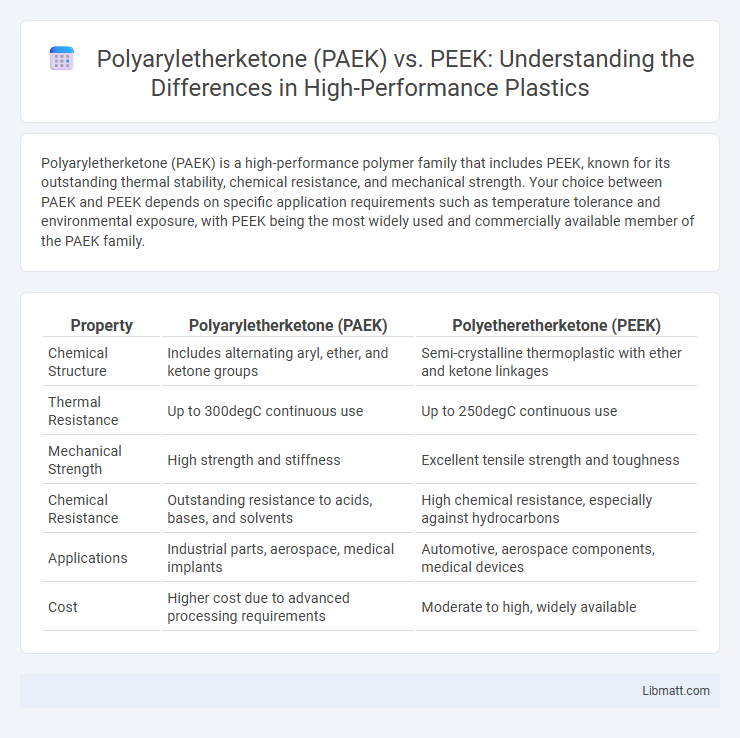
Polyaryletherketone (PAEK) is a high-performance polymer family that includes PEEK, known for its outstanding thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. Your choice between PAEK and PEEK depends on specific application requirements such as temperature tolerance and environmental exposure, with PEEK being the most widely used and commercially available member of the PAEK family.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyaryletherketone (PAEK) | Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Includes alternating aryl, ether, and ketone groups | Semi-crystalline thermoplastic with ether and ketone linkages |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 300degC continuous use | Up to 250degC continuous use |
| Mechanical Strength | High strength and stiffness | Excellent tensile strength and toughness |
| Chemical Resistance | Outstanding resistance to acids, bases, and solvents | High chemical resistance, especially against hydrocarbons |
| Applications | Industrial parts, aerospace, medical implants | Automotive, aerospace components, medical devices |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced processing requirements | Moderate to high, widely available |
Introduction to Polyaryletherketone (PAEK) and PEEK
Polyaryletherketone (PAEK) is a high-performance thermoplastic polymer known for its exceptional mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability, widely used in aerospace, automotive, and medical industries. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) is a specific grade within the PAEK family, distinguished by its superior toughness, high melting point around 343degC, and outstanding resistance to harsh environments. PEEK's unique combination of physical and chemical properties makes it a preferred choice for applications requiring long-term durability and sterilizability.
Chemical Structure Comparison: PAEK vs PEEK
Polyaryletherketone (PAEK) encompasses a family of high-performance polymers characterized by alternating ether and ketone linkages in their backbone, providing exceptional thermal stability and chemical resistance. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) is a specific type within the PAEK family, distinguished by its repeating units containing two ether groups and one ketone group within the polymer chain, which enhances its mechanical strength and crystallinity. The chemical structure difference between PAEK and PEEK results in variations in physical properties, with PEEK exhibiting superior toughness and resistance due to its precise ether-ketone arrangement.
