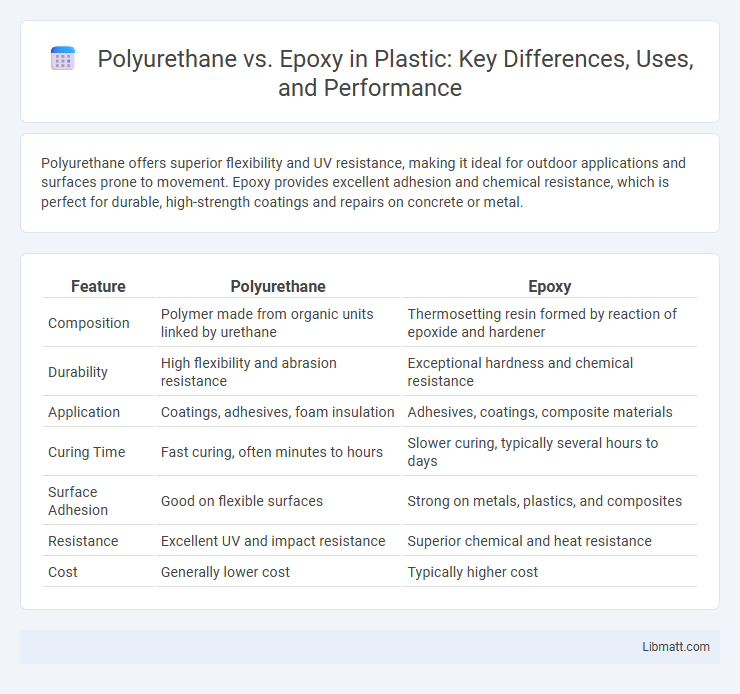
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and UV resistance, making it ideal for outdoor applications and surfaces prone to movement. Epoxy provides excellent adhesion and chemical resistance, which is perfect for durable, high-strength coatings and repairs on concrete or metal.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyurethane | Epoxy |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Polymer made from organic units linked by urethane | Thermosetting resin formed by reaction of epoxide and hardener |
| Durability | High flexibility and abrasion resistance | Exceptional hardness and chemical resistance |
| Application | Coatings, adhesives, foam insulation | Adhesives, coatings, composite materials |
| Curing Time | Fast curing, often minutes to hours | Slower curing, typically several hours to days |
| Surface Adhesion | Good on flexible surfaces | Strong on metals, plastics, and composites |
| Resistance | Excellent UV and impact resistance | Superior chemical and heat resistance |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Typically higher cost |
Introduction to Polyurethane and Epoxy
Polyurethane is a versatile polymer known for its flexibility, durability, and resistance to abrasion, making it ideal for coatings, adhesives, and sealants. Epoxy is a thermosetting resin valued for its strong adhesive properties, chemical resistance, and high mechanical strength, commonly used in industrial coatings and composite materials. Both materials differ significantly in composition and applications, with polyurethane offering elasticity and epoxy providing rigid structural support.
Chemical Composition and Structure
Polyurethane consists of polymers containing urethane linkages formed by the reaction of polyols and isocyanates, resulting in a flexible and durable molecular structure with varied hardness. Epoxy is composed of epoxide groups, typically based on bisphenol A or F, which cure through a cross-linking reaction with hardeners forming a rigid, three-dimensional network. The chemical composition differences in polyurethane and epoxy directly influence their mechanical properties, such as flexibility in polyurethane and high adhesion and chemical resistance in epoxy.
Key Differences in Properties
Polyurethane exhibits superior flexibility and UV resistance compared to epoxy, which is known for its exceptional hardness and chemical resistance. Epoxy provides stronger adhesion and higher tensile strength, making it ideal for structural applications, while polyurethane offers better impact resistance and abrasion durability. The curing process for epoxy is typically slower but results in a more rigid finish, whereas polyurethane cures faster with a more elastic and resilient surface.
Durability and Lifespan
Polyurethane coatings offer excellent flexibility and resistance to abrasion, making them highly durable for surfaces exposed to impact and movement. Epoxy, known for its superior hardness and chemical resistance, provides a longer lifespan in environments prone to heavy wear and exposure to solvents. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize flexibility or ultimate toughness for extended durability.
Application Methods
Polyurethane is typically applied using brushes, rollers, or spray guns, offering versatility on various surfaces including wood, concrete, and metal. Epoxy application often involves mixing two components before using trowels, rollers, or squeegees for coatings, adhesives, and floor systems requiring high durability. Your choice depends on the finish desired, curing time, and environmental conditions suited to each material's application method.
Surface Preparation Requirements
Polyurethane coating requires thorough surface cleaning, including removing dust, oils, and any loose particles to ensure proper adhesion. Epoxy demands more intensive surface preparation, often involving mechanical abrasion like sanding or shot blasting to create a profile for optimal bonding. Your choice depends on the substrate condition and the level of surface preparation you can perform.
Common Uses and Industries
Polyurethane is extensively used in automotive coatings, furniture finishes, and flooring due to its flexibility and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for both industrial and residential applications. Epoxy finds common use in construction, electronics, and marine industries because of its superior adhesion and chemical resistance, often serving as adhesives, sealants, and protective coatings. Understanding the distinct properties of polyurethane and epoxy helps you choose the right material for specific industrial needs and product durability.
Advantages of Polyurethane
Polyurethane offers superior flexibility and abrasion resistance compared to epoxy, making it ideal for surfaces subject to heavy wear or impact. Its excellent UV resistance ensures that it maintains clarity and durability when exposed to sunlight, unlike epoxy which can yellow over time. If you're looking for a coating with durable elasticity and better weather resistance, polyurethane is a more advantageous choice.
Benefits of Epoxy
Epoxy offers exceptional durability, chemical resistance, and superior adhesive strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty flooring and industrial applications. Its high mechanical properties ensure excellent impact and abrasion resistance, providing long-lasting protection in demanding environments. Epoxy coatings also cure quickly and maintain strong bond integrity on various substrates, enhancing structural performance.
Choosing the Right Material
Choosing the right material between polyurethane and epoxy depends on your project's specific needs, such as durability, flexibility, and chemical resistance. Polyurethane offers excellent abrasion resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for surfaces exposed to impact or frequent movement, while epoxy provides superior hardness and strong adhesion suitable for structural repairs and coatings. Understanding your environment and performance requirements ensures you select the most effective protective coating for your application.
Polyurethane vs epoxy Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com