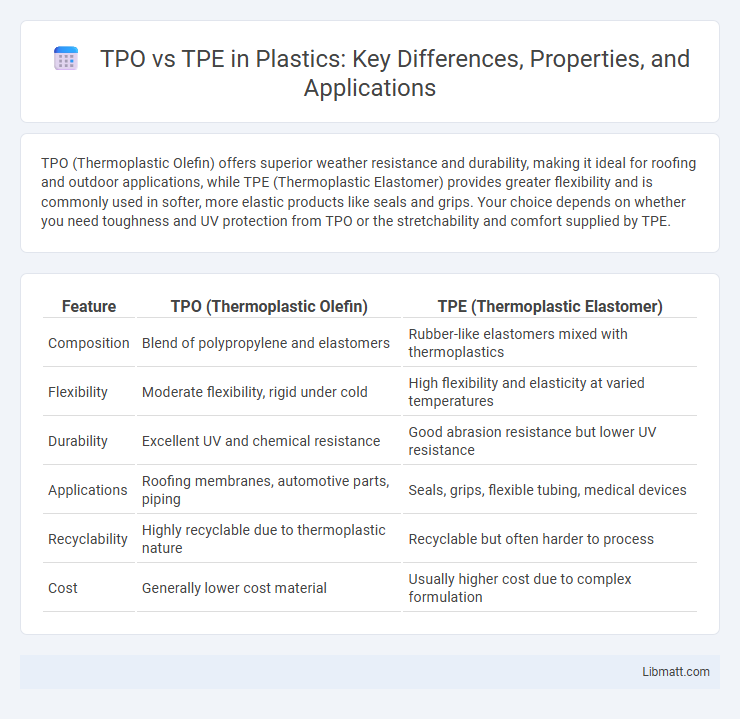
TPO (Thermoplastic Olefin) offers superior weather resistance and durability, making it ideal for roofing and outdoor applications, while TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) provides greater flexibility and is commonly used in softer, more elastic products like seals and grips. Your choice depends on whether you need toughness and UV protection from TPO or the stretchability and comfort supplied by TPE.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | TPO (Thermoplastic Olefin) | TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Blend of polypropylene and elastomers | Rubber-like elastomers mixed with thermoplastics |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, rigid under cold | High flexibility and elasticity at varied temperatures |
| Durability | Excellent UV and chemical resistance | Good abrasion resistance but lower UV resistance |
| Applications | Roofing membranes, automotive parts, piping | Seals, grips, flexible tubing, medical devices |
| Recyclability | Highly recyclable due to thermoplastic nature | Recyclable but often harder to process |
| Cost | Generally lower cost material | Usually higher cost due to complex formulation |
Introduction to TPO and TPE
TPO (Thermoplastic Olefin) and TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) are versatile materials widely used in manufacturing due to their flexibility and durability. TPO combines polypropylene with rubber, offering excellent resistance to UV rays, chemicals, and weather conditions, making it ideal for automotive parts and roofing membranes. TPE blends rubber and plastic properties, providing superior elasticity and softness, which suits applications like seals, grips, and flexible connectors that enhance your product's performance.
Chemical Composition of TPO vs TPE
Thermoplastic Olefins (TPO) consist primarily of a blend of polypropylene (PP) and elastomers such as ethylene-propylene rubber (EPR), characterized by a semicrystalline polypropylene matrix that provides stiffness and thermal resistance. Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE) are a broad category comprising block copolymers, such as styrene-butadiene-styrene (SBS) or styrene-ethylene-butylene-styrene (SEBS), combining elastomeric properties with thermoplastic processability. The chemical composition of TPO emphasizes olefin-based polymers enhancing chemical resistance and UV stability, whereas TPEs incorporate diverse monomers to tailor flexibility, elasticity, and mechanical performance.
Key Physical Properties Compared
TPO (Thermoplastic Olefin) and TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) differ significantly in tensile strength and elasticity, with TPE exhibiting higher elongation at break, typically around 500%, compared to TPO's 300%. TPO offers better chemical resistance and higher stiffness, making it ideal for automotive exteriors, whereas TPE provides superior flexibility and impact resistance suited for soft-touch applications. Both materials have comparable melting points near 230degC, but TPE's superior recovery from deformation enables enhanced durability in dynamic environments.
Manufacturing Processes
Thermoplastic Polyolefin (TPO) manufacturing involves blending polypropylene with ethylene-propylene rubber using extrusion or injection molding, resulting in a durable and flexible material. Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE) production utilizes processes like injection molding, extrusion, or blow molding to combine rubber-like elasticity with plastic melt processability, offering versatile applications. Understanding these manufacturing differences ensures you select the optimal material for your specific product requirements.
Applications of TPO and TPE
TPO (Thermoplastic Olefin) is widely used in automotive parts, roofing membranes, and footwear due to its excellent UV resistance, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) finds applications in medical devices, consumer goods, and flexible tubing thanks to its superior elasticity, soft touch, and recyclability. Both materials serve diverse industries demanding durability and versatility but differ in elasticity and mechanical properties suited for specific functional requirements.
Durability and Performance
TPO (Thermoplastic Olefin) offers exceptional durability with high resistance to UV radiation, chemical exposure, and extreme weather conditions, making it ideal for long-lasting roofing solutions. TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) provides superior flexibility and elasticity, maintaining performance in fluctuating temperatures without cracking or losing shape. Your choice between TPO and TPE should consider the balance between durability and flexibility based on environmental demands and application needs.
Cost Analysis: TPO vs TPE
TPO (Thermoplastic Olefin) generally offers a more cost-effective solution compared to TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) due to its lower raw material and manufacturing expenses. While TPE provides superior flexibility and durability, its production costs are significantly higher, impacting your overall budget for projects requiring elastic properties. Evaluating the balance between performance needs and cost efficiency is crucial when deciding between TPO and TPE materials.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
TPO (Thermoplastic Olefin) and TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) differ significantly in environmental impact and sustainability, with TPO typically offering better recyclability due to its simpler polymer structure, which reduces waste and energy consumption during reprocessing. TPE materials, while versatile and reusable, often contain a mix of elastomers and plastics that can complicate recycling processes and result in higher environmental footprints. Choosing TPO over TPE can contribute to more sustainable production cycles, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and reduced landfill waste, aligning with eco-friendly manufacturing goals.
Pros and Cons of TPO and TPE
TPO (Thermoplastic Olefin) offers excellent weather resistance and cost-effective roofing solutions, making it ideal for commercial buildings, but it can be less flexible in colder climates. TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) provides superior elasticity and recyclability, enhancing durability and environmental benefits, yet it tends to be more expensive and less UV resistant compared to TPO. Understanding these pros and cons helps you choose the best material for your specific roofing or sealing needs.
Choosing the Right Material: TPO or TPE
Choosing the right material between TPO (Thermoplastic Olefin) and TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomer) depends on application-specific requirements such as flexibility, durability, and environmental resistance. TPO delivers excellent UV and chemical resistance, making it ideal for automotive and roofing applications, while TPE offers superior elasticity and softness, suited for consumer goods and medical devices. Evaluating performance needs like temperature tolerance, cost-effectiveness, and recyclability ensures optimal material selection for durable, efficient product design.
TPO vs TPE Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com