Mechanical Properties Analysis
Polyaryletherketone (PAEK) and Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) exhibit high-performance mechanical properties, with PEEK being a prominent member of the PAEK family known for its exceptional tensile strength, stiffness, and impact resistance. PEEK typically offers tensile strength around 90-100 MPa and a Young's modulus of approximately 3.6 GPa, providing superior fatigue resistance and thermal stability compared to other PAEK variants. Mechanical properties of PAEK polymers vary based on molecular structure, but PEEK's balanced strength-to-weight ratio and wear resistance make it the preferred choice in aerospace, medical, and automotive applications.
Thermal Stability and Performance Differences
Polyaryletherketone (PAEK) and Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) both exhibit exceptional thermal stability, with PAEK materials generally demonstrating higher melting points ranging from 360degC to 410degC compared to PEEK's melting point around 343degC. This difference results in PAEK offering enhanced performance in high-temperature applications, including improved resistance to thermal degradation and prolonged mechanical strength at elevated temperatures. Understanding these thermal stability variations helps you select the optimal polymer for demanding environments requiring sustained high performance.
Processability in Manufacturing
Polyaryletherketone (PAEK) and PEEK both exhibit excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance, but PAEK offers greater versatility in processability due to its broader range of molecular structures. PEEK typically requires higher processing temperatures around 370degC, whereas certain PAEK variants can be processed at lower temperatures, improving energy efficiency and reducing manufacturing costs. Your choice between PAEK and PEEK depends on specific manufacturing methods like injection molding or extrusion, where PAEK's adaptable properties can enhance ease of fabrication.
Applications in Various Industries
Polyaryletherketone (PAEK) and Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) are high-performance thermoplastic polymers widely used in aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics industries due to their exceptional mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. While PEEK is renowned for its superior wear resistance and biocompatibility, making it ideal for medical implants and aerospace components, PAEK offers a broader range of compositions and enhanced processability, enabling customized applications in harsh chemical environments and high-temperature automotive parts. Your choice between PAEK and PEEK depends on specific industry requirements such as temperature tolerance, mechanical stress, and chemical exposure to optimize performance and durability.
Advantages and Limitations of PAEK
Polyaryletherketone (PAEK) offers superior chemical resistance, high thermal stability up to 300degC, and excellent mechanical strength, making it ideal for aerospace and medical applications compared to PEEK. However, PAEK's higher processing temperatures and cost limit its widespread adoption in cost-sensitive industries. The material's resistance to hydrolysis and sterilization methods also outperforms PEEK, but PAEK's dense molecular structure can reduce its impact resistance in certain high-stress scenarios.
Advantages and Limitations of PEEK
Polyaryletherketone (PAEK) is a high-performance thermoplastic family that includes PEEK (Polyetheretherketone) as its most widely used member, known for excellent mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal stability up to 250degC. PEEK offers advantages such as biocompatibility, low moisture absorption, and exceptional wear resistance, making it ideal for aerospace, medical implants, and automotive applications. Limitations of PEEK include its high cost compared to other polymers and challenges in processing due to its high melting point and viscosity.
Cost Considerations and Market Availability
Polyaryletherketone (PAEK) encompasses a family of high-performance polymers, with Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) being the most commercially prominent and widely available variant, influencing cost dynamics significantly. PEEK typically commands higher prices due to its extensive industrial applications, established supply chains, and superior mechanical properties compared to other PAEK variants like PEKK or PEKEKK. Market availability for PEEK is robust across various sectors including aerospace, medical, and automotive, whereas other PAEKs face limited production volumes and higher costs linked to niche applications and lower demand.
Choosing Between PAEK and PEEK: Key Factors
Choosing between Polyaryletherketone (PAEK) and PEEK requires evaluating factors such as thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical performance for your specific application. PEEK, a subset of PAEK, offers excellent strength, high melting point (around 343degC), and resistance to harsh environments, making it ideal for aerospace and medical devices. Consider cost differences and processing methods, as PEEK often demands higher processing temperatures and may have a premium price compared to other PAEK variants, ensuring your choice aligns with both performance requirements and budget constraints.
Polyaryletherketone (PAEK) vs PEEK Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com