functionality such as barrier protection or optical characteristics. The structural complexity of multilayer films provides improved mechanical strength and tailored physical or chemical attributes compared to monolayer films.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Monolayer film manufacturing involves a single extrusion or casting process, resulting in a uniform layer with straightforward production and lower costs. Multilayer film production uses co-extrusion or lamination techniques to combine multiple layers with different properties, enhancing barrier performance, strength, and flexibility. Your choice depends on application-specific requirements, balancing complexity in manufacturing with desired film functionality.
Performance Characteristics: Strength and Barrier Properties
Monolayer films offer uniform strength and moderate barrier properties suitable for simple packaging needs, whereas multilayer films combine various materials to enhance both tensile strength and resistance to gases, moisture, and odors. Multilayer films excel in preserving product freshness due to superior barrier performance and greater durability under mechanical stress. Your choice between these films depends on the specific strength requirements and the level of protection needed against environmental factors.
Cost Analysis: Production and Material Expenses
Monolayer film production generally incurs lower material costs due to the use of a single polymer layer, making it more cost-effective for applications requiring basic barrier properties. Multilayer film involves higher production expenses as it combines multiple polymer layers, enhancing performance but increasing raw material and processing costs. Your choice between monolayer and multilayer film should consider the balance between budget constraints and the need for specialized barrier or mechanical properties.
Applications in Packaging Industries
Monolayer films are commonly used in packaging industries for single-layer applications such as shrink wraps and snack packaging due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. Multilayer films offer enhanced barrier properties, mechanical strength, and flexibility, making them ideal for complex packaging needs like food preservation, pharmaceuticals, and frozen goods. The multilayer structure enables tailored protection against moisture, oxygen, and UV light, significantly extending shelf life and maintaining product quality.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Monolayer films are typically easier to recycle due to their single-material composition, reducing contamination during processing and supporting more efficient recycling streams. Multilayer films, composed of multiple bonded materials, often pose significant challenges for recyclability because their layered structures require complex separation techniques that are currently limited in scalability. From an environmental impact perspective, monolayer films generally have a lower carbon footprint and reduced resource consumption, while multilayer films may contribute to increased waste persistence and higher energy use during disposal or recycling.
Recent Technological Advancements
Recent technological advancements in monolayer film focused on enhancing molecular uniformity and improving barrier properties through atomic layer deposition and chemical vapor deposition techniques. Multilayer film innovations emphasize nanolayer stacking and hybrid material integration to achieve superior mechanical strength, thermal stability, and enhanced gas permeability control. These developments enable applications in flexible electronics, food packaging, and advanced coatings, significantly expanding the functional capabilities of both monolayer and multilayer films.
Quality Control and Testing Methods
Monolayer films undergo quality control through techniques such as tensile strength testing and permeability analysis to ensure uniformity and consistent barrier properties. Multilayer films require more complex testing methods including interlayer adhesion tests and differential scanning calorimetry to evaluate the integrity and performance of each layer. Advanced imaging technologies like scanning electron microscopy (SEM) are commonly used to detect defects and layer morphology in both film types.
Choosing the Right Film for Your Application
Selecting the right film requires understanding the distinct properties of monolayer and multilayer films. Monolayer films offer simplicity, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, ideal for applications with minimal barrier needs, while multilayer films provide enhanced protection against moisture, oxygen, and UV light due to their composite structure. Your specific packaging or protection requirements determine the best choice, balancing performance, durability, and budget constraints.
Monolayer Film vs Multilayer Film Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com