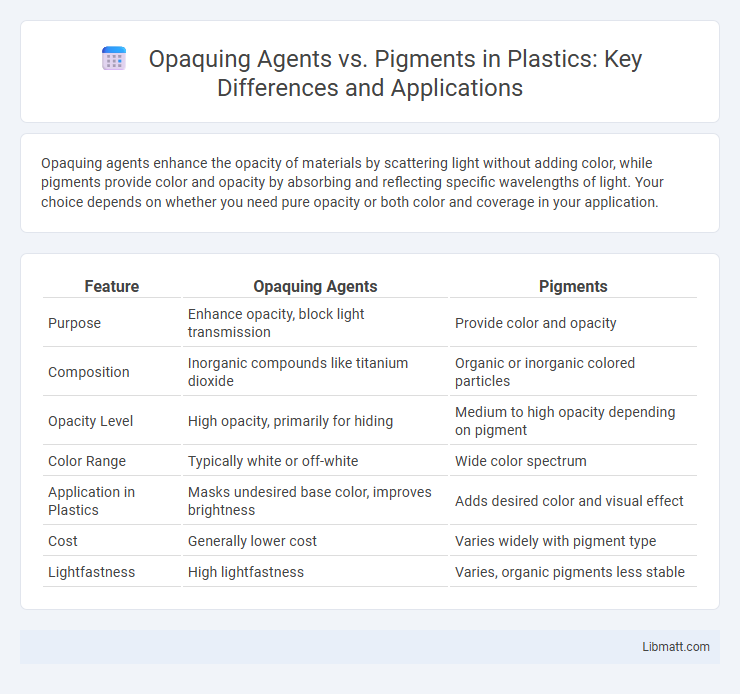
Opaquing agents enhance the opacity of materials by scattering light without adding color, while pigments provide color and opacity by absorbing and reflecting specific wavelengths of light. Your choice depends on whether you need pure opacity or both color and coverage in your application.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Opaquing Agents | Pigments |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Enhance opacity, block light transmission | Provide color and opacity |
| Composition | Inorganic compounds like titanium dioxide | Organic or inorganic colored particles |
| Opacity Level | High opacity, primarily for hiding | Medium to high opacity depending on pigment |
| Color Range | Typically white or off-white | Wide color spectrum |
| Application in Plastics | Masks undesired base color, improves brightness | Adds desired color and visual effect |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Varies widely with pigment type |
| Lightfastness | High lightfastness | Varies, organic pigments less stable |
Introduction to Opaquing Agents and Pigments
Opaquing agents and pigments both serve to impart color and opacity in various materials, but they differ fundamentally in composition and function. Opaquing agents are typically additives that enhance the opacity of a substrate without significantly affecting its color, often made from fine particles like titanium dioxide or barium sulfate. Pigments, on the other hand, are colored substances that provide both opacity and vibrant hues, essential in paints, inks, and coatings to achieve your desired visual effect.
Definition and Core Functions
Opaquing agents are specialized additives used primarily to reduce transparency by scattering light, thereby enhancing the opacity of coatings, plastics, and inks. Pigments are finely ground colored particles that provide color and opacity through light absorption and scattering, playing a critical role in visual aesthetics and protection. While both improve opacity, opaquing agents mainly modify light diffusion without imparting color, whereas pigments contribute both color and opacity.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Opaquing agents and pigments differ significantly in chemical composition; opaquing agents often consist of white or translucent materials like titanium dioxide or zinc oxide, designed to block or scatter light effectively. Pigments usually contain organic or inorganic compounds such as iron oxides, ultramarine, or phthalocyanines, which provide intense and stable coloration. Understanding these chemical distinctions helps you select the right material for achieving desired opacity or vibrant color in your applications.
Mechanisms of Opacity Creation
Opaquing agents create opacity by scattering light through particles with refractive indices significantly different from the surrounding medium, thereby preventing light transmission. Pigments generate opacity primarily by absorbing specific wavelengths of light, converting it into other forms of energy such as heat, which reduces light passage. The efficacy of opacity depends on particle size, concentration, and dispersion quality, influencing the overall light interaction in coatings, plastics, or inks.
Applications Across Industries
Opaquing agents serve to enhance opacity and conceal underlying surfaces in coatings, plastics, and cosmetics, making them essential in industries like automotive paint, packaging, and personal care products. Pigments provide coloration and UV protection while also contributing to opacity, widely used in printing inks, textiles, and construction materials. Your choice between opaquing agents and pigments depends on the specific industry application and desired visual effect, balancing opacity, color vibrancy, and durability.
Benefits of Opaquing Agents
Opaquing agents enhance the opacity of materials by scattering light, which improves coverage and reduces the amount of pigment needed in formulations. They provide better color uniformity and brightness without altering the base color, making them ideal for applications requiring high opacity with minimal color shift. Their cost-effectiveness and compatibility with various media contribute to improved product performance in paints, coatings, and cosmetics.
Advantages of Pigments
Pigments offer superior lightfastness and color stability compared to opaquing agents, ensuring vibrant, long-lasting hues in various applications. Their ability to provide high opacity at lower concentrations enhances cost-efficiency and material performance. You benefit from pigments' chemical resistance and versatility across different substrates, making them ideal for durable coatings and printing.
Key Differences in Performance
Opaquing agents enhance paint opacity by scattering light through finely dispersed particles, resulting in superior coverage with fewer coats, while pigments contribute both color and opacity but may require thicker application for full concealment. Opaquing agents typically improve hiding power more efficiently due to their specialized particle size and shape, optimizing light diffusion without significantly altering tint strength. Pigments provide chromatic properties and durability, influencing color fastness and resistance to environmental factors, whereas opaquing agents primarily focus on maximizing opacity in coatings.
Selection Criteria for Optimal Results
Selection criteria for optimal results between opaquing agents and pigments include opacity level, color stability, and compatibility with the medium. Opaquing agents are chosen for their ability to enhance coverage without significantly altering the color, while pigments provide intense coloration and long-lasting vibrancy. Understanding Your project's specific requirements such as surface type, exposure conditions, and desired finish ensures the best balance between opacity and color intensity.
Future Trends and Innovations
Future trends in opaquing agents and pigments emphasize sustainable materials and eco-friendly production processes, driven by increasing environmental regulations and consumer demand for green products. Innovations include the development of bio-based and nano-engineered pigments that offer enhanced opacity, durability, and color vibrancy while reducing carbon footprint. Advancements in digital formulation and smart pigments incorporating UV resistance and self-cleaning properties are poised to revolutionize coatings, plastics, and cosmetics industries.
Opaquing Agents vs Pigments Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com