Flame retardants reduce the ability of materials to ignite and slow the spread of fire, while smoke suppressants minimize the amount of smoke produced during combustion, enhancing visibility and reducing toxic inhalation risks. Understanding the difference helps you select the right safety additives for fire protection in various applications.
Table of Comparison
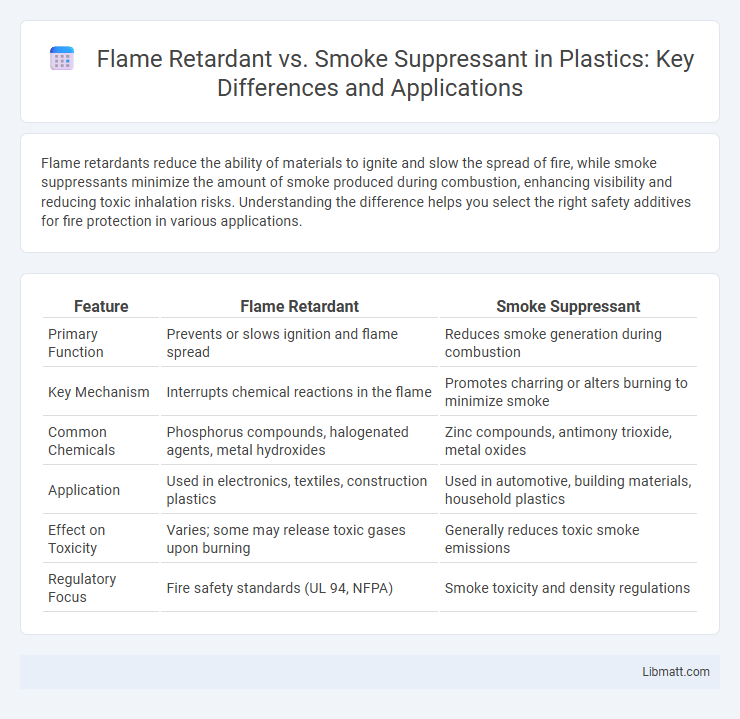
| Feature | Flame Retardant | Smoke Suppressant |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Prevents or slows ignition and flame spread | Reduces smoke generation during combustion |
| Key Mechanism | Interrupts chemical reactions in the flame | Promotes charring or alters burning to minimize smoke |
| Common Chemicals | Phosphorus compounds, halogenated agents, metal hydroxides | Zinc compounds, antimony trioxide, metal oxides |
| Application | Used in electronics, textiles, construction plastics | Used in automotive, building materials, household plastics |
| Effect on Toxicity | Varies; some may release toxic gases upon burning | Generally reduces toxic smoke emissions |
| Regulatory Focus | Fire safety standards (UL 94, NFPA) | Smoke toxicity and density regulations |
Understanding Flame Retardants: Definition and Purpose
Flame retardants are chemical substances added to materials to inhibit or resist the spread of fire by interrupting the combustion process at various stages. These compounds work by forming a protective char layer, releasing flame-inhibiting gases, or altering thermal degradation pathways to reduce flammability. Understanding the purpose of flame retardants helps you select materials that enhance fire safety and minimize fire-related hazards in products and environments.
What Are Smoke Suppressants? Core Functions Explained
Smoke suppressants are chemical additives designed to reduce the amount and density of smoke produced during combustion, enhancing visibility and safety in fire situations. They function by interfering with the pyrolysis process, promoting the formation of a char layer that limits fuel release and inhibits smoke particle generation. Unlike flame retardants that primarily inhibit or slow down flame propagation, smoke suppressants specifically target the reduction of smoke production to minimize toxic inhalation risks.
Key Differences: Flame Retardant vs Smoke Suppressant
Flame retardants primarily reduce the ignition and spread of fire by chemically interfering with the combustion process, whereas smoke suppressants focus on minimizing smoke production and improving visibility during a fire. Your choice between these depends on whether the priority is preventing fire ignition or reducing toxic smoke emissions for safer evacuation. Understanding these key differences helps optimize fire safety solutions tailored to specific hazard scenarios.
How Flame Retardants Work: Chemical and Physical Mechanisms
Flame retardants work by interfering with the combustion process through chemical and physical mechanisms that reduce flammability and slow down fire spread. Chemically, they release free radicals or form a protective char layer that inhibits the flame's ability to sustain itself, while physically, they cool the material or create a barrier that limits oxygen access. Understanding these actions helps you choose effective flame retardants to enhance fire safety in various materials.
Smoke Suppressants: Mechanisms and Applications
Smoke suppressants function by inhibiting the release of volatile organic compounds and radical species during combustion, thereby reducing smoke density and toxicity. They often operate through physical pathways like forming a protective char layer or chemical pathways by scavenging free radicals. These mechanisms make smoke suppressants critical in applications such as building materials, textiles, and transportation to enhance fire safety and visibility during evacuation.
Materials Treated with Flame Retardants vs Smoke Suppressants
Materials treated with flame retardants primarily include textiles, plastics, and building materials to inhibit ignition and slow the spread of fire. Smoke suppressants are often applied to polymers, cables, and foams to reduce the density and toxicity of smoke produced during combustion. Understanding the specific applications of these treatments helps you enhance safety by selecting the right solution for fire resistance or smoke control in various materials.
Safety and Regulatory Standards for Fire Protection Additives
Flame retardants and smoke suppressants play crucial roles in enhancing fire safety by reducing ignition risks and controlling smoke production, which is vital for minimizing harm during fires. Regulatory standards from agencies like UL, NFPA, and EPA ensure these additives meet strict safety criteria, including toxicity, fire resistance, and environmental impact. Your choice of fire protection additives must comply with these regulations to ensure effective flame retardancy and smoke suppression without compromising health or safety.
Environmental and Health Impacts: A Comparative Overview
Flame retardants often contain chemicals that can persist in the environment and accumulate in human tissue, posing potential health risks such as endocrine disruption and respiratory issues. Smoke suppressants, designed to reduce toxic smoke emissions during combustion, generally offer a safer alternative with lower environmental persistence and decreased toxicity. Understanding these differences helps you select materials that minimize both environmental impact and health hazards in fire safety applications.
Choosing the Right Solution: Key Factors to Consider
When selecting between flame retardants and smoke suppressants, consider the specific fire safety requirements of your application, including the material type and regulatory standards. Flame retardants primarily reduce ignition risk and flame spread, while smoke suppressants minimize toxic smoke production during combustion. Your choice should balance fire prevention efficacy with smoke control to ensure optimal protection and compliance.
Future Trends in Fire Safety: Innovations in Flame Retardants and Smoke Suppressants
Future trends in fire safety emphasize the development of eco-friendly flame retardants and smoke suppressants that minimize toxic emissions and enhance material sustainability. Advancements include bio-based compounds and nanotechnology-enhanced formulations that improve fire resistance while maintaining product integrity. Your fire safety solutions will benefit from these innovations by offering safer, more effective protection with reduced environmental impact.
Flame retardant vs smoke suppressant Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com