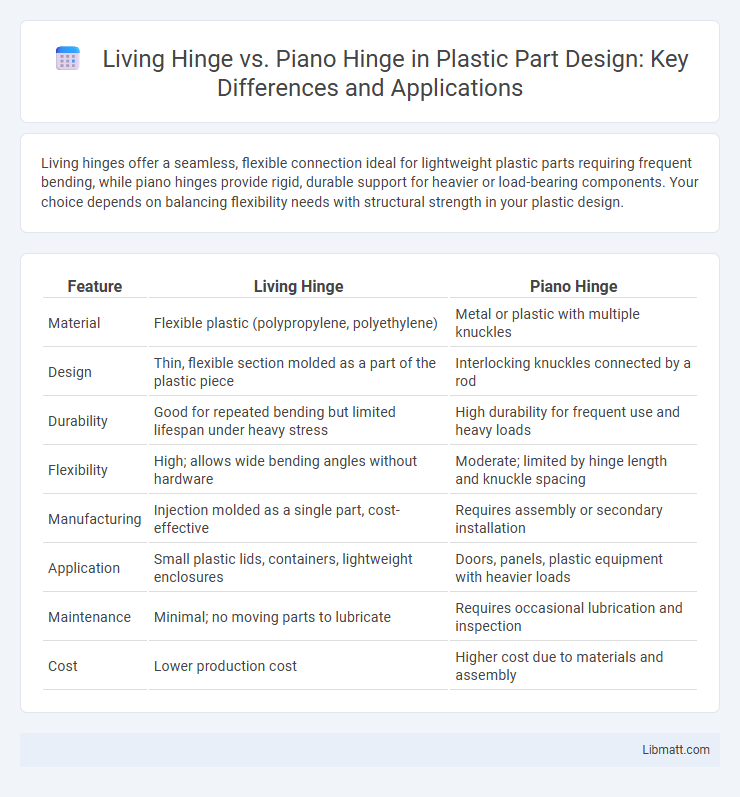
Living hinges offer a seamless, flexible connection ideal for lightweight plastic parts requiring frequent bending, while piano hinges provide rigid, durable support for heavier or load-bearing components. Your choice depends on balancing flexibility needs with structural strength in your plastic design.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Living Hinge | Piano Hinge |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Flexible plastic (polypropylene, polyethylene) | Metal or plastic with multiple knuckles |
| Design | Thin, flexible section molded as a part of the plastic piece | Interlocking knuckles connected by a rod |
| Durability | Good for repeated bending but limited lifespan under heavy stress | High durability for frequent use and heavy loads |
| Flexibility | High; allows wide bending angles without hardware | Moderate; limited by hinge length and knuckle spacing |
| Manufacturing | Injection molded as a single part, cost-effective | Requires assembly or secondary installation |
| Application | Small plastic lids, containers, lightweight enclosures | Doors, panels, plastic equipment with heavier loads |
| Maintenance | Minimal; no moving parts to lubricate | Requires occasional lubrication and inspection |
| Cost | Lower production cost | Higher cost due to materials and assembly |
Introduction to Living Hinges and Piano Hinges
Living hinges are flexible, integral plastic features molded into a single piece, allowing repeated bending without breakage, ideal for lightweight, compact designs such as flip-top lids and small enclosures. Piano hinges, composed of interlocking metal or plastic segments joined by a continuous pin, offer strong, durable, and precise rotational movement suited for heavier or larger applications requiring consistent alignment. Selecting between living hinges and piano hinges depends on functional requirements like flexibility, durability, material compatibility, and load-bearing capacity in plastic part design.
Key Differences Between Living and Piano Hinges
Living hinges are thin, flexible sections of plastic molded into a part, enabling repeated bending without separate components, ideal for lightweight, compact designs requiring seamless integration. Piano hinges consist of two rigid plastic parts connected by a pin, offering greater strength and durability for heavier loads or frequent, wider range movements. Key differences include the living hinge's monolithic construction and flexibility versus the piano hinge's mechanical assembly and enhanced structural support.
Material Considerations for Plastic Hinges
Material considerations for plastic hinges involve selecting polymers with suitable flexibility, fatigue resistance, and chemical stability to ensure durability and functionality. Living hinges typically utilize polypropylene or polyethylene due to their excellent fatigue resistance and ability to withstand repeated bending without cracking. For piano hinges in plastic designs, engineering plastics like polycarbonate or acetal offer added strength and rigidity, making them ideal for applications requiring robust, long-lasting performance.
Design Principles for Living Hinges
Living hinges rely on flexible, durable thermoplastic materials such as polypropylene or polyethylene, designed with thin, uniform thickness to allow repeated bending without fatigue. The hinge's geometry, including minimum bend radius and carefully controlled thickness transitions, is critical to prevent stress concentration and ensure long-lasting functionality. Your plastic part must incorporate precise mold design and material selection aligned with these principles to optimize the performance and durability of a living hinge.
Structural Features of Piano Hinges in Plastic Parts
Piano hinges in plastic parts consist of a continuous, interlocking leaf design that provides consistent alignment and enhanced structural support over the hinge length. Their rigid construction distributes stress evenly, improving load capacity and durability in mechanical applications. You benefit from reliable performance and longevity when choosing piano hinges for plastic component assemblies requiring frequent movement.
Durability and Lifecycle Comparisons
Living hinges, molded from flexible plastics like polypropylene, offer exceptional durability through millions of open-close cycles without mechanical wear or failure, making them ideal for lightweight, low-stress applications. Piano hinges, typically constructed from metal or reinforced materials, provide higher load-bearing capacity and resistance to external forces but may suffer from wear at pivot points and require additional maintenance to prevent corrosion. Your choice between living hinge and piano hinge designs should consider the required lifecycle, load conditions, and environmental exposure to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Manufacturing Process and Cost Implications
Living hinges are typically injection molded as a single piece from flexible plastics like polypropylene, resulting in a cost-effective manufacturing process with minimal assembly required. Piano hinges consist of multiple components, often metal or rigid plastic, requiring machining, joining, or assembly, which increases production time and cost. The simplicity and reduced labor of living hinges make them more economical for high-volume plastic part designs.
Application Scenarios: When to Use Each Hinge Type
Living hinges are ideal for applications requiring flexible, continuous bending in lightweight plastic parts such as battery covers, foldable containers, and disposable packaging due to their cost-effectiveness and seamless integration. Piano hinges suit heavy-duty applications demanding strength and durability, including toolboxes, equipment enclosures, and industrial access panels where repeated opening and closing occur. Choosing between living and piano hinges depends on factors like required flexibility, load-bearing capacity, and lifecycle durability in the product design.
Common Failure Modes and Maintenance
Living hinges commonly fail due to material fatigue, cracking, or environmental stress, especially when subjected to repeated bending or harsh chemicals. Piano hinges in plastic parts may suffer from pin wear, corrosion, or misalignment leading to joint loosening or failure. Proper maintenance of living hinges includes minimizing excessive bending and ensuring material compatibility, while piano hinges require regular inspection, lubrication, and alignment adjustments to extend Your component's lifespan.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Hinge for Plastic Part Design
Living hinges offer seamless flexibility and cost-effectiveness for thin, injection-molded plastic parts requiring frequent bending, while piano hinges provide robust, long-lasting support ideal for heavier applications needing multiple attachment points. Material choice, load requirements, and part geometry crucially impact hinge selection, emphasizing the living hinge's suitability for lightweight, high-cycle uses versus the piano hinge's advantage in strength and durability. Evaluating these factors ensures optimal hinge performance and product longevity in plastic part design.
Living hinge vs piano hinge (plastic part design) Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com