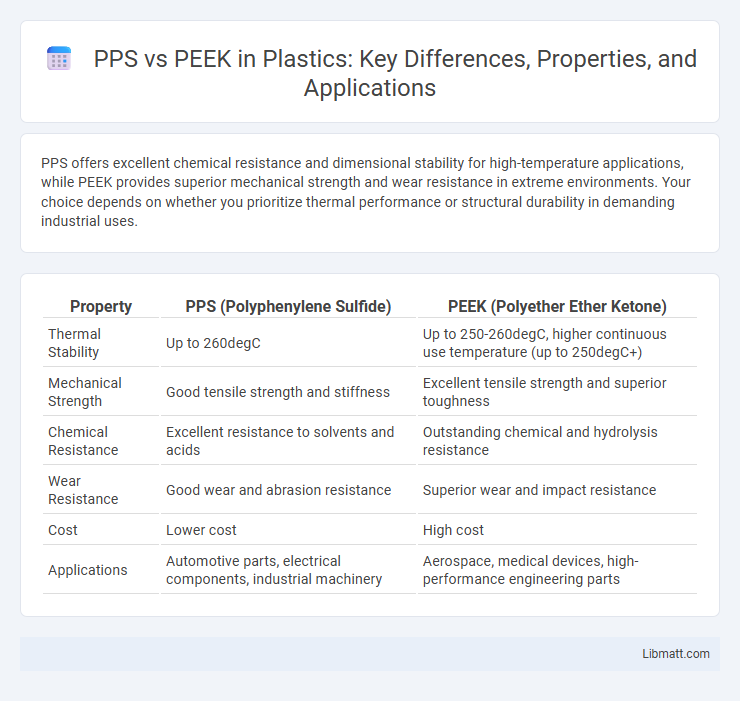
PPS offers excellent chemical resistance and dimensional stability for high-temperature applications, while PEEK provides superior mechanical strength and wear resistance in extreme environments. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize thermal performance or structural durability in demanding industrial uses.
Table of Comparison
| Property | PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide) | PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Up to 260degC | Up to 250-260degC, higher continuous use temperature (up to 250degC+) |
| Mechanical Strength | Good tensile strength and stiffness | Excellent tensile strength and superior toughness |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent resistance to solvents and acids | Outstanding chemical and hydrolysis resistance |
| Wear Resistance | Good wear and abrasion resistance | Superior wear and impact resistance |
| Cost | Lower cost | High cost |
| Applications | Automotive parts, electrical components, industrial machinery | Aerospace, medical devices, high-performance engineering parts |
Introduction to PPS and PEEK
Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its chemical resistance, thermal stability up to 260degC, and excellent electrical properties, commonly used in automotive and electrical industries. Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) offers superior mechanical strength, outstanding resistance to high temperatures up to 480degC, and robust chemical inertness, making it ideal for aerospace, medical, and industrial applications. Both polymers provide exceptional durability and performance under demanding conditions but differ significantly in temperature tolerance and mechanical characteristics.
Chemical Structures and Properties
PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide) features a repeating aromatic backbone linked by sulfide bonds, providing high thermal stability and excellent chemical resistance to acids and solvents. In contrast, PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) contains repeating units with ether and ketone groups between aromatic rings, delivering superior mechanical strength and resistance to hydrolysis and radiation. Your choice between PPS and PEEK depends on specific chemical environments and mechanical requirements due to their distinct molecular structures and resulting properties.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
PPS (polyphenylene sulfide) exhibits high mechanical strength with excellent dimensional stability and resistance to creep under continuous stress, making it suitable for demanding engineering applications. PEEK (polyether ether ketone) surpasses PPS in tensile strength and impact resistance, offering superior performance in high-temperature and chemically aggressive environments. The mechanical strength of PEEK typically ranges from 90 to 100 MPa tensile strength, while PPS generally maintains a lower tensile strength around 80 MPa but offers better stiffness in some formulations.
Thermal Stability and Performance
PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide) and PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) offer exceptional thermal stability, with PPS maintaining performance up to approximately 260degC and PEEK withstanding higher temperatures around 480degC. Your choice depends on the application's thermal requirements, as PEEK delivers superior high-temperature resistance and mechanical strength over prolonged exposure. PPS excels in cost-efficiency and chemical resistance while providing reliable thermal performance for moderate-temperature environments.
Chemical Resistance Capabilities
PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide) exhibits exceptional chemical resistance, particularly against acids, alkalis, and organic solvents, making it suitable for harsh industrial environments. PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) also offers superior chemical resistance, especially towards hydrocarbons, strong acids, and chlorinated solvents, maintaining mechanical integrity under aggressive conditions. Both polymers provide outstanding durability in corrosive environments, with PEEK generally favored for extreme chemical and thermal stability.
Applications in Various Industries
PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide) and PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) are high-performance polymers widely used across automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries due to their excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability. PPS is favored in automotive fuel system components and electrical connectors for its flame retardance and dimensional stability, while PEEK is preferred in aerospace and medical device manufacturing for its superior mechanical strength and biocompatibility. Both materials support advanced manufacturing processes like injection molding and 3D printing, enabling complex part fabrication in demanding industrial applications.
Processing and Manufacturing Differences
PPS (polyphenylene sulfide) offers superior thermal stability and chemical resistance enabling high-temperature processing at around 290-300degC, while PEEK (polyether ether ketone) requires higher processing temperatures near 360-400degC due to its semi-crystalline structure. Manufacturing PPS typically involves injection molding and extrusion with faster cycle times and lower energy consumption, whereas PEEK's processing demands specialized equipment, slower cooling rates, and more stringent control to prevent degradation. Differences in melt viscosity mean PPS flows more easily during molding, improving dimensional stability compared to PEEK, which needs precise temperature profiles for optimal crystallinity and mechanical properties.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide) offers a cost-effective alternative to PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) with lower raw material prices and processing costs, making it suitable for budget-sensitive applications. PEEK, while more expensive, provides superior mechanical properties and chemical resistance, justifying its higher cost in high-performance industries such as aerospace and medical devices. Your choice between PPS and PEEK should balance upfront expenses with long-term durability and application requirements.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide) and PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) differ in environmental impact and sustainability, with PEEK generally having a higher manufacturing energy demand due to its complex polymer structure. PPS offers better flame resistance and chemical stability, enabling longer product lifespan, which can reduce waste and environmental footprint. Your choice between PPS and PEEK should consider the balance of lifecycle durability and the environmental cost of production to achieve sustainable material usage.
Choosing Between PPS and PEEK: Key Factors
Selecting between PPS (Polyphenylene Sulfide) and PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) hinges on factors like temperature resistance, mechanical strength, and chemical stability. PEEK offers superior high-temperature tolerance up to 250degC and excellent mechanical properties, making it suitable for aerospace and medical applications. PPS is more cost-effective with good chemical resistance and dimensional stability, ideal for automotive and electrical components where moderate performance is sufficient.
PPS vs PEEK Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com