Polystyrene offers excellent rigidity and clarity, making it ideal for packaging and insulation, while polyethylene provides superior flexibility and chemical resistance, often used in containers and plastic bags. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize toughness and transparency or durability and softness for specific applications.
Table of Comparison
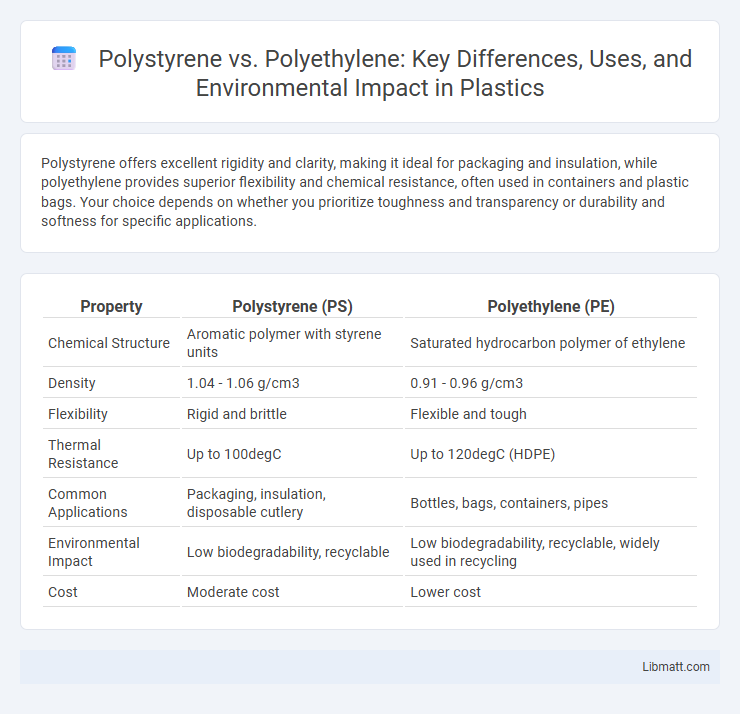
| Property | Polystyrene (PS) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | Aromatic polymer with styrene units | Saturated hydrocarbon polymer of ethylene |
| Density | 1.04 - 1.06 g/cm3 | 0.91 - 0.96 g/cm3 |
| Flexibility | Rigid and brittle | Flexible and tough |
| Thermal Resistance | Up to 100degC | Up to 120degC (HDPE) |
| Common Applications | Packaging, insulation, disposable cutlery | Bottles, bags, containers, pipes |
| Environmental Impact | Low biodegradability, recyclable | Low biodegradability, recyclable, widely used in recycling |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Lower cost |
Introduction to Polystyrene and Polyethylene
Polystyrene is a versatile thermoplastic polymer known for its rigidity, transparent quality, and excellent insulation properties, often used in packaging, disposable cutlery, and insulation materials. Polyethylene, the most common plastic globally, offers exceptional flexibility and chemical resistance, making it ideal for plastic bags, containers, and piping. Your choice between polystyrene and polyethylene depends on the application's durability, flexibility, and environmental impact requirements.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Polystyrene consists of repeating styrene monomers featuring a phenyl group attached to a carbon backbone, resulting in a rigid and aromatic polymer. Polyethylene is composed of long chains of ethylene monomers with a simpler carbon-carbon backbone, providing flexibility and chemical resistance. Understanding your application's requirements helps determine whether the aromatic structure of polystyrene or the linear, saturated composition of polyethylene is more suitable.
Manufacturing Processes
Polystyrene is produced through the polymerization of styrene monomers using methods such as suspension, bulk, and emulsion polymerization, enabling control over molecular weight and polymer structure. Polyethylene is manufactured primarily via addition polymerization of ethylene monomers using techniques like high-pressure free-radical polymerization for low-density polyethylene (LDPE) and catalytic polymerization with Ziegler-Natta or metallocene catalysts for high-density polyethylene (HDPE). These distinct manufacturing processes impact the polymers' molecular configurations, crystallinity, and resulting mechanical and thermal properties.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Polystyrene exhibits higher rigidity and brittleness compared to polyethylene, with a tensile strength typically ranging from 40 to 60 MPa, while polyethylene offers greater flexibility and impact resistance with tensile strength between 20 to 30 MPa. The density of polystyrene is approximately 1.05 g/cm3, making it denser than polyethylene, which ranges from 0.91 to 0.96 g/cm3 depending on its type (HDPE or LDPE). Thermal properties also differ; polystyrene has a melting point around 240degC, whereas polyethylene melts between 115degC and 135degC, contributing to their distinct applications in packaging and insulation.
Common Applications and Uses
Polystyrene is widely used in packaging materials, disposable cutlery, insulation, and consumer products due to its rigidity and clarity. Polyethylene is commonly found in plastic bags, containers, bottles, and pipes, favored for its flexibility, chemical resistance, and durability. Both polymers serve essential roles in manufacturing, with polystyrene excelling in lightweight, rigid applications and polyethylene dominating flexible, impact-resistant uses.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Polystyrene (PS) poses significant environmental challenges due to its slow degradation rate and difficulty in recycling, often ending up in landfills or oceans where it contributes to microplastic pollution. Polyethylene (PE), widely used in packaging, is more readily recyclable through mechanical processes and has a higher recycling rate, although improper disposal still leads to environmental contamination. Both plastics require improved waste management systems and advancements in recycling technologies to mitigate their ecological footprint effectively.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Polystyrene generally has a higher cost per pound compared to polyethylene due to its more complex manufacturing process and specialized applications in packaging and insulation. Polyethylene remains more cost-effective and widely available, dominating markets such as plastic bags, containers, and films because of its versatility and lower production costs. Market availability favors polyethylene with extensive global supply chains and diverse product forms, while polystyrene's niche use results in smaller, more specialized market segments.
Pros and Cons of Polystyrene
Polystyrene offers excellent insulation properties, lightweight structure, and cost-effective production, making it ideal for packaging and disposable containers. It is rigid and clear but prone to brittleness and environmental issues due to poor biodegradability and toxic chemical release when burned. Polystyrene's resistance to moisture contrasts with polyethylene's flexibility and chemical resistance, highlighting its limited durability in high-stress applications.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Polyethylene
Polyethylene offers high chemical resistance and excellent flexibility, making it ideal for packaging, containers, and pipes. Its low cost and ease of processing are advantageous, but polyethylene has limited UV resistance and lower tensile strength compared to polystyrene. Environmental concerns arise from its non-biodegradability, although recycling options are improving.
Choosing the Right Material: Polystyrene vs Polyethylene
Choosing between polystyrene and polyethylene depends on your specific application needs such as strength, flexibility, and insulation properties. Polystyrene offers rigidity and excellent thermal insulation, making it ideal for packaging and disposable containers, while polyethylene provides superior flexibility, impact resistance, and chemical durability suited for bags, bottles, and piping. Assessing factors like environmental exposure, mechanical stress, and recycling potential will help you select the right material for optimal performance and sustainability.
Polystyrene vs Polyethylene Infographic
 libmatt.com
libmatt.com